- •1.Образуйте мн. Ч.:
- •2.Поставьте следующие предложения во мн. Ч.
- •3. Поставьте следующие существительные во множественное число (не забудьте, что перед множественным числом неопределенный артикль нужно опустить),
- •5. Поставьте следующие словосочетания во множественное число.
- •8 Выберите правильный вариант/ Choose the correct variant
- •9. Найдите ошибки и исправьте их.
- •3. Переведите на английский язык, употребляя притяжательный падеж.
- •4. Переведите на английский язык, употребляя притяжательный падеж
- •Поставьте артикли там, где необходимо.
- •2 Вставьте артикль, где необходимо
- •3. Вставьте артикль, где необходимо.
- •4. Вставьте артикль, где необходимо.
- •5. Вставьте артикль, где необходимо.
- •6. Вставьте артикль, где необходимо.
- •7. Вставьте артикль, где необходимо.
- •12. Вставьте артикль, где необходимо.
- •15. Вставьте артикль, где необходимо.
- •16. Вставьте артикль, где необходимо.
- •18. Вставьте артикль, где необходимо.
- •1.Вставьте нужное местоимение.
- •2.Дополните предложения следующими местоимениями:
- •9. Переведите на английский язык.
- •1.Поставьте следующие предложения в нужной форме:
- •Вставьте am, is, are в следующих предложениях:
- •2.Закончите предложения, используя следующие словосочетания:
- •3 Вставьте глагол to be в Present Simple.
- •5. Переведите на английский язык, употребляя глагол to be в Present Simple.
- •Образовать степени сравнения от следующих прилагательных:
- •Дополните предложения, используя сравнительную степень и than.
- •3.Составьте предложения по образцу:
- •4 Переведите следующие предложения на английский язык.
- •1 Переведите на английский язык, употребляя предлоги on, in, at, to, into.
- •Поставьте глаголы в Present Simple
- •Укажите глаголы в Past Simple:
- •2. Поставьте предложения в Past Simple:
- •1.Поставьте глаголы в нужном времени (Past Simple or Past Continuous)
- •2 Раскройте скобки, употребляя глаголы в Past Simple или Past Continuous.
- •3. Раскройте скобки, употребляя глаголы в Past Simple или Past Continuous.
- •1.Поставитьпредложения в нужном времени Past Simple or Present Perfect:
- •2 Раскройте скобки, употребляя глаголы в Present Perfect или Past Simple.
- •1. Поставьте предложения в вопросительной и отрицательной форме:
- •2 Раскройте скобки, употребляя глаголы в Past Simple, Past Continuous и Past Perfect.
- •1.Поставьте глаголы в скобках : Present, Past, Future:
- •2.Поставьте предложения в страдательном залоге:
- •3.Поставьте глаголы в скобках в действительном или страдательном залоге:
- •4. Переведите предложения на русский язык:
- •1.Переведите следующие предложения из прямой речи в косвенную речь:
- •2.Переведите с русского на английский, обращая внимание на Закон согласования времен.
- •3 Передайте следующие повествовательные предложения в косвенной речи.
- •4. Передайте следующие повествовательные предложения в косвенной речи,
- •5. Передайте следующие повествовательные предложения в косвенной речи.
- •6. Передайте следующие повествовательные предложения в косвенной речи.
- •Модальные глаголы и их эквиваленты (modal verbs)
- •Переведите предложения. Проанализируйте употребление модальных глаголов в следующих предложениях:
- •Переведите предложения на русский язык:
- •Замените модальные глаголы соответствующими эквивалентами:
- •Вставьте необходимые модальные глаголы: (must, should, would, ought to, have to, needn't, can, could, may)
- •Сгруппируйте следующие инфинитивы по группам:
- •2.Переведите предложения на английский язык.
- •1.Выберите правильную форму инфинитива.
- •2. Переведите на английский язык.
- •2 Раскройте скобки, употребляя герундий в активной или пассивной форме.
- •Условные предложения
- •Imitation-имитация
- •Instrumentation-инструментовка
- •Item-номер
- •Variation-вариация
- •Variety-эстрада
- •Virtuoso-виртуоз
- •Intermenzzo – интермеццо
- •Introduction – вступление
- •Viola-player-альтист
- •Violinist-скрипач
- •Vocalist-вокалист
- •Incrustation – инструкция
- •Impressionism – импрессионизм
- •Inlay – насечка
- •Vocalism – вокализм
- •Vulgarism – вульгаризм
- •Ideogram – идеограмма
- •Vampire – вампир, упырь
- •Illustration – иллюстрация
- •Image – изображение
- •Imposition - верстка
- •Variety show-эстрадный концерт
- •Versatile actor-одаренный актер, разноплановый актер
- •I enjoyed it immensely-я получил огромное удовольствие
- •It was a waste of time-зря только потратил время
- •Virtue Triumphs-Добро побеждает зло. Добродетель восторжествует.
1.Поставитьпредложения в нужном времени Past Simple or Present Perfect:
Last year the dancing company ( to become) the participant in the international festival.
I (to know) him since 2000.
The actors (to do) their best to make the performance interesting.
We (to get) excellent seats.
Yesterday we (to go) to the concert.
Maksimova (to dance) the main part in the ballet last time.
The performance ( not to start) yet.
Yesterday we ( to leave) our coats in the cloak -room.
They already (to see) the ballet Swan Lake.
2 Раскройте скобки, употребляя глаголы в Present Perfect или Past Simple.
1. We (to travel) around Europe last year. 2. My father knows so much because he (to travel) a lot. 3.1 (to see) Pete today, 4. She (to see) this film last Sunday. 5. Alex (to meet) his friend two hours ago. 6.1 just (to meet) our teacher. 7. The children already (to decide) what to do with the books. 8. Yesterday they (to decide) to help their grandmother. 9. Helen speaks French so well because she (to live) in France. 10. She (to live) there last year. 11. The rain (to stop) and the sun is shining in the sky again. 12. The rain (to stop) half an hour ago. 13. Mary (to buy) a new hat. 14.1 (to buy) a pair of gloves yesterday. 15. The wind (to blow) off the man's hat, and he cannot catch it. 16. The weather (to change), and we can go for a walk. 17. The wind (to change) in the morning.
Past Perfect
Had + V 3
Употребляется
-для обозначения действия, которое закончилось к определенному моменту в прошлом. Этот момент в прошлом обычно обозначается обстоятельством времени, выраженным существительным с предлогом by или другим действием в прошлом
-для выражения действия, которое завершилось раньше другого действия в прошлом.
Часто употребляется в сложноподчиненных предложениях с придаточными времени, вводимыми союзами when, after, before, until, by the time.
Спряжение глаголов в Pаst Реrfесt.
утвердительная форма |
вопросительная форма |
отрицательная форма |
He had asked |
Had he asked |
He had not (hadn’t) asked |
e.g. He had written a play by 5 o clock yesterday.
Had he written a play by 5 o clock yesterday?
He had not written a play by 5 o clock yesterday.
When we went to the theatre, the concert had started.
Задания.
1. Поставьте предложения в вопросительной и отрицательной форме:
The director had read a play by last night.
The film had already begun before we came to the cinema.
She had translated the text by 6 o clock yesterday.
By the end of the last year I had read five of Show s plays.
They had come when you finished your translation.
2 Раскройте скобки, употребляя глаголы в Past Simple, Past Continuous и Past Perfect.
I. When I called at his house, they (to tell) me that he (to leave) an hour before. 2. When I came to the station, I (not to) find my friend there as I (to be) five minutes late and the train (to leave). 3. He (to want) to visit the place where he (to live) in his childhood. 4. The telegram (to come) some minutes after he (to leave). 5. She (to look) very tired as she (to work) hard. 6.1 (to return) to the hotel only late at night as I (to lose) my way in the fog. When I (to come) up to my room, I (to see) Pete who (to stand) at the door of the room. He (to wait) for me as he (to lose) his key and could not get in. 7. When I (to wake) up, it (to be) already ten o'clock. I (to call) my brother. Nobody (to answer). He already (to leave). 8. I (to go) up to the open window. The rain (to stop) and the sun (to shine) brightly. The birds in the garden (to sing). The morning (to be) fine. 9. When the rain (to stop) I (to look) out of the window and (to see) John who (to stand) under a tree waiting for me.
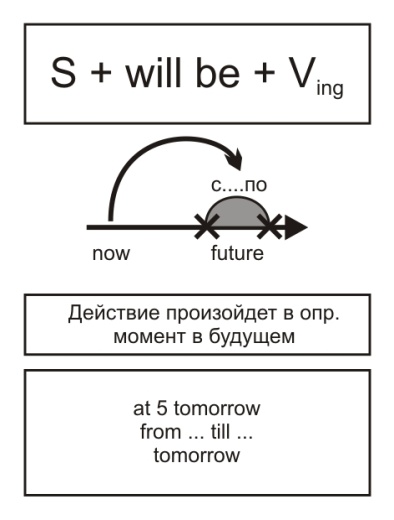
Future Perfect Tense
Shall/ will + have +V3
Употребляется
- для обозначения действия, которое завершится к определенному моменту в будущем. Этот момент обычно обозначается обстоятельством времени с предлогом by или другим будущим временем.
Спряжение глаголов в Future Perfect
число |
лицо |
утвердительная форма |
вопросительная форма |
отрицательная форма |
един |
1 |
I shall have done |
Shall I have done? |
I shall not have done |
2 |
You will have done |
Will you have done? |
You will not have done |
|
3 |
He She will have He done |
he Will she have it done? |
He She will not have He done |
|
множ |
1 |
We shall have done |
Shall we have done? |
We shall not have done |
2 |
You will have done |
Will you have done? |
You will not have done |
|
3 |
They will have done |
Will they have done? |
They will not have done |
e. g. They will have finished their work by 6 o clock tomorrow.
Will they have finished their work by 6 o clock tomorrow?
They will not have finished their work by 6 o clock tomorrow.
Задания.
1.Поставьте предложения в нужную форму Perfect:
My brother just (to go) back to his house after the concert.
Before he entered the University he ( to finish school).
They (to be) at the theatre by 6 o clock tomorrow.
I already (to buy) tickets to this play.
When I came to the station, the train (to go) away.
He is a schoolboy, but by this time next year he (to leave) school.
I (not to see) so many stars in one film.
I heard that our film ( to arouse ) a great interest at the festival.
The concert (to finish) by 6 o” clock.
2 Раскройте скобки, употребляя глаголы в одном из будущих времен: Future Simple, Future Continuous или Future Perfect.
1. I (to do) my homework tomorrow. 2. I (to do) my homework at six o'clock tomorrow. 3. I (to do) my homework by six o'clock tomorrow. 4. When I come home tomorrow, my family (to have) supper. 5. When you come to my place tomorrow, I (to read) your book. I (to do) my homework by the time you come. 6. Don't come to my place tomorrow. I (to write) a composition the whole evening. 7.1 (not to go) to the cinema tomorrow. I (to watch) TV the whole evening. 8. What you (to do) tomorrow? 9. What you (to do) at eight o'clock tomorrow? 10. You (to play) volley-ball tomorrow? 11. You (to do) this work by next Sunday? 12. When you (to go) to see your friend next time? 13. How many pages you (to read) by five o'clock tomorrow? 14. Tomorrow I (to begin) doing my homework as soon as I come from school. I (to do) my homework from three till six. My father (to come) home at seven o'clock tomorrow. I (to do) all my homework by the time he comes, and we (to go) for a walk together.
Present Perfect Continuous
- обозначает действие, которое началось в прошлом, длилось вплоть до настоящего и продолжается в настоящем
Have been +Ving
Спряжение Present Perfect Continuous
Число |
лицо |
утвердительная форма |
вопросительная форма |
отрицательная форма |
един. |
1 |
I have (I’ve) been working |
Have I been working? |
I have (I’ve) not been working |
2 |
You (You’ve) have been working |
Have you been working? |
You (You’ve) have not been working |
|
3 |
He has been She (‘s been) It working |
Has he been she working? it |
He has not been She (‘s not)working It |
|
множ |
1 |
We have (We’ve) been working |
Have we been working? |
We have (We’ve) not been working |
2 |
You (You’ve) have been working |
Have you been working? |
You (You’ve) have not been working |
|
3 |
They have (They’ve) been working |
Have they been working? |
They have (They’ve) not been working |
e.g. The actor has been learning his role for a long time.
I have been living Simferopol since my childhood.
1 Переведите на английский язык, употребляя глаголы в Present Continuous или в Present Perfect Continuous.
1. а) Они все еще спорят. Ъ) Они спорят уже два часа. 2. а) Она еще спит. Ь) Она спит уже два часа. 3. а) Он еще делает уроки. Ь) Он делает уроки уже три часа. 4. а) Мальчики все еще играют в футбол. Ь) Они играют в футбол уже сорок минут. 5. а) Девочки еще переодеваются. Ь) Они переодеваются уже полчаса. 6. а) Она все еще изучает испанский язык. Ь) Она уже два года изучает испанский язык. 7. а) Они все еще живут на даче. Ь) Они уже четыре месяца живут на даче. 8. а) Она все еще разговаривает по телефону. Ь) Она разговаривает по телефону уже двадцать минут. 9. а) Мой брат все еще решает эту трудную задачу. Ь) Он решает эту задачу уже полчаса. 10. а) Она все еще пишет письмо бабушке. Ь) Она уже целый час пишет это письмо. И. а) Они все еще ловят рыбу. Ь) Они ловят рыбу уже пять часов. 12. а) Дедушка и бабушка все еще играют в лото. Ь) Они играют в лото уже два часа. 13. а) Артисты все еще репетируют эту сцену. Ь) Они репетируют эту сцену уже три часа. 14. а) Дети все еще бегают во дворе. Ь) Они уже три часа бегают во дворе. 15. а) Он все еще пишет свою новую книгу. Ь) Он пишет свою новую книгу уже два года. 16. а) Он все еще учит монолог Гамлета. Ь) Он учит монолог Гамлета уже два дня. 17. а) Мы все еще ремонтируем нашу квартиру. Ь) Мы ремонтируем нашу квартиру уже полмесяца.
Past Perfect Continuous
- обозначает действие, которое началось до какого-то момента в прошлом и продолжалось вплоть до этого момента
Had been+ Ving
Образование Pаst Реrfect Continuous
Глагол в Past Perfect Cоntinuоus имеет одну и ту же форму для всех лиц единственного и множественного числа.
утвердительная форма |
вопросительная форма |
отрицательная форма |
She had (She’d) been cooking |
Had she been cooking? |
She had not (hadn’t) been cooking |
e.g. The news did not surprise me for I had been expecting it for some time.
He was tiered because he had been working for 6 hours.
Future Perfect Continuous
Shall/Will have been+ V3
- обозначает длящееся действие в будущем, которое начнется до какого-либо момента или периода будущего времени и будет продолжаться вплоть до этого момента. Эта форма мало употребительна. (отдается предпочтение Future Continuous or Future Perfect)
Обрaзование Future Perfect Continuous
число |
лицо |
утвердительная форма |
вопросительная форма |
отрицательная форма |
един. |
1 |
I shall (I’ll) have (‘ve) been running |
Shall I have (‘ve) been running? |
I shall not (shan’t) have (‘ve) been running |
2 |
You will (you’ll) have (‘ve) been running |
Will you have (‘ve) been running? |
You will not (won’t) have (‘ve)been running |
|
3 |
He will (‘ll) She have (‘ve) been It running |
he have(‘ve) Will she been it running? |
He will (‘ll) not She (won’t) have (‘ve) It been running |
|
множ. |
1 |
We shall (We’ll) have (‘ve) been running |
Shall we have (‘ve) been running? |
We shall not (shan’t) have (‘ve) been running |
2 |
You will (you’ll) have (‘ve) been running |
Will you have (‘ve) been running? |
You will not (won’t) have (‘ve) been running |
|
3 |
They will (they’ll) have (‘ve) been running |
Will they have (‘ve) been running? |
They will not (won/t) have (‘ve) been running |
e. g. He will have been writing the report for two hours when you come.
By next year she will have been living in this town for 5 years.
THE FUTURE IN THE PAST TENSES (Будущие времена в прошедшем)
В каждой из описанных выше групп времен будущее время может переводиться в план прошлого.
Так, в целях соблюдения правила согласования времен в косвенной речи вместо Future Indefinite ставится Future-in-the-Past Indefinite:
Cпряжениe Future Indefinite in the Past
число |
лицо |
утвердительная форма |
вопросительная форма |
отрицательная форма |
един. |
1 |
I should (I’d) ask |
Should I ask? |
I should not (shouldn’t) ask |
2 |
You would (you’d) ask |
Would you ask? |
You would not (wouldn’t) ask |
|
3 |
He She would (‘d) It ask |
he Would she ask? it |
He would not She (wouldn’t) It ask |
|
множ. |
1 |
We should (We’d) ask |
Should we ask? |
We should not (shouldn’t) ask |
2 |
You would (you’d) ask |
Would you ask? |
You would not (wouldn’t) ask |
|
3 |
They would (they’d) ask |
Would they ask? |
They would not (wouldn’t) ask |
Не said he would come to London in March. — Он сказал, что приедет в Лондон в марте.
The Future Continuous Tense преобразуется в the Future in the Past Continuous Tense:
He said he would be reading at that time. — Он сказал, что в это время будет читать.
The Future Perfect Tense изменяется и приобретает форму the Future in the Past Perfect Tense:
He said he would have finished the report by 7 o'clock. — Он сказал, что закончит доклад к 7 часам.
The Future in the Past Perfect Continuous Tense употребляется вместо The Future Perfect Continuous Tense:
He said that by next April we should have been living in the town for 5 years. — Он сказал, что к апрелю следующего года мы будем жить в городе уже 5 лет.
Формообразование в данной группе времен связано с изменением вспомогательных глаголов shall/will на формы прошедшего времени should/would.
Сводная таблица времен активного залога
Time
|
Indefinite |
Continuous |
Perfect |
Perfect Continuous |
Present |
write пишу writes пишет |
am writing пишу is/are writing пишет/пишут |
have written написали has written написал |
have been writing писали и еще пишут has been writing писал и пишет |
Past |
wrote писал(и) |
was/were writing писал/писали |
had written написал(и) |
had been writing писал(и) |
Future |
shall write напишу will write напишет |
shall be writing буду писать will be writing будет писать |
shall have written допишу will have written допишет |
shall have been writing буду писать will have been writing будет писать |
Future in the Past |
should write напишу would write напишет |
should be writing буду писать would be writing будет писать |
should have written допишу would have written допишет |
should have been writing буду писать would have been writing будет писать |
|
Indefinite |
Continuous |
Perfect |
Perfect Continues |
Present |
|
|
|
|
Past |
|
|
|
|
Future |
|
|
|
|
Задания
1.Поставьте глаголы в нужном времени ( Present, Past, Future Perfect Continuous):
He (to study) English for only two years before he was able to translate films.
The writer (to work) on the novel before he sent it to the publisher.
Mike (to learn) to sing for two years before he took part in the competition.
Peter work (to work ) at the Art Theatre since his graduation.
The producer and the director (to discuss) a play for some weeks before the actors arrive.
I (to look) for my glasses the whole morning before I finally found them.
2 Раскройте скобки, употребляя глаголы в требующемся времени.
1. The first person whom Andrew (to see) as he (to enter) was his old nurse. She (to sit) on the sofa. During the last five years she greatly (to change) and now (to look) a very old woman. 2. She is going to read the letter she just (to receive). 5. How long you (to wait) for me? I am really very sorry. 4. Yesterday I (to meet) a friend of mine whom I (not to see) for a long time. 5. Ring me up at eleven o'clock, I (not yet to sleep). 6. You (to be) late for the concert if you (not to take) a taxi. 7. The sun (to set) a long time ago, and it (to begin) to get really cold. 8. When I (to come) home yesterday, my sister already (to return) and (to sit) at the fireplace looking through some old photographs. 9. He (to smoke) three cigarettes and (to look) through all the books on the shelf, when at last he (to hear) his friend's steps approaching the door. 10. He just (to approach) the door, when she (to enter). 11. He (to write) the composition for three hours and he (to say) he soon (to finish) it as he (to think) over the conclusion now. 12. Hardly1 I (to go) out when I (to remember) that I (to forget) to take my umbrella. 13. Where is the baby? — The nurse (to put) it to bed. 14. He said he (to work) for a long time without achieving good results.
3 . Раскройте скобки, употребляя глаголы в требующемся времени.
1. When I (to come) to Pete's house last Sunday, he (to read) a new book. He (to say) he (to give) it to me soon. Today I (to take) it from him. Now I (to read) it. I (to finish) it by Friday. If you like, I (to give) it to you on Saturday when you (to come) to see me. 2. When will he come? We (to wait) for him for already half an hour. 3. On leaving the hall the students (to thank) the professor who (to deliver) the lecture. 4. We already (to cover) about ten miles when Peter, who (to look) out of the window for the last five or ten minutes, suddenly exclaimed: "Here is the station!" 5. When morning came, the storm already (to stop), but the snow still (to fall). 6. Yesterday by eight o'clock he (to finish) all his homework, and when I (to come) to his place at nine, he (to read). 7. I (to wait) for permission to go abroad for already three weeks, but I (not to receive) the visa yet. 8. Everybody (to be) at the door of the museum, but my friend (not yet to come). 9. We (to drink) tea when the telephone (to ring). 19. Johnny noticed that everybody (to look) at him, and he (to feel) shy. Ц. Light (to travel) more quickly than sound.
4. Раскройте скобки, употребляя глаголы в требующемся времени.
Peter (to read) by the fireplace when the door (to open) and the maid (to enter). The cook (to follow) her. 2. When the mother (to satisfy) herself that the children (to sleep) peacefully in their beds, she (to take) out the Christmas presents and carefully (to put) them into the stockings which (to hang) at the beds. 3. If you (to ring) me up tomorrow, I (to tell) you all about it. 4. The lesson (not yet to begin), and the children (to talk) loudly in the corridor. 5. I (to live) in St. Petersburg since 1991. 6. By the fifteenth of January the students (to pass) all the examinations. 7. The students (to write) the paper by dinner-time. 8. They (to sail) down the river for many hours before they (to come) to the village. 9. I (not to be) to my home town for five years. 10. The rain (to stop) by the time we (to reach) home. 11. The message (to arrive) five minutes after he (to leave) the house. 12. It (to be) nearly eleven o'clock when we (to begin) doing this work. 13. At last the reply from my grandmother (to come), and my mother (to tell) me that she (to come) soon. 14. Here you (to be) at last! I (to wait) for you for twenty minutes. You (not to be) ashamed?
5. Раскройте скобки, употребляя глаголы в требующемся времени.
1. The day (to be) cold and it (to rain). When I (to reach) home, my raincoat (to be) all wet. I (to take) it off, (to shake) the water off it, (to hang) it up and (to go) into the living-room. My children (to play) on the carpet. When they (to see) me, they (to jump) up and (to run) up to me. 2. I (to hear) this song several times already, but I cannot remember the words. I (to write) them down as soon as I (to hear) this song again. 3. Hardly1 he (to open) the suit-case, when he (to find) the tie which he (to think) he (to lose) long before. 4. Shut the door! The room (to be) full of smells which (to come) from the kitchen. Mother (not to like) kitchen smells in the room. 5. Last night he (to finish) the book which he (to begin) writing a year ago. 6. He said he (to listen) to the same stories for a long time. 7. By the evening he (to translate) ten pages. 8. You ever (to be) to the new stadium? — Yes, I (to be) there last Saturday. 9. The old lady was happy: she (not to see) her son for three years. 10. What you (to do) yesterday? 11. How many pages you (to translate) for today?
6. Раскройте скобки, употребляя глаголы в требующемся времени.
1. What you (to do) here? — I (to prepare) for my report. — How long you (to prepare) for it? — Oh, I (to work) since morning. 2. He (to teach) at school for five years when the war (to break) out. 3. She (to study) English since last year. 4. What you (to read)? — I (to read) a magazine. — How long you (to read) it? — I (to read) it for half an hour. 5. She (to live) in Moscow for ten years when her sister (to come) to live with her. 6. Our teacher (to come). Now he (to speak) with our monitor. 7. They (to speak) when I (to look) at them. 8. I (to walk) about an hour when I (to see) a little house not far from the river. 9. When he (to read) the newspaper, he (to give) it to his brother. 10. Ho (to leave) for Rostov in 1990 and since then he (to live) there. 11. At this time tomorrow we (to discuss) your report. 12. Now she (to read) the book which I (to give) her yesterday. 13. You ever (to be) to London? — Yes, I (to be) there last summer. 14. What your friend (to do) now? — She (to have) dinner. She usually (to have) dinner at this time. 15. I (to buy) a new dress. I (to show) it to you tomorrow when you (to come) to my place. 16. So you begin working tomorrow! And who (to take) care of your children when you (to go) to work? 17. Hello, Peter! Where you (to go)? — I (to go) to the library.
7. Раскройте скобки, употребляя глаголы в требующемся времени.
1. On entering the drawing-room he (to find) that his two friends (to get) up and (to wait) for him. 2. The sportsmen (to train) since early morning; now they (to go) over the high jump, as they (not to be) satisfied with their results. 3. Five minutes (not to pass) when the train for which we (to wait) (to appear) in the distance. 4. Tomorrow father (to come) late. We (to do) all our homework and (to drink) tea when he (to come). 5. When Mrs. Smith (to come) home yesterday, she (to see) that her daughter (to cook) supper and (to wait) for her with the table laid. 6. Where is Nick? — He (not to be) at home, he (to go) to the cinema. Wait for him, he (to come) in half an hour. 7. It was very late. I (to go) to bed and (to fall) asleep when my father (to return) home. 8. I'll join you when I (to drink) my tea. 9. When I (to come), he (to live) in the same old house where I first (to meet) him. He (to tell) me he (to wait) for me for already some time. 10. The pupils (to do) a lot of exercises before they (to learn) to write dictations well. 11. I could not hear a sound: they (to stop) talking.
2 Present Tenses
Simple Present, Present Continuous, Present Perfect, or Present Perfect Continuous? Choose the right answer.
1. Peter ______ to the swimming pool every day.
goes
is going
has gone
has been going
2. I usually ________ till nine in the evening.
work
am working
have worked
have been working
3. She ________ apple pie for dessert quite often.
makes
is making
has made
has been making
4. Please be quiet. My children________ .
sleeping
are sleeping
have slept
have been sleeping
5. The sun ________ in the east.
rises
is rising
has risen
has been rising
6. Listen! Someone________ the piano.
plays
is playing
has played
has been playing
7. Where is Linda? – She _________ dinner in the kitchen.
cooks
is cooking
has cooked
has been cooking
8. She can't go to the movies. She ______ her homework yet.
doesn't do
isn't doing
hasn't done
hasn't been doing
9. Tanya _______ France several times.
visits
is visiting
has visited
has been visiting
10. We ________ this report for four hours. Let's have a break.
write
are writing
have written
have been writing
3 Past Tenses
Simple Past, Past Continuous, Past Perfect, or Past Perfect Continuous? Choose the right answer.
1. It _______ me two hours to get to the airport.
took
was taking
had taken
had been taking
2. Their car was stolen while they ______ lunch at a cafe.
ate
were eating
had eaten
had been eating
3. My grandmother_________ fairy tales to me when I was a child.
read
was reading
had read
had been reading
4. When he lived in Mexico, he ________ in a bank.
worked
was working
had worked
had been working
5. He _______ for his bus at the bus stop when the robbers attacked him.
waited
was waiting
had waited
6. She __________ all the letters by the time her boss asked her to type them again.
sent
was sending
had sent
7. Until last night, she________ him about it.
never asked
was never asking
had never asked
8. He _________ for twenty years when he finally quit smoking.
smoked
was smoking
had been smoking
9. Yesterday I went to an interesting museum that I_________ before.
didn't visit
wasn't visiting
hadn't visited
10. By the time we arrived, she ___________ for us at the train station for three hours.
waited
was waiting
had been waiting
4 Future Tenses
Simple Future, Future Continuous, Future Perfect, or Future Perfect Continuous? Choose the right answer.
1. I'm sure that he__________ you.
will help
will be helping
will have helped
will have been helping
2. She __________ when you come back.
will sleep
will be sleeping
will have slept
will have been sleeping
3. I _________ you in the morning.
will call
will be calling
will have called
will have been calling
4. I ________ at 11:30 tomorrow.
will work
will be working
will have worked
will have been working
5. I think that we ________ to Italy next summer.
will go
will be going
will have gone
will have been going
6. You will recognize him. He __________ a brown leather jacket and a red scarf.
will wear
will be wearing
will have worn
will have been wearing
7. Say goodbye to Ann. By the time you return, she ________ for New York.
will leave
will be leaving
will have left
will have been leaving
8. She buys too many things. She_________ all her money long before her next pay.
will spend
will be spending
will have spent
will have been spending
9. By 2014, he __________ as the director of this company for thirty years.
will work
will be working
will have been working
10. She ______ him about it.
won't tell
won't be telling
won't have told
won't have been telling
5 All Tenses. Choose the right answer.
1. Who ______ food in your family when your Mom is away?
cooks
is cooking
has been cooking
cooked
2. Where is John? – He_________ his car in the garage.
repairs
is repairing
has repaired
repaired
3. I love this film. I __________ it four or five times already.
see
have seen
saw
had seen
4. I think I _______ home tonight. I'm a little tired.
stay
am staying
will stay
will be staying
5. She_________ the living room when she heard a strange noise in the kitchen.
has cleaned
has been cleaning
cleaned
was cleaning
6. I envy you. At five tomorrow you _________ some tan on a nice beach in Greece.
will get
will be getting
will have gotten
will have been getting
7. You arrived two days ago. You are going to leave next Sunday. By the time you leave, you _______nine days here.
spend
have spent
will spend
will have spent
8. Where is he? I ________ for him since three o'clock!
am waiting
have been waiting
was waiting
had been waiting
9. I went to Belgium last month. I _________ there before. It's a beautiful country.
have never been
had never been
never was
never been
10. He said that his mother would be very upset when she _______ that he had lost his job.
learns
learned
had learned
would learn
THE PASSIVE VOICE (Страдательный залог)
The Passive Voice показывает, что лицо или предмет, обозначенные подлежащим, являются объектами действия, выраженного сказуемым:
She was woken from her sleep by his singing. — Она была разбужена пением.
Образование
The Passive Voice образуется при помощи вспомогательного глагола to be в соответствующем времени, лице и числе и причастия прошедшего времени смыслового глагола Participle II:
The Passive Voice |
to be + Participle II |
Таблица форм глагола to give в страдательном залоге
Passive Voice |
Present |
Past |
Future |
Indefinite |
am/are/is given |
was/were given |
will be given |
Continuous |
am/are/is being given |
was/were being given |
____________________ |
Perfect |
has/have been given |
Had been given |
will have been given |
Perfect Continuous |
________________ |
________________ |
__________________ |
Пассивный залог показывает, что подлежащее не выполняет действие, а подвергается действию другого лица или предмета. Если указано, кем произведено действие, то употребляется предлог by:
e. g. The new play was staged by R. Simonov.
В Passive Voice употребляются глаголы, имеющие предложные дополнения такие как:
hear of – слышать о
laugh at – смеяться над
look after – присматривать за (кем-либо)
look at – смотреть на
rely on – полагаться на
send for – посылать за
speak of (about) – говорить о
pay attention to – обращать внимание на
take care of – заботиться о
The book is much spoken about. Об этой книге много говорят.
He can't be relied on. На него нельзя положиться.
В русском переводе не все глаголы сохраняют предлог:
to listen to – слушать что-либо, кого-либо
to look for – искать что-либо
to provide for – обеспечить кого-либо, чем-либо
to explain to – объяснять кому-либо
He was listened to with great attention. Его слушали с большим вниманием.
The new performance was much talked about.
( Об этом спектакле много говорили).
Задания


 Aspect
Aspect