
- •Unit 1 computer applications
- •Computers
- •What can computers do?
- •Unit 2 computer essentials
- •What is a computer?
- •Unit 3 inside the system
- •What’s inside a pc system?
- •Structure of the processor
- •Unit 4 bits and bites
- •Units of memory
- •Unit 5 magnetic drives
- •Technical details
- •Unit 6 optical breakthrough
- •Optical disks and drives
- •Iomega's removable drives
- •Unit 7 input / output devices
- •Voice recording device h. Keyboard
- •Unit 8 capture your favourite image
- •Vivid easy-to-use faster fashionable wide shots
- •Unit 9 viewing the output
- •The monitor
- •Unit 10 choosing a printer
- •Types of printers
- •Unit 11 operating systems Exercise 1.Look at the diagram below. What is the function of the operating system?
- •Exercise 4. Language work
- •Unit 12 the graphical user interface
- •Unit 13 a walk through word processing
- •Word-processing facilities
- •Unit 14 spreadsheets
- •Unit 15 databases
- •Basic features of database programs
- •Exercise 6. Writing
- •Unit 16 faces of the internet
- •Exercise 2. Maybe we can find it on the Internet.
- •Exercise 3. Reading.
- •Internet software
- •Irc, audio and video chatting
- •MIrc for Windows is a typical Internet relay chat program. You can get it at http://www.Mirc.Co.Uk/
- •Unit 17 programming and languages
- •Programs and programming languages
- •Exercise 3. These are answers to questions about the text. Write the questions.
- •Variables and the Declaration Statement
- •Unit 18 computer networks
- •Computer networks
- •Network configurations
- •4 Bus/Ethernet
- •Unit 19 computer viruses
- •How computer viruses work
- •Unit 20 computers in the office
- •Information systems
- •Using Computers
- •Information Technology (it)
- •Exercise 5. Link each statement (1-) with a purpose (a-j).
- •Exercise 6. Match the words from the box with their definitions.
- •The future? We’re virtually there!
Unit 13 a walk through word processing
Exercise 1. Before you read, try to answer these questions.
What is a word processor?
What makes word processors superior to traditional typewriter?
Make a list of the most important features offered by word processors?
N owread
the text below and write down any word processing capabilities that
you didn’t list in question 3.
owread
the text below and write down any word processing capabilities that
you didn’t list in question 3.
A screen from Microsoft word for the Macintosh. Word for Windows works the same way. WordPerfect, Lotus Word Pro and Nisus Writer also have multiple typefaces, windows, pull-down menus and other graphical tools.
Word-processing facilities
Writing letters, memos or reports are the ways most people use computers. They manipulate words and text on а screen — primarily to print at some later time and store for safe keeping. Computers alleviate much of the tedium associated with typing, proofing and manipulating words. Because computers can store and recall information so readily, documents need not be retyped from scratch just to make corrections or changes. The real strength of word processing lies in this ability to store, retrieve and change information. Typing is still necessary (at least, for now) to put the information into the computer initially, but once in, the need to retype only applies to new information.
Word processing is more than just typing, however. Features such as Search and Replace allow users to find а particular phrase or word no matter where it is in а body of text. This becomes more useful as the amount of text grows.
Word processors usually include different ways to view the text. Some include а view that displays the text with editor's marks that show hidden characters or commands (spaces, returns, paragraph endings, applied styles, etc.). Many word processors include the ability to show exactly how the text will appear on paper when printed. This is called WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get, pronounced 'wizzy-wig'). WYSIWYG shows bold, italic, underline and other type style characteristics on the screen so that the user can clearly see what he or she is typing. Another feature is the correct display of different typefaces and format characteristics (margins, indents, super- and sub-scripted characters, etc.). This allows the user to plan the document more accurately and reduces the frustration of printing something that doesn't look right. Many word processors now have so many features that they approach the capabilities of layout applications for desktop publishing. They can import graphics, format multiple columns of text, run text around graphics, etс.
Two important features offered by word processors are automatic hyphenation and mail merging. Automatic hyphenation is the splitting of а word between two lines so that the text will fit better on the page. The word processor constantly monitors words typed and when it reaches the end of а line, if а word is too long to fit, it checks that word in а hyphenation dictionary. This dictionary contains а list of words with the preferred places tо split it. If one of these cases fits part of the word at the end of the line, the word processor splits the word, adds а hyphen at the end and places the rest on the next line. This happens extremely fast and gives text а more polished and professional look.
Mail merge applications are largely responsible for the explosion of 'personalized' mail. Form letters with designated spaces for names and addresses are stored as documents with links tо lists of names and addresses of potential buyers or clients. By designating what information goes into which blank space, а computer can process а huge amount of correspondence substituting the 'personal' information into а form letter. The final document appears to be typed specifically to the person addressed.
Many word processors can also generate tables of numbers or figures, sophisticated indexes and comprehensive tables of contents.
Exercise 2. Look at the words in the box and complete the following sentences with them. Use the information in the text if necessary.
|
type style WYSIWYG format indent font menu justification mail merging |
_____ stands for 'What you see is what you get'. It means that your printout will precisely match what you see on the screen.
_____ refers to the process by which the space between the words in а line is divided evenly to make the text flush with both left and right margins.
You can change font by selecting the font name and point size from the ___.
_____ refers to а distinguishing visual characteristic of а typeface; 'italic', for example is а _____ that may be used with а number of typefaces.
The _____ menu of а word processor allows you to set margins, page numbers, spaces between columns and paragraph justifications.
_____ enables you to combine two files, one containing names and addresses and the other containing а standard letter.
An _____ is the distance between the beginning of а line and the left margin, or the end of а line and the right margin. Indented text is usually narrower than text without _____.
Exercise 3. Match the words and expressions on the left with their explanations on the right.
retrieve а) text printed in the top margin
typefaces b) recover information from а computer system
header с) letter, number or symbol that appears below the baseline of the row of type; commonly used in maths formulas
footer d) text printed in the bottom margin
subscripted character е) division of words into syllables by а short dash or hyphen
hyphenation f) styles for а set of characters; sometimes called 'fonts'
Exercise 4. Two friends are talking about how to move text by using the ‘Cut and Paste’ technique. Read the conversation and complete it with words from the box.
|
Finally command First Edit now mistake Next insertion |
A: Do you know how I can move this paragraph? I want to put it at the end of this page.
B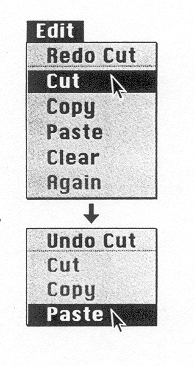 :
Er ... I think so. 1_____ you use the mouse to select the text that
you want to move ... and then you choose the Cut 2_____ from the Edit
menu ...
:
Er ... I think so. 1_____ you use the mouse to select the text that
you want to move ... and then you choose the Cut 2_____ from the Edit
menu ...
A: Like this?
B: Yes. The selected text disappears and goes onto the Clipboard. And 3_____ you find where you want the text to appear and you click to position the 4_____ menu in this place.
А: Mm ... is that OK?
B: Yes, if that's where you want it. 5_____ choose Paste from the 6_____ menu, or hold down Command and press V. 7_____ check that the text has appeared in the right place.
A: What do I do if I make а 8_____?
B: You can choose Undo from the Edit menu which will reverse your last editing command.
A: Brilliant! Thanks а lot.
B: That' s ОК.
Exercise 5. Moving text in a process of cutting and pasting, as if you were using scissors and glue. The picture below represents this process. Write a short description of it.

Exercise 6. Writing tools
A Three major features that word processor offer are spell checkers, online thesauruses and grammar checkers. Read the descriptions of these features and match them with the windows or dialogue boxes.
1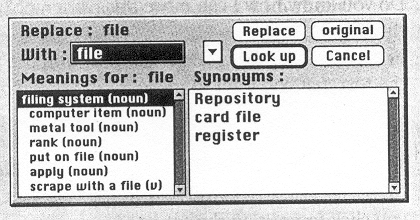 .Spell
checkers can
be used tо compare words in the program's dictionary to those used
in the user's document. The spell checker points out any words it
cannot match, notifies the user and allows them to make any changes;
it sometimes even suggests possible correct spellings.
.Spell
checkers can
be used tо compare words in the program's dictionary to those used
in the user's document. The spell checker points out any words it
cannot match, notifies the user and allows them to make any changes;
it sometimes even suggests possible correct spellings.
L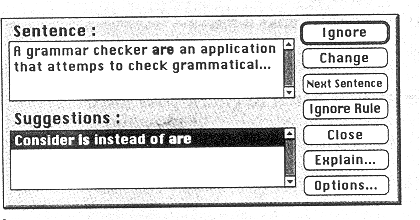 ike
а conventional thesaurus, this database of words contains
definitions and suggestions of words with similar and opposite
meanings. А word may be spelled correctly but still be wrong (too
instead of two,
for
instance). This is а good first step at proofing а document because
it can find many common errors, but users will still need to
proofread documents to ensure complete accuracy.
ike
а conventional thesaurus, this database of words contains
definitions and suggestions of words with similar and opposite
meanings. А word may be spelled correctly but still be wrong (too
instead of two,
for
instance). This is а good first step at proofing а document because
it can find many common errors, but users will still need to
proofread documents to ensure complete accuracy.
2. Many word processors include an online thesaurus with which users can look up different words to use in similar instances. Their power comes not from knowing every grammatical rule, but from questioning the writer about certain parts of the text. Some even include information about pronunciation and histories of evolving meaning.
3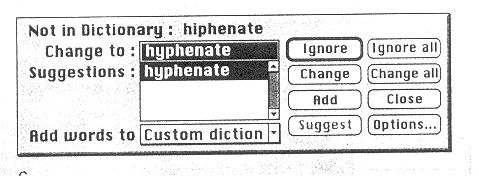 .Grammar
checkers are
applications that attempt tо check more than just spelling. They
count words in sentences to flag possible run-on sentences. They look
for words that show possible conflicts between verbs and subjects and
they offer advice about corrections. Grammar checkers are а step
beyond spell checkers, but they are still not а substitute for а
human editor. However, this does not mean that all of the words in
the document are spelled correctly. This gives the writer another
chance tо think about what he or she has written; the computer can
alert writers to problems that wouldn't be obvious tо them
otherwise.
.Grammar
checkers are
applications that attempt tо check more than just spelling. They
count words in sentences to flag possible run-on sentences. They look
for words that show possible conflicts between verbs and subjects and
they offer advice about corrections. Grammar checkers are а step
beyond spell checkers, but they are still not а substitute for а
human editor. However, this does not mean that all of the words in
the document are spelled correctly. This gives the writer another
chance tо think about what he or she has written; the computer can
alert writers to problems that wouldn't be obvious tо them
otherwise.
(Texts adapted from Understanding Computers by N. Shedroff et al. Sybex, 1993)
B. Read through the descriptions again. There are three sentences which have been printed in the wrong position. Decide which are the intruding sentences and where they should go.
Exercise 7. Speaking
Work in pairs. Read the table below which summarizes the most relevant features of two word-processing programs. The characteristics of each program are marked with а tick. Student А has Printext and Student В has Publisher. Explain to your partner why your program is better.
Example
A: With Printext I can ...
B: Yes, but you can't ...
A: However, it is possible to ... whereas with Publisher you can't ...
B: Yes, but don't forget that with Publisher you can ... Moreover, ...
A: ОК. I understand what you mean, but what about ...?
|
Characteristics |
Student А Printext |
Student В Publisher |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Automatic generation of indexes and tables of contents. Cross-reference facilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
