
- •Table of Contents
- •Lexicology as a Science. The Object of Lexicology The main lexicological units. Their similarity and distinctive functions
- •Questions:
- •Types of Lexicology. Approaches to Language Study
- •Questions:
- •The Aims and Tasks of the Course of Modern English Lexicology
- •Questions
- •Links of Lexicology with Other Branches of Linguistics
- •Questions:
- •Semasiology Meaning as a Linguistic Notion. Approaches to Meaning Study
- •Questions:
- •The Semantic Triangle. The Interrelation of Meaning with Sound-form, Referent and Concept.
- •Questions:
- •Types of Meaning
- •Questions:
- •Semantic Structure of Words. Componential Analysis
- •Questions:
- •Aspects of Lexical Meaning
- •Questions:
- •Word-Meaning and Motivation
- •Questions:
- •Polysemy and Homonymy Diachronic and Synchronic Approaches to Polysemy
- •Questions:
- •Polysemy and Context. Types of Context
- •Questions:
- •Two Processes of the Semantic Development of a Word
- •Questions:
- •Homonymy Sources of Homonyms
- •Questions:
- •Classification of Homonyms
- •Questions:
- •Polysemy and Homonymy: Etymological and Semantic Criteria
- •Questions:
- •Change of Meaning Causes of Semantic Change
- •Questions
- •Nature of Semantic Change. Metaphor, Metonymy and Other Minor Types
- •Questions:
- •Results of Semantic Change
- •Questions:
- •Historical Changeability of Semantic Structure
- •Questions:
- •Lexical Paradigmatics English Vocabulary as a System
- •Questions:
- •Types of Semantic Relations of Words
- •Questions:
- •Different Groupings of Words Morphological Groupings
- •Questions:
- •Semantic Groupings Synonyms
- •Questions:
- •Antonyms
- •Questions:
- •Syntagmatic Relations of Words Lexical and Grammatical Valency
- •Questions:
- •Types of Word-Groups
- •Questions:
- •Phraseology Criteria of phraseological units
- •Questions:
- •Classification of Phraseological Units
- •Questions:
- •The Ways of Forming Phraseological Units
- •Questions:
- •Proverbs and Sayings
- •Questions:
- •Morphological Structure of English Words and Word-Formation Morphemes, Their Definition. Allomorphs
- •Questions:
- •Classification of Morphemes
- •Questions:
- •Morphemic and Derivational Analyses
- •Questions:
- •Productive Ways of Word-Building Affixation. Synonymity, homonymity and polysemy of affixes
- •Questions:
- •Conversion. Approaches to Conversion. Synchronic and Diachronic Treatment of Conversion. Types of Relations between Converted Pairs
- •I. Verbs converted from nouns (denominal verbs).
- •II. Nouns converted from verbs (deverbal substantives).
- •Questions:
- •Compounding
- •Questions:
- •Shortening and Other Minor Types
- •Questions:
- •Questions:
- •Historical Changeability of Word-Structure
- •Questions:
- •Etymology Words of Native Origin
- •Questions:
- •Borrowings Causes and Ways of Borrowing. Criteria of Borrowings
- •Questions:
- •Assimilation of Borrowings
- •Questions:
- •Influence of Borrowings
- •Influence on semantics
- •Influence on lexical territorial divergence
- •Questions:
- •Etymological Doublets
- •Questions:
- •International Words
- •Questions:
- •Lexicological analysis of the text
- •11.Etymology.
- •Example analysis:
- •Mind-map of lexicology terms
- •Definitions Seminar 1. Lexicology as a science. The object of lexicology.
- •Seminar 2. Semasiology.
- •Seminar 3. Polysemy and Homonymy.
- •Seminar 4. Change of Meaning.
- •Seminar 6. Syntagmatic relations o words.
- •Examination Questions
Mind-map of lexicology terms

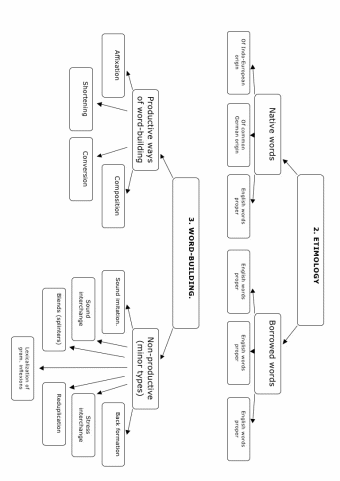
Appendix C
Definitions Seminar 1. Lexicology as a science. The object of lexicology.
Lexicology – the branch of linguistics, concerned with the vocabulary of the language and the properties of words.
Word– 1) a basic unit of any language, which serves as a name of things, actions, qualities; it is a two-faced unit, possessing both the form and the content.
2) one of the fundamental units of language, dialectical unity of form and content. It is related both to extralinguistic reality and to human notions, and its basic function is to reflect reality in its content. It is used for purposes of human communication, materially representing a group of sounds, possessing a meaning and characterized by formal and semantic unity.
Morpheme – the smallest meaningful unit, two-faced one, but in contrast to the word it cannot function independently. We use them only when we speak of word structure and word formation.
Phraseological units – set-phrases with transferred meaning, which may even function as word equivalents.
Phraseology – the branch of lexicology specializing in word-groups which are characterized by stability of structure and transferred meaning.
System – a certain abstraction, a whole constituted by intodepended elements of the same order, and we study the properties of these elements and the relationships they enter.
Syntagmatic relations– those,which are based on the linear character of speech and they are studied by means of contextual, transformational and other types of analysis. In syntagmatic relations, context is most important.
Context– the minimal stretch of speech necessary and sufficient to determine which of the possible meaning of a word is used. Syntagmatic relations are reflected in the collocability of words and phonological units.
Paradigmatic relations reveal themselves in the morphemic structure of words. They are described in terms of morphemes and their arrangement.
The synchronic approach– one which is concerned with the state of a language at a given state of its development. This method of study is applied in descriptive lexicology which analyses the present day state of the vocabulary.
The diachronic approach deals with the change and development of a language in a course of time. It results in historical lexicology which studies the language in its flux.
The special lexicologydeals with rather not universals but with specific features of the given language.
The general lexicology– one which is concerned with properties and features common to the vocabulary of any language. The special lexicology concentrates rather not on the universal but on specific features of a given language.
Sociolinguistics- a branch of science which deals with correlations between the facts of social life and linguistic facts, the system of the language and its development.
Linguostylistic- a branch of linguistics dealing with the investigation of the styles of speech and stylistic expressive means with relation to the contents expressed.
