
- •LIVER DISEASES
- •LIVER DISEASES
- •Do you know that …
- •Liver structure v. portae system
- •Liver
- •Liver functions
- •Major risk factors for liver disease
- •Symptoms of liver disorders
- •Fatigue
- •Jaundice
- •Jaundice or icterus
- •Jaundice: major types
- •Causes of jaundice
- •Darkening of the Urine
- •Pale (light) Stools
- •Liver Pain
- •Ascites
- •Ascites, umbilical hernia
- •Ascites
- •Симптомы и синдромы заболеваний печени
- •ПОРТАЛЬНАЯ ГИПЕРТЕНЗИЯ
- •Possible levels of block in portal hypertension
- •Hepatocellular cytolisis
- •Stigmata of chronic liver disease
- •Cholestasis syndrom
- •CHOLESTASIS
- •Etiology of Dupuitren contracture
- •Etiologic factors of gynecomastia
- •polyneuropathia
- •ПРИЧИНЫ ПОРТАЛЬНОЙ ГИПЕРТЕНЗИИ
- •Расширенные вены передней стенки живота, асцит
- •ЭГДС.
- •Расширение v. рortae и vv. hepaticae
- •ПЕЧЕНОЧНОКЛЕТОЧНАЯ
- •ПРИЧИНЫ ПЕЧЕНОЧНОЙ НЕДОСТАТОЧНОСТИ
- •Синдром печеночно-клеточной недостаточности
- •Печеночная энцефалопатия
- •ГЕПАТОРЕНАЛЬНЫЙ СИНДРОМ I и II тип
- •Патогенеза гепаторенального синдрома
- •Типы гепаторенального синдрома
- •ФАКТОРЫ, ПРОВОЦИРУЮЩИЕ РАЗВИТИЕ ГЕПАТОРЕНАЛЬНОГО СИНДРОМА (на фоне поражения печени)
- •Желтуха, ксантелазмы
- •ГИПЕРСПЛЕНИЗМ
- •Маркеры хронической алкогольной интоксикации
- •Классификация тяжести поражения печени по Чайлд-Пью
- •ЭГДС – расширенные вены пищевода
- •Пункционная биопсия печени под контролем УЗИ (цирроз)
- •Мелкоочаговое поражение печени при остром гепатите
- •Асцит, расширенная v.portae, неровность контуров при циррозе печени
- •Сцинтиграфия печени с метастазами
- •Сцинтиграфия мелкоузлового цирроза
- •Лапароскопия – крупноузловой цирроз
- •Передняя стенка живота при синдроме портальной гипертензии
- •Компьютерная томография
- •FibroScan®
- •Выраженность фиброза при фибросканировании печени
- •Stages of Liver Disease
- •Progression of Hepatitis B Infection
- •Healthy Liver
- •Healthy Liver
- •Types of Hepatitis
- •Hepatitis B is a Devastating Global Healthcare Issue
- •Hepatitis – Disease Terminology
- •How Hepatitis B is Acquired?
- •How the Infection is Acquired in the West?
- •Hepatitis B – Diagnosis Terminology
- •Diagnosis of Chronic Hepatitis B
- •Signs and Symptoms of HBV Infection
- •Universal Hepatitis B Vaccination
- •Global Control of Hepatitis B
- •Types of viral Hepatitis
- •Healthy Liver
- •Liver biopsy
- •Detection of serologic markers of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, as a function
- •Lamivudine is a Potent Inhibitor of HBV Replication
- •Lamivudine has an Excellent Pharmacokinetic Profile
- •Patient Entry Criteria
- •One Year of Lamivudine - Conclusions
- •Resistance to Anti-Viral Drugs
- •Prevention of Hepatitis B
- •Universal Hepatitis B Vaccination
- •Recommendations for Pre-exposure Vaccination
- •Recommendations for Post-exposure Vaccination
- •Global Control of Hepatitis B
- •Concurrent immunologic diseases in type 2 autoimmune hepatitis.
- •Probabilities of clinical, biochemical, and histologic remission during corticosteroid therapy.
- •Clinical features of type 2 autoimmune hepatitis.
- •Liver transplantation for autoimmune hepatitis.
- •Survival expectations and probability of developing cirrhosis during and after corticosteroid treatment.
- •liver biopsy
- •Detection of serologic markers of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, as a function
- •The Efficacy and Safety of Lamivudine in HBeAg-positive Chronic Hepatitis B
- •Lamivudine is a Potent Inhibitor of HBV Replication
- •Lamivudine has an Excellent Pharmacokinetic Profile
- •What Patient Populations Have Been Studied
- •Key Lamivudine Clinical Studies (1)
- •Key Lamivudine Clinical Studies (2)
- •Patient Entry Criteria
- •Lamivudine Rapidly Suppresses
- •One Year of Lamivudine - Conclusions
- •Resistance to Anti-Viral Drugs
- •Concurrent immunologic diseases in type 1 autoimmune hepatitis.
- •Probabilities of clinical, biochemical, and histologic remission during corticosteroid therapy.
- •Clinical features of type 2 autoimmune hepatitis.
- •Liver transplantation for autoimmune hepatitis.
- •Survival expectations and probability of developing cirrhosis during and after corticosteroid treatment.
- •ALCOHOLIC LIVER DISEASE
- •Principal alcohol-induced hepatic lesions
- •Alcohol-induced hepatic lesions
- •Pathogenesis of liver injury secondary to chronic ethanol ingestion
- •Equivalents of pure alcohol
- •Alcoholic fatty liver
- •Two-Hit Model of the Progression of Fatty Liver Disease
- •Alcoholic fatty liver
- •Similarities between Alcoholic and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases
- •Alcoholic hepatitis
- •This figure depicts a laparoscopic view of a patient with chronic active hepatitis
- •Percutaneous liver biopsy with or without ultrasonic guidance
- •Alcoholic hepatitis: liver biopsy
- •Treatment of severe alcoholic hepatitis
- •Причины смерти при алкогольном гепатите
- •Alcoholic cirrhosis
- •Alcoholic cirrhosis
- •Alcoholic cirrhosis: clinical manifestations

One Year of Lamivudine - Conclusions
Virology
•Suppresses serum HBV DNA
•Leads to HBeAg seroconversion Liver disease
•Improves hepatic necro-inflammation
•Reduces progression of fibrosis
•Reduces progression to cirrhosis
•Normalises serum ALT
•Improves liver histology irrespective of baseline ALT

Resistance to Anti-Viral Drugs
Genotypic resistance – changes in the virus that disrupt interactions between the drug and its molecular target
Clinical resistance – loss of efficacy due to above changes


Concurrent immunologic diseases in type 1 autoimmune hepatitis.
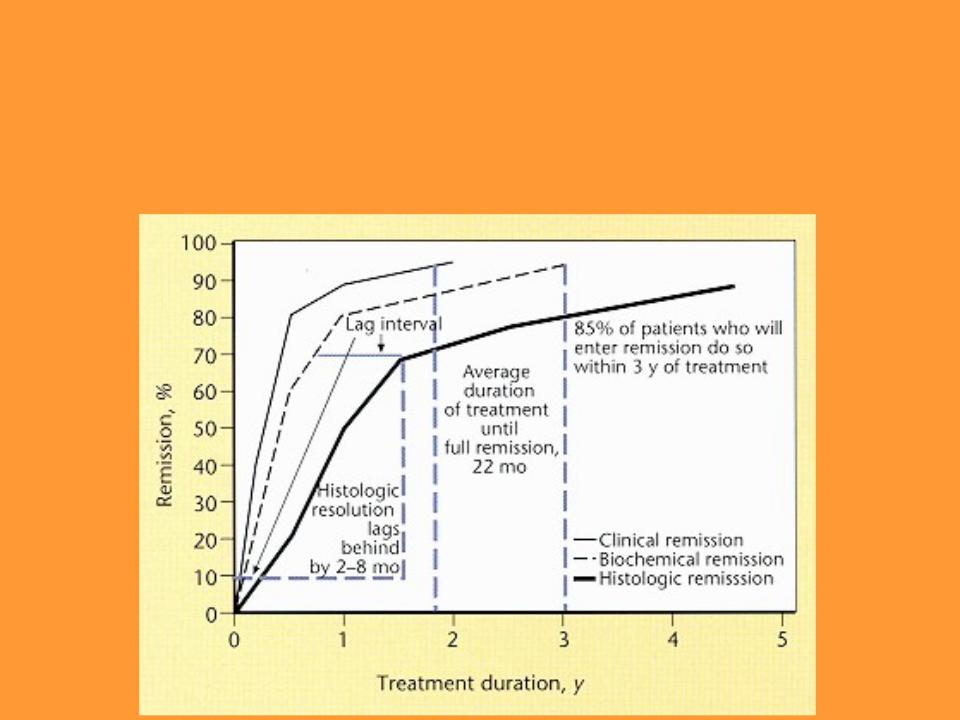
Probabilities of clinical, biochemical, and histologic remission during corticosteroid therapy.

Clinical features of type 2 autoimmune hepatitis.
•The diagnosis requires the presence of antibodies to liver–kidney microsome type 1 (Anti-LKM1)But antibodies to hepatitis C virus and hepatitis C virus RNA may be present
•The disease has been described mainly in pediatric patients in Western Europe, but adults may also be afflicted]. In the United States, seropositivity for Anti-LKM1 has been found in only 4% of adults and hepatitis C virus infection has not been a feature of the disease.
•Patients with type 2 autoimmune hepatitis typically have concurrent immunologic diseases, including autoimmune thyroiditis, insulin- dependent diabetes, vitiligo, and ulcerative colitis
•They have a high frequency of organ-specific autoantibodies, such as parietal cell antibodies, antibodies to the islets of Langerhans, and thyroid antibodies .
•An acute, even fulminant, presentation may occur, and patients uncommonly have a pronounced hypergammaglobulinemia

Liver transplantation for autoimmune hepatitis.
•Decompensated patients should be considered for liver transplantation.
•The 5-year survival rate after transplantation is 92%.
•Recurrence of disease is rare but possible in inadequately immunosuppressed recipients and in HLA-DR3–positive recipients of HLA- DR3–negative grafts

Survival expectations and probability of developing cirrhosis during and after corticosteroid treatment.
•Patients without cirrhosis at presentation have better 5- and 10-year survival rates than patients with cirrhosis at presentation
•Cirrhosis develops in 47% of patients within 10 years after presentation despite corticosteroid treatment
•The highest probability of cirrhosis is during initial therapy when the disease is most active. The mean annual incidence of cirrhosis after initial remission is 2.6%
•Survival after the development of cirrhosis during or after treatment is similar to that of patients without cirrhosis

ALCOHOLIC LIVER DISEASE

Principal alcohol-induced hepatic lesions
•alcoholic fatty liver (steatosis)
•alcoholic hepatitis (steatohepatitis)
•alcoholic cirrhosis
•hepatocellular carcinoma
•These morphologic categories are rarely found in a pure form
•Features of each may be present to varying degrees in an individual patient.
