
- •Unit 1 computer applications
- •Computers
- •What can computers do?
- •Unit 2 computer essentials
- •What is a computer?
- •Unit 3 inside the system
- •What’s inside a pc system?
- •Structure of the processor
- •Unit 4 bits and bites
- •Units of memory
- •Unit 5 magnetic drives
- •Technical details
- •Unit 6 optical breakthrough
- •Optical disks and drives
- •Iomega's removable drives
- •Unit 7 input / output devices
- •Voice recording device h. Keyboard
- •Unit 8 capture your favourite image
- •Vivid easy-to-use faster fashionable wide shots
- •Unit 9 viewing the output
- •The monitor
- •Unit 10 choosing a printer
- •Types of printers
- •Unit 11 operating systems Exercise 1.Look at the diagram below. What is the function of the operating system?
- •Exercise 4. Language work
- •Unit 12 the graphical user interface
- •Unit 13 a walk through word processing
- •Word-processing facilities
- •Unit 14 spreadsheets
- •Unit 15 databases
- •Basic features of database programs
- •Exercise 6. Writing
- •Unit 16 faces of the internet
- •Exercise 2. Maybe we can find it on the Internet.
- •Exercise 3. Reading.
- •Internet software
- •Irc, audio and video chatting
- •MIrc for Windows is a typical Internet relay chat program. You can get it at http://www.Mirc.Co.Uk/
- •Unit 17 programming and languages
- •Programs and programming languages
- •Exercise 3. These are answers to questions about the text. Write the questions.
- •Variables and the Declaration Statement
- •Unit 18 computer networks
- •Computer networks
- •Network configurations
- •4 Bus/Ethernet
- •Unit 19 computer viruses
- •How computer viruses work
- •Unit 20 computers in the office
- •Information systems
- •Using Computers
- •Information Technology (it)
- •Exercise 5. Link each statement (1-) with a purpose (a-j).
- •Exercise 6. Match the words from the box with their definitions.
- •The future? We’re virtually there!
Unit 9 viewing the output
Exercise 1. After the information has been processed by the CPU, we can see the results on the screen. This is also called a monitor or visual display unit (VDU).
Describe the monitor of your computer to another student. Use these questions to help you.
Is it a monochrome or a colour monitor?
What size is the screen?
D
 oes
it have a cathode ray tube or a flat LCD screen?
oes
it have a cathode ray tube or a flat LCD screen?How can you change the picture using the controls?
Does it produce a high quality image?
Exercise 2. Reading.
A Read the text and try to guess the meaning of any new words in the box below. Refer to the Glossary if necessary.
dot pixel display resolution cathode ray tube
electron beam scan (verb) hertz refresh rate
flicker bit-mapped visualize
The monitor
The characters and pictures that we see on the screen are made up of dots, also called picture elements (pixels). The total number of pixels in which the display is divided both horizontally and vertically is known as the resolution. If the number of pixels is very large, we obtain a high resolution display and therefore a sharp image. If the number of pixels is small, a low resolution is produced.
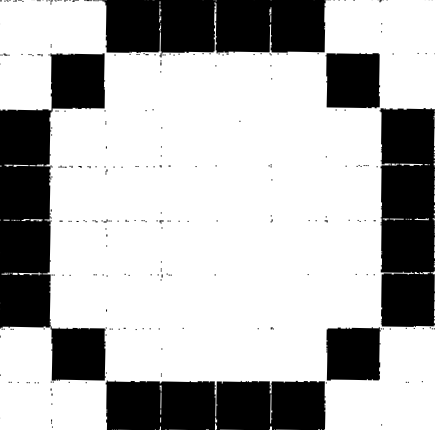
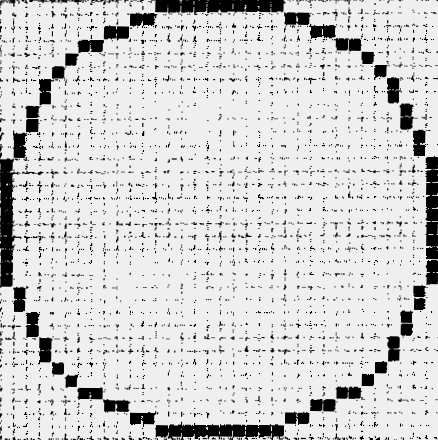
Low resolution display High resolution display
Typical resolutions are 640 X 480 or 1,024 x 768 pixels. The diagrams on page 35 show how pixel density affects the image: a larger number of pixels gives a much clearer image.
The cathode ray tube of the monitor is very similar to that of a TV set. Inside the tube there is an electron beam which scans the screen and turns on or off the pixels that make up the image. The beam begins in the top left corner, and scans the screen from left to right in a continuous sequence, similar to the movement of our eyes when we read, but much faster. This sequence is repeated 50, 70 or 85 times per second, depending on the system. If the rate of this repetition is low, we can perceive a flickering, unsteady screen, which can cause eye fatigue. However, a fast-moving 75, Hz 'refresh rate' eliminates this annoying flicker.
What we see on the screen is created and stored in an area of RAM, so that there is a memory cell allocated to each pixel. This type of display is called bit-mapped. On monochrome monitors, bits 0 are visualized as white dots, and bits 1 as black dots.
On colour displays, there are three electron guns at the back of the monitor's tube. Each gun shoots out a beam of electrons for each of the primary colours: red, green and blue. These electrons strike the inside of the screen which is coated with substances called phosphors that glow when struck by electrons.
Three different phosphor materials are used -one each for red, green and blue. To create different colours, the intensity of each of the three electron beams is varied.
The monitor is controlled by a separate circuit board, known as the display adaptor, which plugs into the motherboard of the computer. Different boards drive different types of displays. For example, the VGA (video graphics array) card has become a standard for colour monitors.
Now flat-screen monitors are fashionable. They are inherently flat, and therefore require less space. In addition, they give crisp, clear images and eliminate screen flicker.
Portable computers use a flat liquid-crystal display (LCD) instead of a picture tube. An LCD uses a grid of crystals and polarizing filters to show the image. The crystals block the light in different amounts to generate the dots in the image.
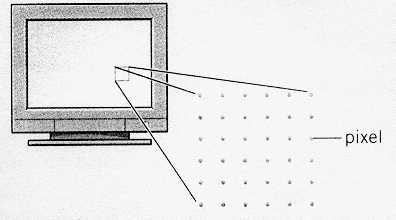
Each dot on the screen is a pixel
B Read the text again and answer these questions.
According to the writer, what is the importance of 'pixel resolution'?
Which unit of frequency is used to measure the refresh rate of a monitor?
In the writer's opinion, why can a low refresh rate produce eye fatigue?
What substance is hit by electrons in a monitor?
What is the standard display system for many PCs?
What does 'LCD' stand for? What type of computers use LCD displays?
Exercise 3. Writing.
A Tables often include abbreviations and technical words that are not easy to understand. Look at this table and the explanation of Monitor A's specifications.
|
|
Type |
Size |
Pixel res |
Visual display |
Refresh rate |
Tilt-and-swivel |
Other features |
|
Monitor A Compaq TFT 8020 |
Flat-panel LCD |
18.1" |
1024 x 768 |
16.7 million colours |
75 Hz flicker-free |
|
energy saver mode |
|
Monitor B Paintview |
CRT monitor |
19" |
1280 x 1024 |
16.7 million colours |
85 Hz flicker-free |
|
anti-glare filter |
The specifications of Superview (Monitor A) may be explained like this:
T
 his
is a flat-panel Liquid Crystal Display.
his
is a flat-panel Liquid Crystal Display.The screen size is 18.1 inches (diagonal viewable image size).
You get a resolution of 1024 by 768 pixels.
It offers support for 16.7 million saturated colours.
This digital display has a 75 hertz refresh rate. It never flickers (the images are bright, sharp, and distortion-free).
You can change the orientation of the display, adjusting your viewing angle back and forth.
It has a built-in power feature that saves a lot of energy consumption.
B Use the example above to help you describe Monitor B.
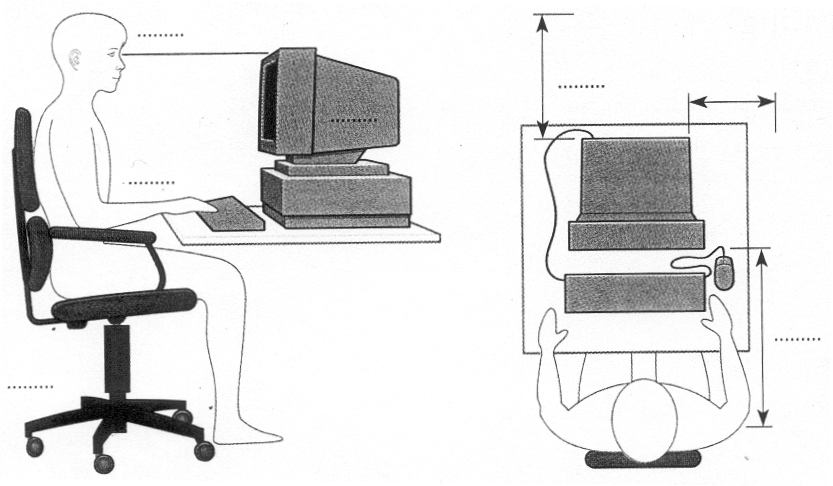
Exercise 4. Computer ergonomics.
Imagine that you are a specialist in computer ergonomics. Work out the rules about health and safety in a computer classroom. Complete the sentences below. Then decide where they should go in the pictures below. Write the number of each in the correct place.
You should get a good chair, one that ........................................................
Position the keyboard .................................................................................
Position the monitor..................eye level, or just ........................................
A tilt-and-swivel display lets you .................................................................
You should stay an arm's length away from …............................................
I
 f
you work in a room with a lot of computers, sit
........................................
f
you work in a room with a lot of computers, sit
........................................
Think of some other rules that can help computer users protect their health.
Share your ideas with your classmates.
Exercise 5. Language work: instructions and advice.
Look at the HELP box and then rewrite the sentences below about what you should do to protect your eyes. Use modal auxiliary verbs in your sentences.
|
HELP box Instructions and advice
Imperatives Position your keyboard at the same height as your elbows. Don't use a monitor that is fuzzy or distorts the image. |
|
Should/ought to You should position your keyboard at the same height as your elbows. = You ought to ... You shouldn't use a monitor that is fuzzy or distorts the image. = You ought not (oughtn't) to use... |
Do not stare at the screen for long periods of time.
Avoid placing the monitor so that it reflects a source of bright light, such as a window.
Keep the screen clean to prevent distorting shadows.
If you work in an office with a large number of computers, don't sit too close to the sides or backs of the monitors.
Buy a protective filter that cuts down the ELF (extremely low frequency) emissions.
