
- •Infotech 1
- •Module 7 Programming / Jobs in ict 119
- •In this module, you will:
- •Write a short presentation summarizing your discussion. Then ask one person from your group to give a summary of the group's ideas to the rest of the class.
- •In pairs, label the elements of this computer system.
- •X is a type of...
- •In pairs, answer these questions. If necessary, look at the Glossary.
- •Complete this diagram of a pc system. Look at Units 1,2 and 3 to help you.
- •In pairs, compare your answers.
- •6 Your ideal computer system
- •In a computer shop
- •Listen again and complete the product descriptions.
- •MacBook
- •Vocabulary tree
- •In this module, you will:
- •Interacting with your computer
- •Interact with a computer by using one of these: a light pen, a scanner, a trackball, a graphics tablet, a game controller or a microphone.
- •This is a device the cursor and selecting items on the screen.
- •Alphanumeric keys represent letters and numbers, as arranged on a typewriter.
- •6 Speech recognition systems
- •I In pairs, discuss how many ways there are of capturing an image on a computer.
- •I oolaere ljOo can manLpulate Lt.
- •2. TVie scaled
- •In small groups, compare your answers and decide about the following.
- •Image you don't need.
- •In pairs, discuss these questions.
- •- The width of the screen in proportion to its height
- •Vertically
- •What substance produces light and colour when hit by electrons in a crt monitor?
- •Display screens and ergonomics
- •Get a good chair, one that your lower back and is
- •Instructions and advice
- •Find words in the article with the following meanings.
- •Output quality, measured in dots per inch (lines 10-15)
- •Comparatives
- •Good —► better bad —► worse little —► less
- •6 Reading quiz - printer adverts
- •In pairs, read the adverts and then answer these questions. See who in your class can finish first.
- •Which printer would you recommend to someone who wants to print advertising graphics?
- •If you have the wide-format printer from Vutek, what kinds of material can you print on?
- •In pairs, discuss these questions.
- •(2! Listen to an interview with Mike Hartley, the director of the Assistive Technology Project for the Blind in Washington dc. Make notes about these topics.
- •Investing in assistive technologies
- •In this module, you will:
- •Indicating addition furthermore in addition besides moreover and
- •Iomega portable hard drive
- •I Read these posts from a forum about the topic of'Blu-ray versus hd-dvd'and then add your response, giving your opinion on the topic.
- •Dragon flash drive
- •Vocabulary revision
- •Like music.
- •Summarize the text on page 64 in 90-100 words. Follow these steps:
- •In pairs, read the instructions and complete the puzzle.
- •Instructions
- •Insert ] Fgmat look ТдЫе V£jndow Help
- •0 ( Replace All ) Replace ( Cancel ) f Fmd Next *
- •I In pairs, discuss the advantages and disadvantages of showing the information above as a graph, rather than as a worksheet.
- •In this module, you will: of the Internet page
- •Internet basics
- •Make a list of all the things you can use the Internet for.
- •Internet faQs
- •Internet faQs: Part 1
- •Internet faQs: Part 2
- •To connect to a computer by typing your username and password (in Telnet paragraph)
- •In pairs, make questions using these prompts. Then practise asking and в
- •In pairs, discuss these questions. Give reasons for your answers.
- •Virtual meetings
- •In pairs, discuss these questions.
- •Virtual meetings
- •In pairs, discuss these questions. Give
- •ISl Listen again and decide whether these sentences are true or false. Correct
- •In pairs, discuss these questions.
- •How old was the hacker that broke into the us defence computer in 1989?
- •1981 - Ian Murphy, a 23-year-old known as Captain Zap on the networks, hacked into the White House and the Pentagon.
- •A Canadian hacker (4) - a massive denial of service attack against websites like
- •The iLoveYou virus, cleverly disguised as a love letter, (5) so quickly that email had to be shut down in many companies.The worm (6) image and sound files
- •6 Internet issues
- •In this module, you will:
- •In pairs, look at the computer graphics (a-d) and discuss these questions.
- •В Read the text on page 101 and check your answers to 3 and 4 in a.
- •What type of graphics software is used to make maps or 3-d models of the Earth?
- •In total.
- •Read the text and check your answers to a.
- •In pairs, discuss the question What is desktop publishing? in as much detail as you can. Then look back at the text on page 105 to see how much you remembered.
- •1 Multiple forms of media
- •In pairs, discuss these questions.
- •In pairs, discuss these questions.
- •Web page design
- •Visual basic and VoiceXml Work in pairs. Student a reads about Visual basic, Student в reads about VoiceXml. Try not to look at your partner's text. Complete your part of the table.
- •Click here -V-'
- •It professionals
- •I've never worked with databases.
- •Vacancies at eJupiter.Co.Uk Webmaster
- •In this module, you will:
- •Information and communications technologies (ict)
- •In pairs, discuss these questions.
- •VoIp technology
- •In pairs, describe your mobile phone.
- •In pairs, discuss these questions.
- •Small networks
- •How many types of network are there?
- •How do I install a wired modem router?
- •How do I log on to the Internet Service Provider?
- •What is wireless networking?
- •What do I need to set up a home wireless lan?
- •Which is better, a wired or wireless lan?
- •Internet Service
- •Ish aerial
- •In pairs, discuss these questions. Give reasons for your answers.
- •In pairs, discuss if you agree with everything that Matt says in his interview
- •In pairs, look at the statements about gaming (1-4) and say if you agree or disagree with them. Give reasons for your answers.
- •In pairs, discuss these questions.
- •Language work: future forms
- •Integrated into our lives. What do you think about number.
- •Curriculum vitae
- •It skills
- •Irregular verbs
Display screens and ergonomics
Ergonomics
Unit 7
A bJ Listen to Tony Clark, an expert in computer ergonomics, talking to some office workers about health and safety. What health problems associated with computer use do the office workers mention?
в В Listen again and complete these extracts.
-
Get a good chair, one that your lower back and is
-
Make sure your feet rest firmly or on a footrest.
-
Position the keyboard your elbows, with your arms
the work surface ...
-
... position the monitor at, or just below,
-
You should sit at from the front of the monitor, about 50 to 70
centimetres away.
-
... a kind of stand that lets you move the monitor , so you can use it
at the correct angle and height’.
Match the extracts above (1-6) with the correct parts of the diagram (a-f).
Ergonomics
- the study
of how people interact safely and efficiently with machines and
their work conditions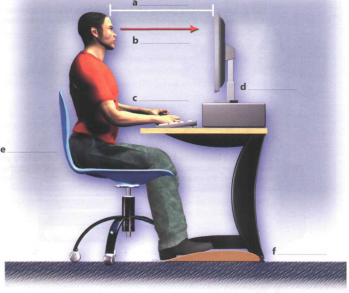

Instructions and advice
always use a
copyholder if you are working from documents.The best position is between the screen and the keyboard, or at the same height as the screen; this can reduce neck, back and eyestrain.
Irresponsible disposal of electronic waste can cause severe environmental and health problems. You just throw your old monitor or video system into the bin.
Language work: instructions and advice
Look at the HELP box and then complete these health and safety guidelines with should/shouldn't.
-
If you type a lot at your computer each
day, you buy an ergonomic
keyboard; it can help reduce the risk of repetitive strain injury.
-
You place your mouse
within easy reach and support your forearm.
-
If you decide to build your own PC, protect yourself from electric shocks. You
touch any components
unnecessarily.
-
You
-
We use the imperative to give instructions. Get an adjustable chair.
Don't put your monitor in front of a window.
-
We use should and shouldn't + infinitive to give advice or to talk about what we think is a good or bad idea.
You should look down at the monitor, not up.
You shouldn't use a monitor that's fuzzy or distorts the image.
-
We can also give advice by using set phrases like It's a good idea to or It's a bad idea to
+ infinitive.
It's
a good idea to have
a monitor with a tilt-
and-swivel
stand.
В IW| In pairs, practise giving advice about how to use a monitor safely using should/shouldn't or It's a good/bad idea to. Look at these guidelines for help.
-
Don't open the monitor. It's dangerous.
-
Don't stare at the screen for long periods of time.
-
Position the monitor at eye level or just below.
-
Leave enough space behind the monitor for unobstructed movement.
-
Don't sit near the sides or back of CRT monitors. Use LCD screens instead - they're free from radiation.
-
Keep the screen clean to prevent distorting shadows.
An ergonomic school or office
ЁЦ You have been asked to write a list of guidelines for making your school or office more ergonomic. Look at the definition of ergonomics at the bottom of page 35 and then write an email to your teacher/manager explaining your guidelines. Consider 1-8 below.
-
Physical layout of the work site; desk areas, computer equipment, filing cabinets, etc.
-
Lighting (overhead lights, desk lamps), glare and ventilation
-
Computer and office furniture: ergonomic chairs and desks
-
User-friendly and ergonomic devices: keyboards, mice, monitors, wrist rests, copyholders, etc.
-
Location and features of telephones
-
Layout of cables and switches for a wired network
-
Wireless internet access and wireless network
-
Maintenance and technical repairs

nit8 Choosing a printer
Types of printer
How many types of printer can you think of? Make a list.
Read the article on page 38 and then label the types of printer (1-5). Which types of printer aren't pictured?

The quality (resolution) of the images goes up to 2,400 dots per inch (dpi)
1

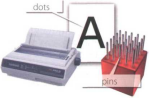
Provides high quality output: a resolution of 1,200-2,400 dpi
The resolution depends on the number of pins
2



Provides high quality for linework (lines and curves)
Provides the highest resolution: more than 3,000 dpi
WHICH TYPE OF

SHOULD I BUY?
Printing is the final stage in creating a document. Since the results you can obtain with different types of printer will vary substantially, here is a guide to help you decide which one is most suitable for your needs.
-
To begin with, you should take into account that printers vary in cost, speed, print quality, and other factors such as noise or printing method. Technology is evolving so quickly that there is always a printer for every application or need.
10 Dot-matrix printers use pins to print the dots required to shape a character. They can print text and graphics; however, they produce relatively low resolution output — 72 to 180 dots per inch (dpi).They are used to print multi-part forms, self-copying paper 15 and continuous-form labels.They are slower than laser printers (see below) but much cheaper.
Inkjet printers operate by projecting small ink droplets onto paper to form the required image. Colour and hues are created by the precise mixing 20 of cyan, magenta, yellow and black inks. Inkjets are fairly fast, quiet, and not as expensive as laser printers. Nevertheless, you can still expect high quality results because there are some inkjet printers on the market with a resolution of 2,400 dpi.
Laser printers produce output at great speed and with a very high resolution of 1,200-2,400 dpi. They scan the image with a laser beam and transfer it to paper with a special ink powder called toner. They are constantly being improved. In terms of speed and image quality, laser printers are preferred by experts for various reasons; for instance, they have a wider range of scalable fonts than inkjets, can emulate different language systems, and can produce high- quality graphics; however, they are still expensive for home users.
Thermal transfer printers are used to produce colour images by transferring a wax-based ink onto the paper. They are popular for printing bar codes, labels and medium-resolution graphics.
Imagesetters produce very high-resoludon output (up to 3,540 dpi) on paper or on the actual film for making the printing plates. In addition, they are extremely fast. Imagesetters are most often used in desktop publishing (DTP). Although they produce the highest quality output, they have one important disadvantage: they are too expensive for homes or small offices.
In modern lithographic printing, images are created on a DTP computer and then output directly to the printing plates, without requiring film as an intermediate step. This technology is called computer to plate, or CTP, and the machine used is called a platesetter.
Finally, we have plotters. Plotters use ink and fine pens held in a carriage to draw very detailed designs on paper. They are used for construction plans, engineering drawings and other technical illustrations. Nowadays, traditional plotters are being replaced with wide-format inkjets.
