
- •Foreword
- •Preface to the Fourth Edition
- •Contents
- •Instructions for Use
- •Bones
- •Sutures, joints and ligaments
- •Muscles
- •Muscles, synovial bursae and sheaths
- •Digestive system
- •Digestive and respiratory system
- •Urogenital system
- •Peritoneum
- •Endocrine glands
- •Heart
- •Veins
- •Lymphatic system
- •Spinal cord
- •Cranial nerves
- •Autonomic nervous system
- •Sense organs
- •Skin and its appendages
- •General terms
- •References
- •Index

390 Skin and its appendages
1 |
|
1 |
SKIN (INTEGUMENT). Integumentum com- |
16 |
Papillary layer. Stratum papillare. The delicate |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
mune. Common integument (skin). The outer |
|
upper layer of the dermis with numerous con- |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
covering of the body consisting of three layers, |
|
nective tissue papillae connecting it to the |
||||||||||
2 |
|
|
|
the epidermis, dermis (corium) and subcutis. In |
|
epidermis. A |
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
the adult it covers an area of about 1.8 square |
17 |
Papillae. Conical extensions of connective tissue |
||||||||||
3 |
|
|
|
meters. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
projecting into the epidermis. They may form |
||||
|
2 |
Cutis. Collective term for epidermis and der- |
|
rows (dermal ridges) or branches and vary |
||||||||||||
4 |
|
|
|
mis. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
markedly in form and organization. A E |
|
||
|
3 |
Sulci of skin. Sulci cutis. Variably sized depres- |
Reticular layer. Stratum reticulare. Part of der- |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
sions or furrows on the surface of the skin, e. g., |
|
mis adjoining the papillary layer. It consists of |
||||||||||
5 |
|
|
|
the nasolabial sulcus, |
the deep sulci of |
the |
|
more compact, densely interwoven connective |
||||||||
|
|
|
joints, the fine depressions on the smooth areas |
|
tissue. A |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
of the skin, and the dermal ridges on the palms |
19 |
Subcutaneous tissue. Tela subcutanea. Layer of |
||||||||||
6 |
|
|
|
and soles. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
subcutaneous fatty tissue compartmentalized |
|||||
|
|
|
4 Dermal ridges. Cristae cutis. Ridges produced |
|
by fibrous tracts and firmly connected with the |
|||||||||||
7 |
|
|
|
by the underlying papillae of the corium on the |
|
corium with mobile connections to the fascia. A |
||||||||||
|
|
|
thick skin of the palms of the hands and soles of |
20 |
Panniculus adiposus. The thicker layer of fat in |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
8 |
|
|
|
the feet. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the subcutaneous tissue. A |
|
|||
|
5 |
Retinacula cutis. Bands of connective tissue |
21 |
Terminal nerve corpuscles. Corpuscula nervosa |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
which attach the skin to the underlying tissue. |
|
terminalia. Collective term for encapsulated |
||||||||||
9 |
|
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
nerve endings. |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
Tactile elevations. Toruli tactiles. Skin regions |
22 |
End bulbs of Krause (bulboid corpuscles). |
|||||||||||
10 |
|
|
|
with more abundant fat deposits, e. g., near the |
|
Corpuscula bulboidea. Oval convolutions of |
||||||||||
|
|
|
phalanges, thenar and hypothenar eminences. |
|
nerve fibers found especially in the lamina pro- |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
pria of the mucosa. They are considered to be |
|||
11 |
|
7 |
Coccygeal foveola. [Foveola coccygea]. Pit |
|
cold receptors. E |
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
above the coccyx caused by the caudal reti- |
23 |
Lamellated [[Vater-Pacini, pacinian]] cor- |
||||||||||
12 |
|
|
|
naculum. C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
puscles. Corpuscula lamellosa. Oval bodies, 2− |
|||||
|
8 |
Caudal |
retinaculum. |
Retinaculum |
caudale. |
|
3 mm long, with concentric layers of connective |
|||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
Connective tissue remains of the embryonic |
|
tissue surrounding an inner core (axon and |
||||||||||
13 |
|
|
|
notochord lying between the coccygeal foveola |
|
Schwann cells). They are pressure receptors |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
and the coccyx. C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
found in the subcutaneous fat muscles and |
|||||
14 |
|
9 |
Epidermis. |
Stratified, |
keratinized |
squamous |
|
viscera. A |
|
|
||||||
|
24 |
Tactile |
[[Meissner’s]] corpuscles. Corpuscula |
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
epithelium covering the body. Its thickness var- |
||||||||||||
15 |
|
|
|
ies from 30 µm to 4 mm or more. A |
|
|
|
tactus. These encapsulated sensory organs in the |
||||||||
|
10 |
Stratum corneum. Most superficial, cornified |
|
connective papilla of the dermis measure about |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
(keratinized) layer of the epidermis which un- |
|
0.1 mm in length and consist of transversely |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
oriented tactile cells within a ramified nerve |
|||||||||||
16 |
|
|
|
dergoes continual desquamation. A |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
network. A |
|
|
||||||||
|
11 |
Stratum |
lucidum. |
Located |
between |
the |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
25 |
Genital corpuscles. [[Corpuscula genitalia]]. El- |
|||||||||||||
17 |
|
|
|
stratum granulosum and stratum corneum. It is |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
liptical, encapsulated nerve endings similar to |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
a homogeneous, strongly refractile layer rich in |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
the end bulbs of Krause and found abundantly in |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
eleidin fibers. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the clitoris, glans and nipple. E |
|
|||||
|
12 |
Stratum granulosum. It consists of 1−5 |
cell |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
26 |
Tactile |
menisci |
[[Merkel’s discs or cor- |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
layers |
with degenerative nuclear changes. It |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
puscles]]. Menisci tractus. Flat group of light |
|||||||||||
19 |
|
|
|
contains |
stongly |
refractory |
keratohyaline |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
cells with intracellular neurofibrils. They occupy |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
granules. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the epithelium. D |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
13 Stratum spinosum. Prickle cell layer. It consists |
|
|
|
||||||||||
20 |
|
|
27 |
Articular corpuscles. [[Corpuscula |
articu- |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
of polygonal cells |
with spinous |
processes |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
laria]]. Modified |
pacinian corpuscles |
within |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
which project from their surfaces and contact |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
joint capsules. |
|
|
|||||||||
21 |
|
|
|
each other by means of a desmosome. They ap- |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
pear to bridge over relatively large intercellular |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
spaces (shrinkage artifact). A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
14 |
Stratum basale [cylindricum]. Deepest, cylin- |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
drical cell layer of the epidermis. Cell prolifera- |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
23 |
|
|
|
tion occurs here and in the stratum spinosum, |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
thus ensuring the continual renewal of the |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
24 |
|
|
|
epidermis. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
15 |
Dermis (corium). The layer of skin consisting of |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
an intimate network of collagenous and elastic |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
25 |
|
|
|
fibers rich in nerves and blood vessels and |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
devoid of fat. A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||

Skin and its appendages 391
|
3 |
3 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
10 |
10 |
9 |
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
14 |
17 |
24 |
17 |
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
17 |
|
|
15
18
23
23 |
5 |
19;20 |
|
6
7
8
B Tactile elevation C Coccygeal dimple
26
26
D Tactile discs (tactile menisci)
17
22
5 |
25 |
A |
Skin and subcutaneous layer |
E |
Corpuscular nerve endings |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25

392 Skin and its appendages
1 |
1 |
Pili. Collective term for any type of hair. |
28 |
Lunula. Crescentic, whitish area at the base of |
2 |
Lanugo. Fine woolly hair which is distributed |
|
the nail. Its anterior margin corresponds to the |
|
|
|
over the entire body, especially in the newborn. |
|
anterior border of the nail-forming tissue. C |
2 |
|
|
||
|
29 |
Margo occultus. Proximal, posterior margin of a |
||
|
It usually lacks a medulla. |
|||
|
3 |
Scalp hairs. Capilli. |
|
nail located deep within the nail sinus. D |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
34 Hairs of eyebrow. Supercilia.
5Eyelashes. Cilia.
46 Hairs of beard. Barba.
7Hairs of external acoustic meatus. Tragi.
58 Hairs of the nasal vestibule. Vibrissae.
9 Axillary hairs. Hirci.
610 Pubic hairs. Pubes.
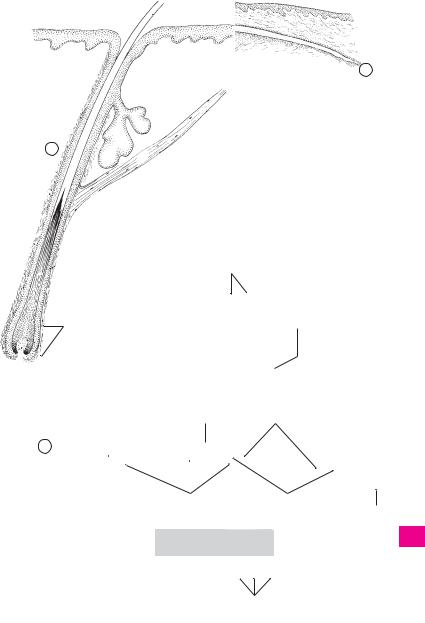
11 Hair follicle. Folliculus pili. Connective tissue
7epithelium covering of the hair root. A
12 |
Hair papilla. Papilla pili. Connective tissue |
|
8 |
|
papilla which projects into the bulb-like, dis- |
|
tended lowermost part of the hair root. A |
|
|
|
|
13 |
Hair shaft. Scapus pili. Part of the hair that pro- |
|
9 |
|
jects out from the skin. A |
14 Hair root. Radix pili. A
1015 Bulb of hair. Bulbus pili. Bulb-like enlargement at the lower end of the hair root. A
1116 Mm. arrectores pilorum. Bundles of smooth muscle passing from the middle of the hair follicle to the papillary layer of the dermis. They are
12absent on hair of eyelashes, eyebrows, nose, ear and beard. A.: erect hairs (goose-bumps), prob-
13ably also compression and emptying of sebaceous glands. Innervation: sympathetic fibers from the sympathetic ganglion. A
1417 Hair streams. Flumina pilorum. Orientational patterns of hair. B
1518 Whorled pattern of hair growth. Vortices pilorum. B
1619 Cruciate pattern of hair growth. Cruces pilorum. It is found at sites where the hair patterns meet from two directions and continue
17two new directions perpendicular to each other. B
1820 Nails. Unguis. Fingernails and toenails. C D
21 Nail matrix (bed). Matrix unguis. Tissue
19(epidermis) upon which the nail rests (root and lunula). Nail substance is formed in the region of the lunula. D E
2022 Crests of nail matrix. Cristae matricis unguis. Longitudinal ridges in nail bed. E
2123 Nail groove (fold). Sulcus matricis unguis. Cutaneous slit into which the lateral nasal margins are embedded. C
2224 Nail sinus. Sinus unguis. Deep furrow into which the root of the nail is inserted. D
2325 Wall of nail. Vallum unguis. Cutaneous fold overlapping the sides and proximal end of the
24nail. C D
26 Body of nail. Corpus unguis. C D E
2527 Root of nail. [[Radix unguis]]. Part of nail situated in the nail sinus. D
|
|
Skin and its appendages |
393 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
18 |
|
3 |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
14 |
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
16 |
|
|
7 |
||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
Hair follicle |
|
B |
Hair growth patterns |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
|
28 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fingernail |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
27 |
|||
|
|
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
24 |
|
|
|
D |
Nail matrix, longitudinal section |
|
|
|
||||||||
26
21
E |
Nail matrix, cross section |
22 |
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2921
22
23
24
25

394 Skin and its appendages
1 |
1 |
Lateral margin. Margo lateralis. Lateral margin |
21 |
Mammary gland. Glandula mammaria. Glan- |
|
|
of nail lying beneath the nail wall. B |
|
dular tissue of female breast. D |
||
|
2 |
Free margin. Margo liber. Anterior, free margin |
22 |
Lateral (axillary) process; axillary tail. Proces- |
|
2 |
|||||
|
of nail. It corresponds to the abrasive or cutting |
|
sus lateralis (axillaris). Glandular process ex- |
||
|
|
edge of the nail. B |
|
tending toward the axilla. |
|
|
|
|
33 Perionyx. Projecting edge of the eponychium 23 Lobes of mammary gland. Lobi glandulae
covering the proximal strip of the lunula. A |
mammariae. 15−20 conical lobes. D |
44 Eponychium. Cuticle. The small band of 24 Lobules of mammary gland. Lobuli glandulae epithelium that extends from the posterior nail mammariae. Subdivisions of each lobe produced
|
|
wall onto the base of a nail. A |
|
by connective tissue septa. D |
||
5 |
|
|
||||
5 |
Hyponychium. Epithelium of nail bed located |
25 |
Lactiferous ducts. Ductus lactiferi. Excretory |
|||
|
|
beneath the nail. Its posterior portion in the re- |
|
ducts, 15−20, one from each lobe. They have a di- |
||
6 |
|
gion of the lunula and nail root form the matrix. A |
|
ameter of 1.7−2.3 mm and open on the nipple. D |
||
|
26 |
Lactiferous sinus. Sinus lactiferi. Spindle-shaped |
||||
|
6 |
Stratum |
corneum unguis. Already cornified |
|||
|
||||||
7 |
|
part of nail. A |
|
|
dilatation of the lactiferous duct with a diameter |
|
7 |
Stratum germinativum unguis. Layer of nail |
|
of 5−8 mm shortly before opening at the apex of |
|||
|
|
the nipple. D |
||||
|
|
bed epithelium still undergoing cell prolifera- |
|
|||
8 |
|
|
||||
|
27 |
Areola mammae. Round, pigmented area |
||||
|
tion. A |
|
|
|||
|
8 |
[[Retinacula unguis]]. Anchoring tracts of con- |
|
around the nipple with a ring of small, rounded |
||
|
|
|||||
9 |
|
papillae produced by the areolar glands. D |
||||
|
nective tissue extending from the nail bed to the |
|
||||
|
28 Areolar glands (of Montgomery). Glanduale |
|||||
|
|
periosteum of the nail segement. A |
||||
|
|
|
areolares. 10−15 apocrine glands in the region of |
|||
10 |
9 |
Cutaneous glands. Glandulae cutis. Glands aris- |
|
|||
|
the areola. D |
|||||
|
|
ing from the epidermis and standing in close re- |
29 |
Male mammary gland. Mamma masculina. |
||
|
|
lationship to the skin. |
|
|||
11 |
|
|
|
Rudimentary mammary gland of the male. |
||
10 Sweat glands. [[Gll. glomiformes]]. Collective |
|
|||||
|
30 Accessory mammary glands. [Mammae acces- |
|||||
|
|
term for the small eccrine sweat glands and the |
||||
12 |
|
|
soriae]. The acessory mammary glands lying |
|||
|
large apocrine sweat or odoriferous glands. |
|
||||
|
|
along the embryonic milk ridge. C |
||||
|
11 |
Eccrine |
(merocrine) |
sweat (sudoriferous) |
|
|
|
31 Suspensory ligaments of breast. Ligg. suspen- |
|||||
13 |
|
glands. Gll. sudorifer merocrina (eccrina). Ec- |
||||
|
|
soria mammaria. Tracts of connective tissue |
||||
|
|
crine sweat glands, as opposed to the apocrine |
|
from the skin of the breast to the pectoral fascia |
||
|
|
sweat glands of the anal, genital and axillary re- |
|
|||
14 |
|
|
with which they are united by a thin layer of |
|||
|
gions. E |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
loose displaceable tissue. D |
||
|
12 |
Terminal |
secretory |
part. Portio terminalis. |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
15Coiled, secretory body of a sweat gland lying in the subcutaneous tissue or in the deep portion of the dermis. E F
1613 Sweat gland duct. Ductus sudorifer. Excretory duct passing to the surface. It is shaped like a
17corkscrew within the highly cornified squamous epithelium of palms and soles and opens on the
dermal ridges. E F
18
14Pore of sweat gland. Porus sudorifer. Opening of the excretory duct of a sweat gland on the skin.
19 E
|
15 |
Circumanal glands. Gll. circumanales. Large |
|
20 |
|||
|
apocrine sweat glands grouped around the anus. |
||
|
16 |
Ceruminous glands. Gll. ceruminosae. Apocrine |
|
|
|||
21 |
|
glands that secrete a proteinaceous material |
|
|
|
called cerumen (ear wax). |
|
22 |
17 |
Sebaceous glands. Gll. sebaceae. Holocrine |
|
|
|
glands opening into the hair follicles. F |
|
|
18 |
Breast. Mamma. It consists of glandular tissue, |
|
23 |
|||
|
connective tissue tracts and fat. D |
||
|
|
|
19 Nipple. Papilla mammae. It contains openings of
24the lactiferous ducts and smooth muscle tissue. D
2520 Body of mammary gland. Corpus mammae. Glandular body surrounded by adipose tissue.

Skin and its appendages 395
6 |
3 |
4 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
5 |
7 |
|
|
|
||||||
|
Nail matrix, longitudinal section |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
29 |
31 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
24 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
Nail from above |
|
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Milk line |
|
|
Mammary gland |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|||||||||
 13
13
17 |
13 |
|
 12
12
12
E |
Sudoriferous gland |
F |
Skin glands |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
