
- •Передмова
- •Understanding Marketing
- •What is Marketing?
- •IV. Find in the text the following words and word combinations and translate the sentences in which they are used:
- •V. Find English equivalents to the words and word combinations given below:
- •VI. Memorize the following terms and use them in your own sentences:
- •VII. Match the English and Ukrainian equivalents:
- •VIII. Fill in the blanks from the words below. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian:
- •IX. Adjectives versus adverbs. Look at the following sentences:
- •X. Adjective modification. Look at the following sentence:
- •XI. Read the following statements about the role of marketing and give answers to the questions below:
- •Questions:
- •XII. Translate the following text. Compare your translation with the original given in Text a. Що таке маркетинг?
- •XIII. Read and translate the following definitions:
- •XIV. Act as an interpreter for a and b:
- •XV. Read and summarize the following text: Marketer Profile Lee a. Iacocca of Chrysler Corporation
- •XVI. Role-play.
- •XVII. Action problem.
- •Types of writing expected at the University
- •Text b The core marketing concepts
- •IV. Find in the text the following words and word combinations and translate the sentences in which they are used:
- •V. Find English equivalents to the words and word combinations given below:
- •VI. Memorize the following terms and use them in your own sentences:
- •VII. Match the Ukrainian and English equivalents:
- •VIII. Fill in the blanks from the words below. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian:
- •IX. Synonyms and antonyms. Complete the following table:
- •X. Join the halves.
- •XI. Translate the following text and summarize it in about 50 words:
- •Is Microsoft a Marketer?
- •XII. Translate the following text: Основні поняття маркетингу
- •XIII. Act as an interpreter for a and b:
- •XIV. Round-table discussion:
- •Marketing Management and strategic planning
- •Marketing management philosophies
- •V. Find English equivalents:
- •Vі. Memorize the following terms and their Ukrainian equivalents:
- •VII. Match the Ukrainian and English equivalents:
- •VIII. Read and analyze the following discussion about the direction a certain company should take and give answers to the questions below:
- •Questions
- •IX. Opinion-giving. Look at the following sentences:
- •I feel we must certainly ensure quality...
- •X. Agreeing and disagreeing. Look at the following sentences:
- •I think we’d all agree with you as far as you ...
- •I’m not sure I agree with either of you
- •XI. Fill in the blanks from the words below. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian:
- •XII. Translate into English:
- •XIII. Act as an interpreter for a and b:
- •XIV. Consider the following chart and speak about the difference between the sales or production orientation, and the consumer or market orientation: Sales and production orientation
- •Consumer and market orientation
- •XV. Read the following text and give a short summary of it: Marketing In Action: Polaroid Adopts Marketing Concept
- •XVI. Round-table discussion:
- •XVII. Action problem:
- •The Essay Test
- •XVIII. Case Study: the electric feather pirogue: going with the marketing flow
- •Questions
- •Text b Strategic Planning
- •Analyzing the Current Business Portfolio
- •I. Key terms:
- •IV. Vocabulary notes:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Find in the text the following words and word combinations and translate the sentences in which they are used:
- •V. Find English equivalents:
- •VI. Memorize the following terms and use them in your own sentences:
- •VII. Match the Ukrainian and English equivalents:
- •VIII. Read an edited extract from the Principles of Marketing (Kotler and Armstrong) and complete Charts 1 and 2.
- •IX. Sequence. Look at the following sentences.
- •X. Expressing purpose, look at the following sentences:
- •XI. Fill in the blanks from the words below. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •XII. Read the following text and summarize it in 100 words. The Boston Consulting Group Approach
- •XIII. Find the closest synonym for the words on the left. Select from a-k on the right.
- •XIV. Translate into English:
- •XV. Act as an interpreter for a and b
- •XVI. Look through the text and answer the questions given below. Hewlett-Packard: Strategies for Leadership
- •Tier Three
- •Questions
- •XVII. Case Study. Maytag corporation: expanding the appliance portfolio
- •Questions
- •Marketing Management process
- •Factors of the Marketing Management process
- •Market Segmentation
- •Market Targeting
- •Market Positioning
- •I. Key terms:
- •II. Vocabulary notes:
- •III. Answer the following questions:
- •IV. Find in the text the following words and word combinations and translate the sentences in which they are used:
- •V. Find English equivalents:
- •VI. Memorize the following terms and their Ukrainian equivalents:
- •VII. Match the Ukrainian and English equivalents:
- •VIII. Fill in the blanks from the words below. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •IX. Synonyms and antonyms. Complete the following table:
- •X. Join the halves.
- •XI. Translate the following text and summarize it in about 100 words. Canadians Battle in Florida
- •XII. Translate the following text into Ukrainian: Процес маркетингового менеджменту
- •Процес маркетингового менеджменту
- •XIII. Act as an interpreter for a and b.
- •XIV. Role play. Enact an imaginary interview between a university student and a well-known marketing specialist.
- •XV. Case Study. The artist
- •The company
- •The issues
- •Questions:
- •Text b Developing the Marketing mix
- •IV. Find in the text the following words and word combinations and translate the sentences in which they are used:
- •V. Find English equivalents:
- •Vі. Memorize the following terms and their Ukrainian equivalents:
- •VII. Match the Ukrainian and English equivalents:
- •VIII. Fill in the blanks from the words below. Translate the sentences into Ukrainian.
- •IX. Synonyms and antonyms. Complete the following table:
- •X. Complete the following sentences:
- •XI. Translate the following text and summarize it in about 120 words. British Airways Caters to Seniors; Age Has Its Privileges, Even in the Air
- •XII. Translate into English.
- •XIII. Act as an interpreter for a and b.
- •XIV. Action problems.
- •XV. Case Study. Trap-ease america: the big cheese of mousetraps
- •Questions:
Questions
-
Is Mr. Wadlington practicing the marketing concept? If not, which of the marketing philosophies does he I follow?
-
What are the characteristics of the people who make up the market for the Electric Feather Pirogue? Describe the needs and wants that are satisfied by the product.
-
Mr. Wadlington seems to be opposed to changing his present marketing system. Apparently, he believes that his current plan is working because sales are strong and profits are satisfactory, and he would ask, «Why not stick with a winner?» How would you respond to Mr. Wadlington’s assumptions?
-
What recommendations would you make to Mr. Wadlington if he wanted to adopt the marketing concept?
Text b Strategic Planning
Strategic planning is deciding today what to do in the future. It sets the stage for the rest of the planning in the firm and consists of analysis and strategy. Strategic planning can be defined as the process of developing and maintaining a strategic fit between the organization’s goals and capabilities and its changing marketing opportunities. It relies on developing a clear company mission, supporting objectives, a sound business portfolio, and coordinated functional strategies.
At the corporate level, the company first analyses its present position and defines its overall purpose and mission. This mission is then turned into detailed supporting objectives that guide the whole company. Next, headquarters decides what portfolio of businesses and products is best for the company and how much support to give each one. Each business and product unit must in turn develop detailed marketing and other departmental plans that support the company-wide plan. Thus, marketing planning occurs at the business-unit, product, and market levels. It supports company strategic planning with more detailed planning for specific marketing opportunities.
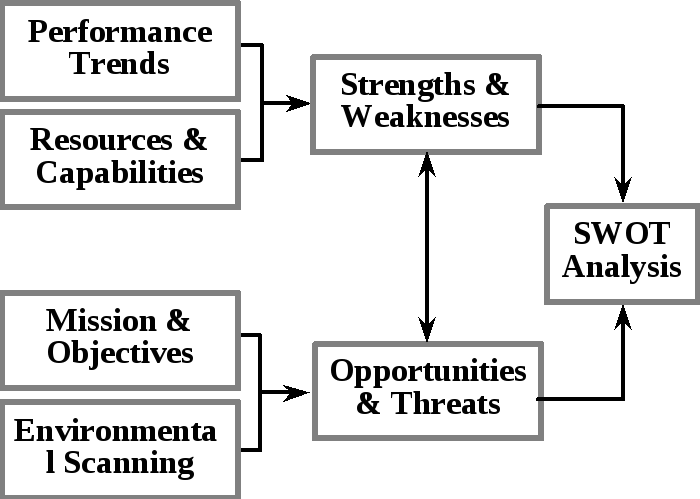
The first step in the strategic marketing management process is analysis. It consists of identifying the firms Strengths and Weaknesses as well as Opportunities and Threats. Note that the first letters in each of these words compose the acronym SWOT. A SWOT analysis consists of studying a firm’s performance trends, resources, and capabilities to assess a firm’s strengths and weaknesses, explicitly stating a firm’s mission and objectives, and scanning the external environment to identify opportunities and threats facing the organization.
A firm’s strengths and weaknesses can be identified and analyzed by studying performance trends, resources, and capabilities. Past performance typically is measured in financial terms, such as sales and profits. Profits act as prophets, in a sense. For example, yearly increases in profits are a sign of strength, while a steady decline in profits indicates that the firm has a problem. Current resources and capabilities also help to determine a firm’s strengths and weaknesses. Resources and capabilities refer to various things; special talents (i.e., the company has one of the most creative advertising departments In the country), areas of expertise (i.e., the company is a beer producer and is the industry leader in developing new brewery technologies), unique assets (i.e. the company holds 12 patents on new products or has $ 50 million in available cash), or any other advantage that can be drawn on for support (i.e. a pharmaceutical company may have excellent working relationships with retail druggists).
Opportunities and threats can be identified by stating the organization’s mission and objectives and engaging in the process of environmental scanning.
The marketer wants to identify market opportunities that exist because there is an unmet or unsatisfied need or want in the marketplace and for which the firm has an interest in and capability to satisfy. At the same time the marketer should try to convert threats into opportunities. For example, toy industry marketing managers should view the decline in birth rates as an opportunity to broaden their market base to appeal to adults by developing more sophisticated toys and games.
Defining the Company Mission
What is our business? Who is the customer? What do consumers value? What will our business be? What should our business be? These simple-sounding questions are among the most difficult the company will ever have to answer. Successful companies continuously raise these questions and answer them carefully and completely.
Many organizations develop formal mission statements that answer these questions. A mission statement is a statement of the organization’s purpose — what it wants to accomplish in the larger environment. A clear mission statement acts as an «invisible hand» that guides people in the organization so that they can work independently and yet collectively toward overall organizational goals.
Companies traditionally defined their business in product terms, such as «We manufacture furniture,» or in technological terms, such as «We are a chemical-processing firm.» But market definitions of a business are better than product or technological definitions. Products and technologies eventually become out-of-date, but basic market needs may last forever. A market-oriented mission statement defines the business in terms of satisfying basic customer needs. Thus, AT&T is in the communications business, not the telephone business. Visa defines its business not as credit cards, but as allowing customers to exchange value—to exchange such assets as cash on deposit or equity for virtually anything, anywhere in the world. And Sears’s mission is not to run department stores but to provide a wide range of products and services that deliver value to middle-class, home-owning families.
Management should avoid making its mission too narrow or too broad. A leading pencil manufacturer that says it is in the communication equipment business is stating its mission too broadly. Mission statements should be specific and realistic. Many mission statements are written for public relations purposes and lack specific, workable guidelines. The statement «We want to become the leading company in this industry by producing the highest-quality products with the best service at the lowest prices» sounds good but is full of generalities and contradictions. It will not help the company make tough decisions.
Setting Company Objectives and Goals
The company’s mission needs to be turned into detailed supporting objectives for each level of management. Each manager should have objectives and be responsible for reaching them.
Marketing strategies must be developed to support these marketing objectives. To increase its national market share, the company may increase its product’s availability and promotion. To enter new foreign markets, the company may cut prices and target large farms abroad. These are its broad marketing strategies.
Designing the Business Portfolio
Guided by the company’s mission statement and objectives, management must now plan its business portfolio. A company’s business portfolio is the collection of businesses and products that make up the company. The best business portfolio is the one that best fits the company’s strengths and weaknesses to opportunities in the environment. The company must (1) analyze its current business portfolio and decide which businesses should receive more, less, or no investment, and (2) develop growth strategies for adding new products or businesses to the portfolio.
