
- •Unit 1 computer applications
- •Computers
- •What can computers do?
- •Unit 2 computer essentials
- •What is a computer?
- •Unit 3 inside the system
- •What’s inside a pc system?
- •Structure of the processor
- •Unit 4 bits and bites
- •Units of memory
- •Unit 5 magnetic drives
- •Technical details
- •Unit 6 optical breakthrough
- •Optical disks and drives
- •Iomega's removable drives
- •Unit 7 input / output devices
- •Voice recording device h. Keyboard
- •Unit 8 capture your favourite image
- •Vivid easy-to-use faster fashionable wide shots
- •Unit 9 viewing the output
- •The monitor
- •Unit 10 choosing a printer
- •Types of printers
- •Unit 11 operating systems Exercise 1.Look at the diagram below. What is the function of the operating system?
- •Exercise 4. Language work
- •Unit 12 the graphical user interface
- •Unit 13 a walk through word processing
- •Word-processing facilities
- •Unit 14 spreadsheets
- •Unit 15 databases
- •Basic features of database programs
- •Exercise 6. Writing
- •Unit 16 faces of the internet
- •Exercise 2. Maybe we can find it on the Internet.
- •Exercise 3. Reading.
- •Internet software
- •Irc, audio and video chatting
- •MIrc for Windows is a typical Internet relay chat program. You can get it at http://www.Mirc.Co.Uk/
- •Unit 17 programming and languages
- •Programs and programming languages
- •Exercise 3. These are answers to questions about the text. Write the questions.
- •Variables and the Declaration Statement
- •Unit 18 computer networks
- •Computer networks
- •Network configurations
- •4 Bus/Ethernet
- •Unit 19 computer viruses
- •How computer viruses work
- •Unit 20 computers in the office
- •Information systems
- •Using Computers
- •Information Technology (it)
- •Exercise 5. Link each statement (1-) with a purpose (a-j).
- •Exercise 6. Match the words from the box with their definitions.
- •The future? We’re virtually there!
Iomega's removable drives
The Zip series uses 100 MB and 250 MB disks. In the near future it could replace the floppy disk as the portable storage medium.
The Jaz series can hold 2 GB cartridges. Ideal to back up hard disks.
CD-ROM drive
Each CD disk holds 650 MB.
CD-Recordable drive
Makes it possible to write data to CDs as well as read it.
Magneto-optical (MO) disk systems
Erasable optical-magnetic 5.25" cartridges with 5.2 GB of storage capacity. Can be erased and written on like a hard disk.
Rewritable 3.5" floptical disks with a storage capacity of 1.3 GB.
DAT Data tape drive
Digital audio tape drives to store computer data. Used for back-up purposes. Slow access. Huge amounts of information (about 10 GB).
Digital Video Disk-ROM drive
Each DVD-ROM disk has a capacity of up to 17 GB, and can hold various full-screen movies. The drive can also read your CD-ROMs.
Unit 7 input / output devices
Input devices are the pieces of hardware which allow us to enter information into the computer. The most common are the keyboard and the mouse. We can also interact with a computer by using one of these: a lightpen, a scanner, a trackball, a graphics tablet, a joystick or a voice recording device.
E
lightpen e. graphics
tablet
scanner f. joystick
trackball g. mouse
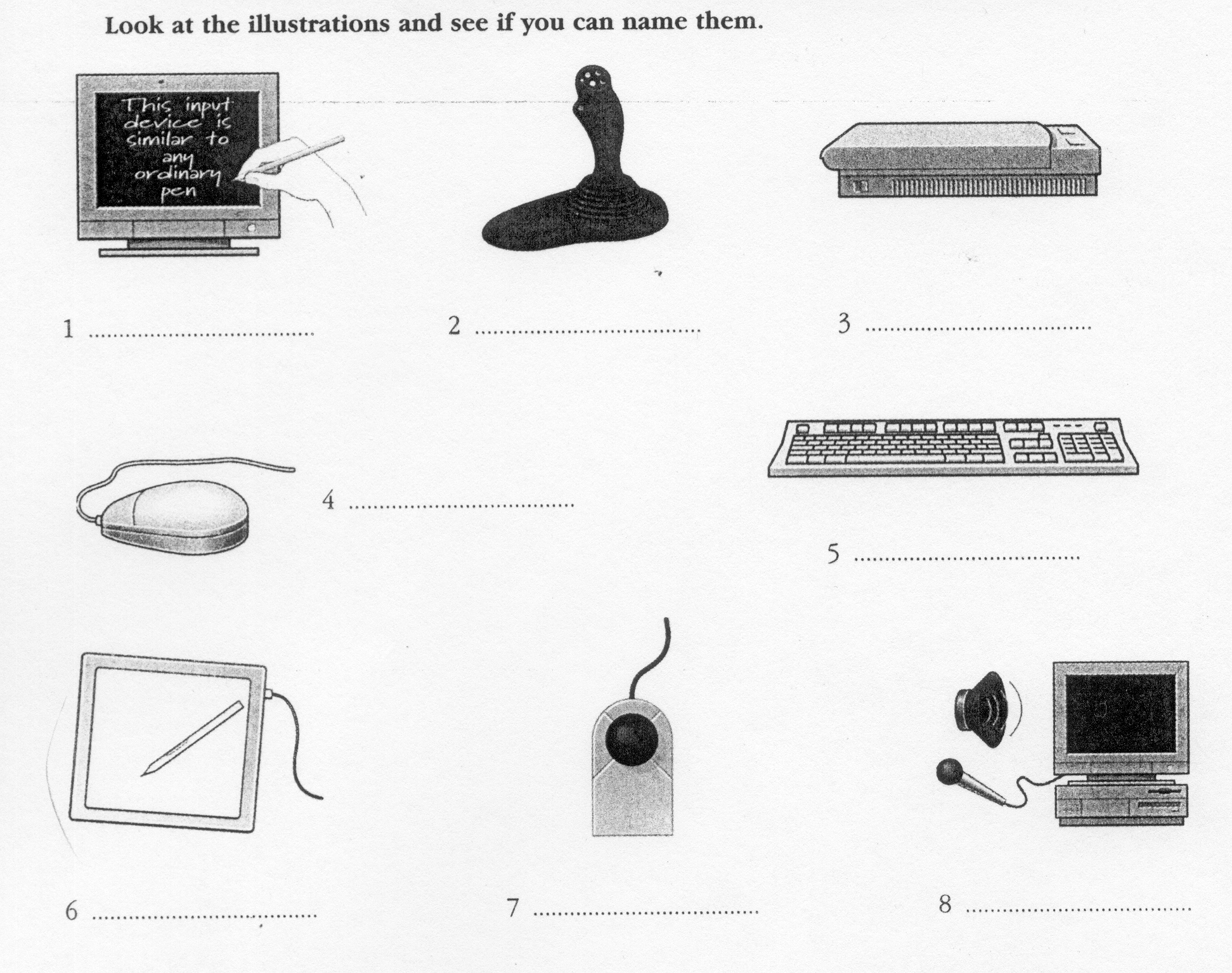
Voice recording device h. Keyboard
1
2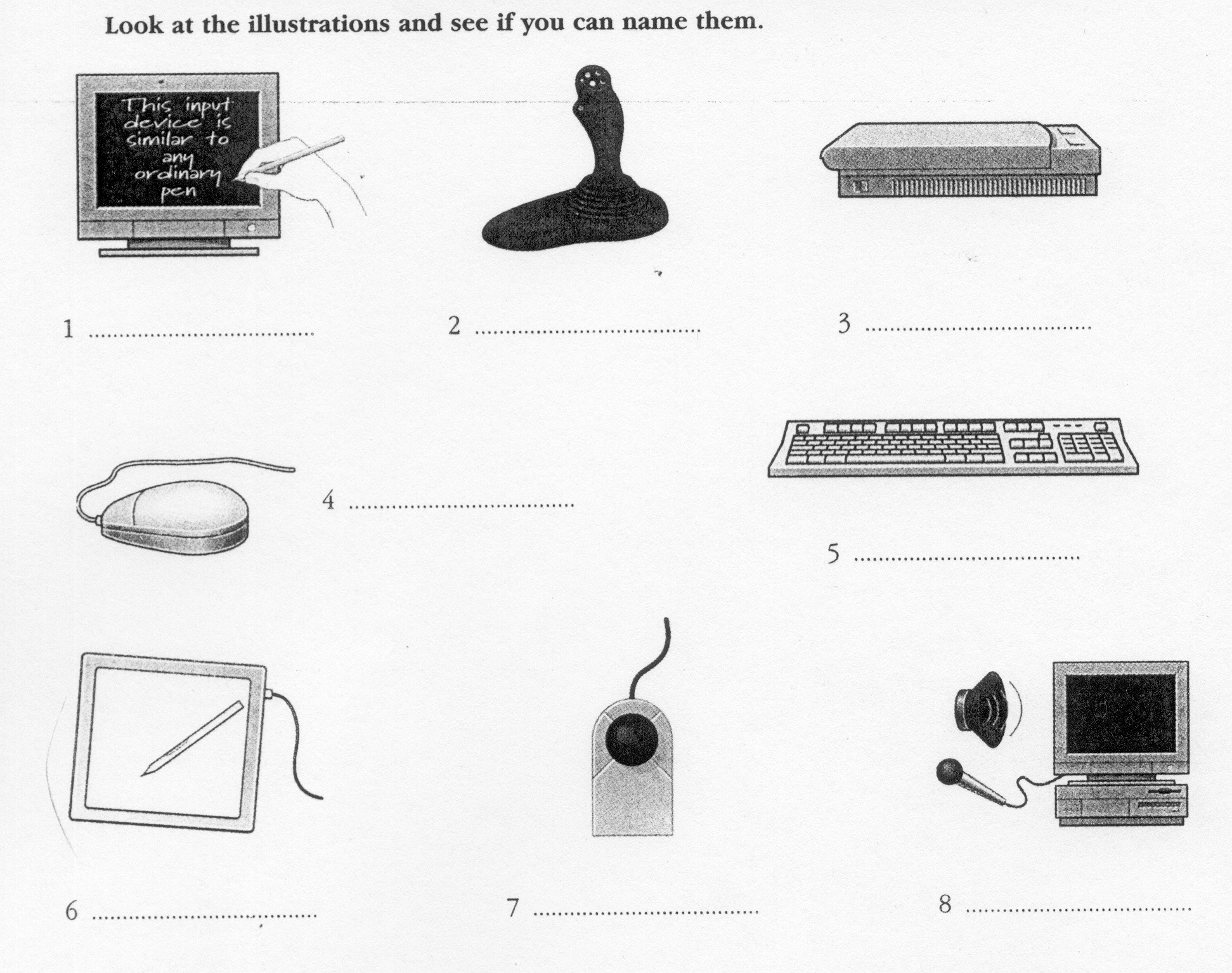
a
device that uses light-sensing equipment to scan paper or another
medium, translating the pattern of light and dark (or color) into a
digital signal that can be manipulated by either optical character
recognition software or graphics software. a
device used to record sound information by a computer a
device, linked to a computer terminal by an electrical wire, which
is moved by hand over a flat surface thereby causing the cursor to
move correspondingly on screen the
manually operated range of keys or levers in a computer a
pen-shaped photoelectric device that can communicate directly with
a computer, entering or altering data on a visual display unit a
peripheral input device which digitizes the movements of a pen over
the sensitive pad (tablet), so that a traced pattern will appear on
the screen Popular
pointing device, used mostly for playing computer games
a spherical ball
mounted in a small
boxlike
device, that can be rotated with the palm
of
the
hand
causing the cursor to move across the
screen
3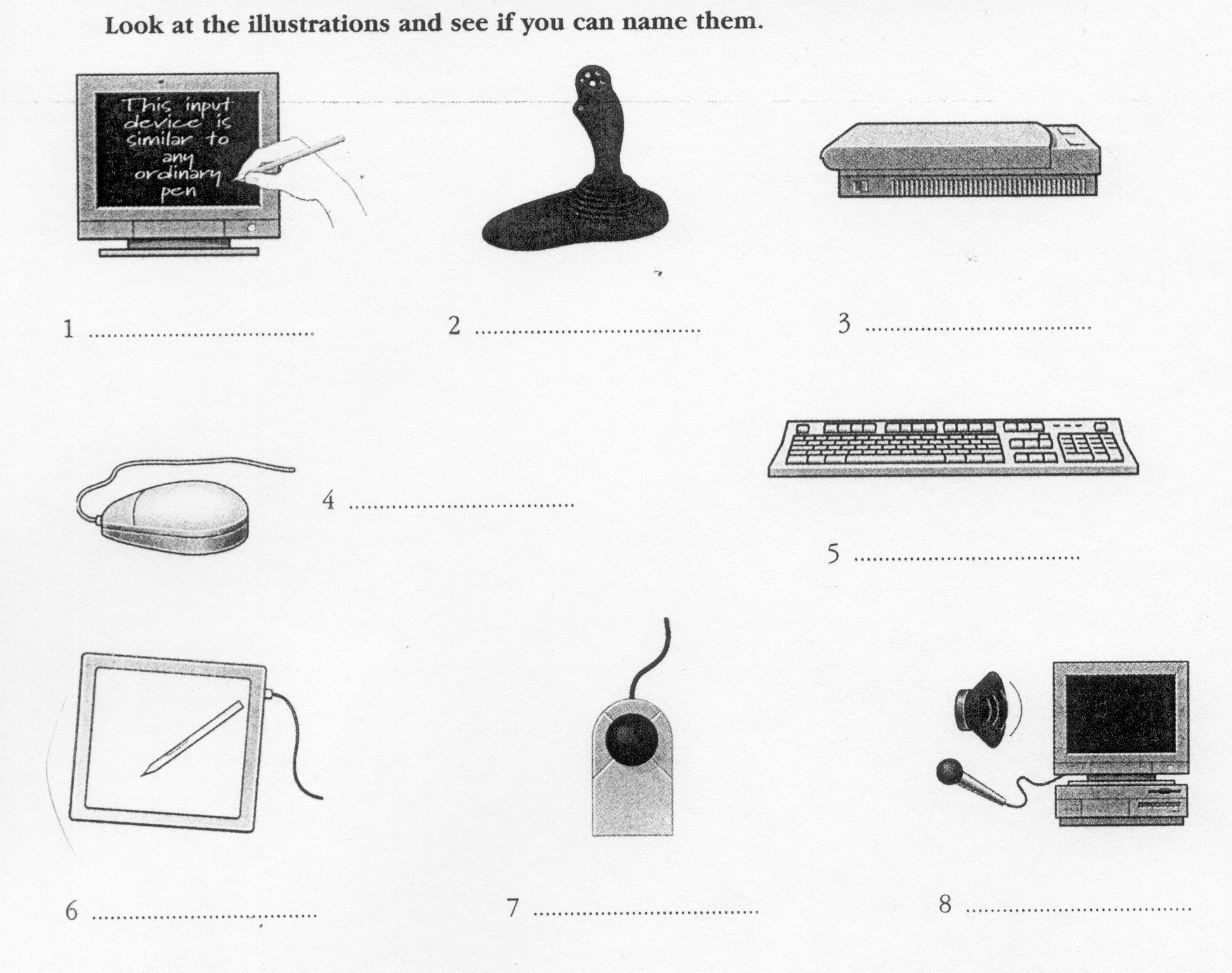
4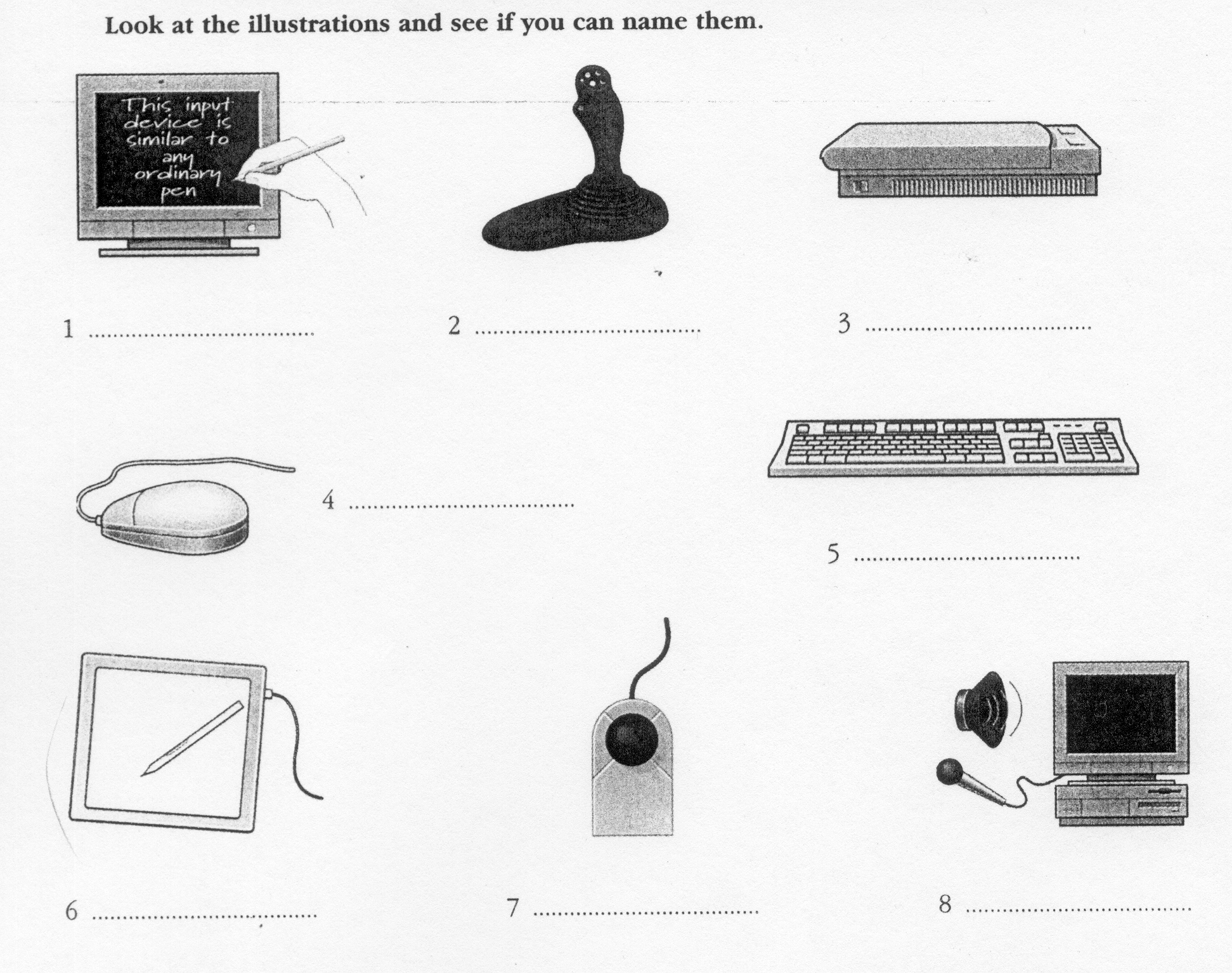
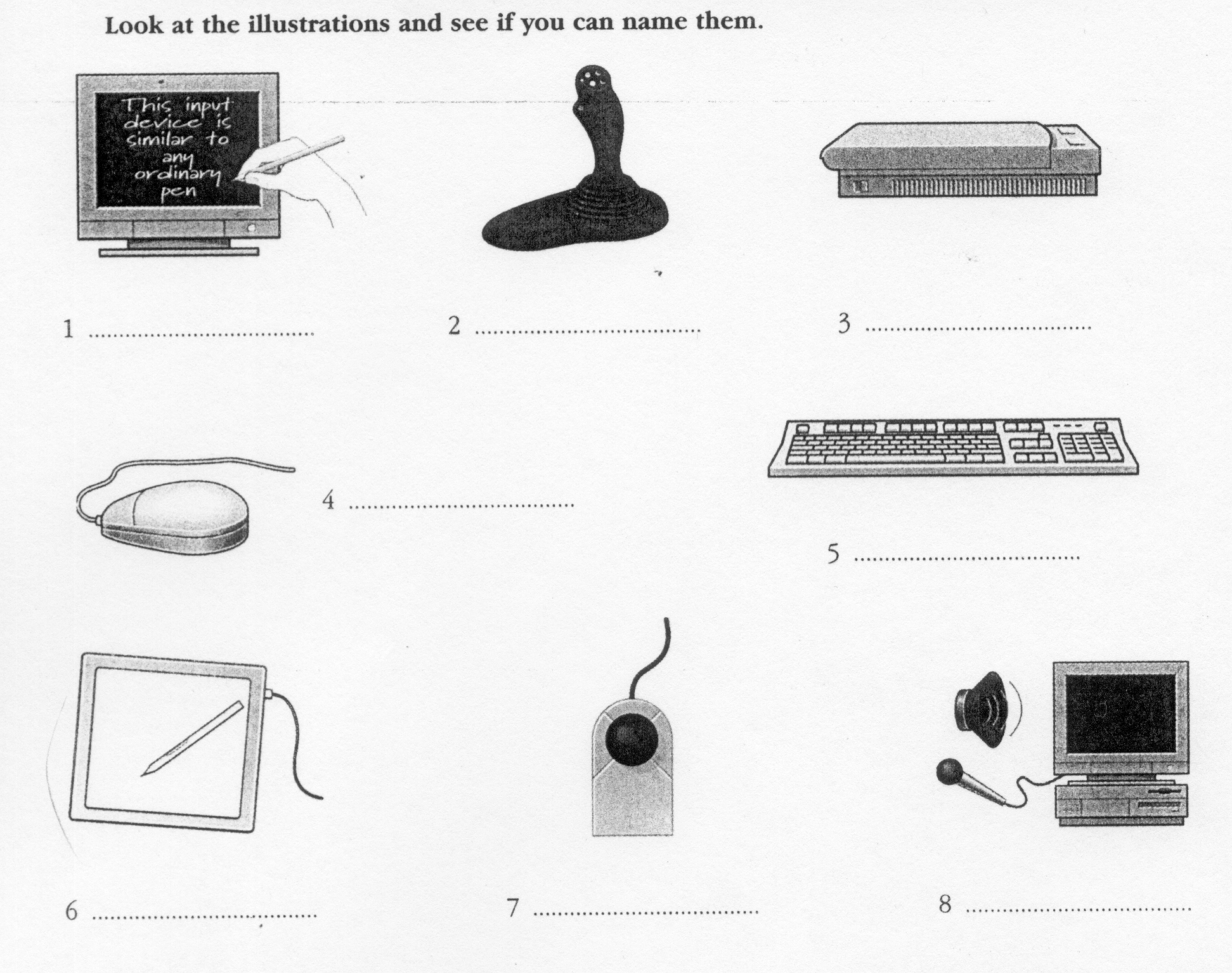
5
6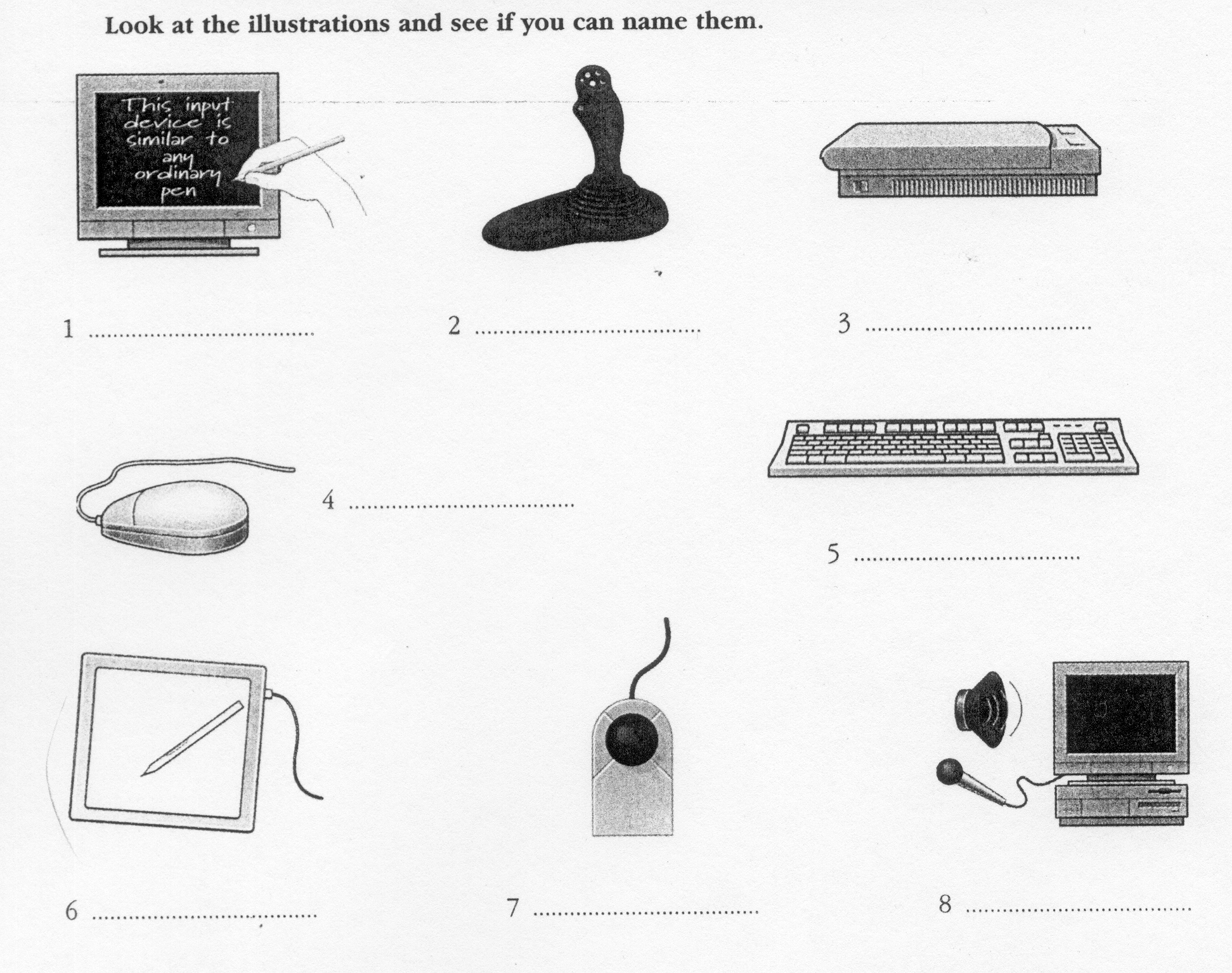
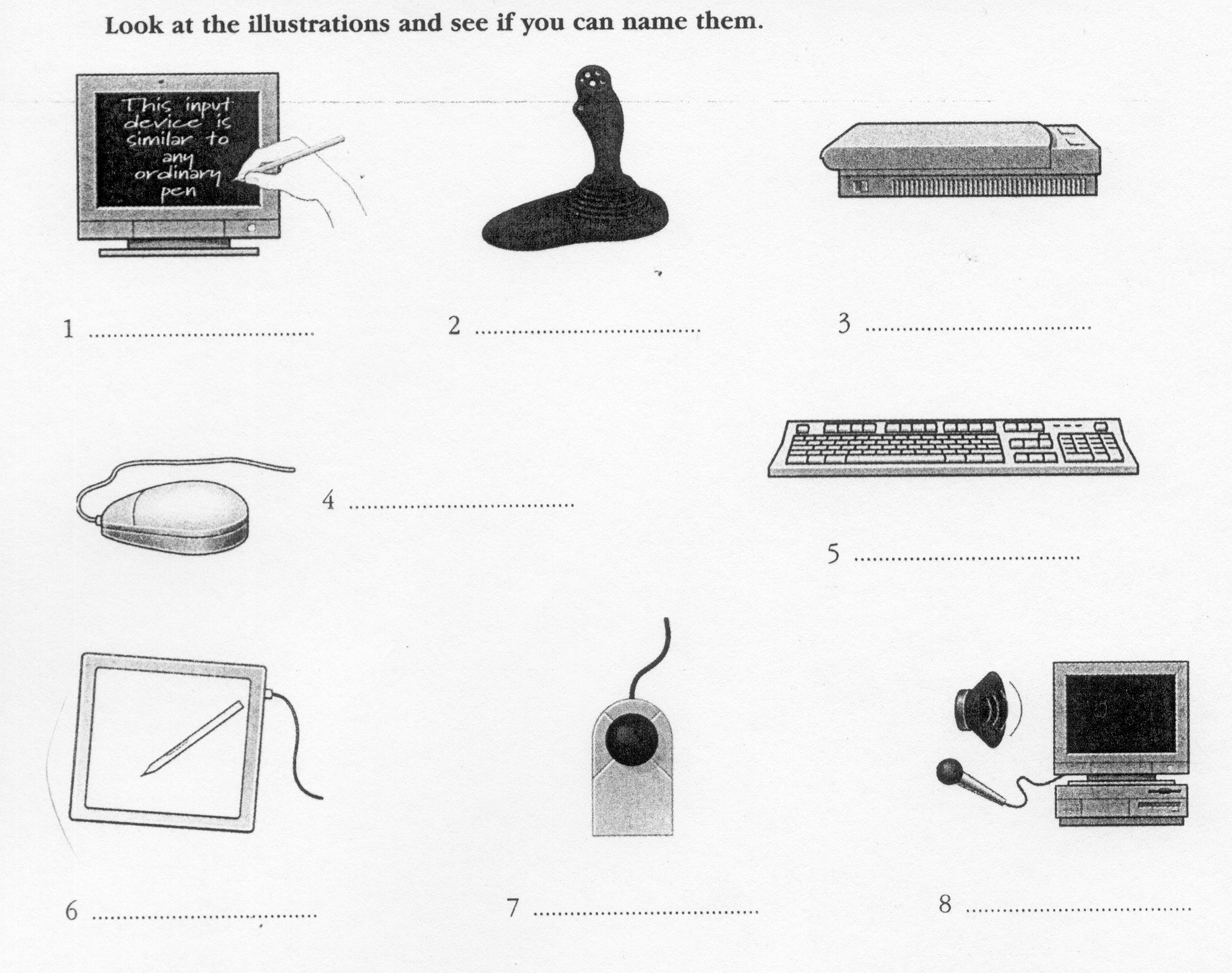
7
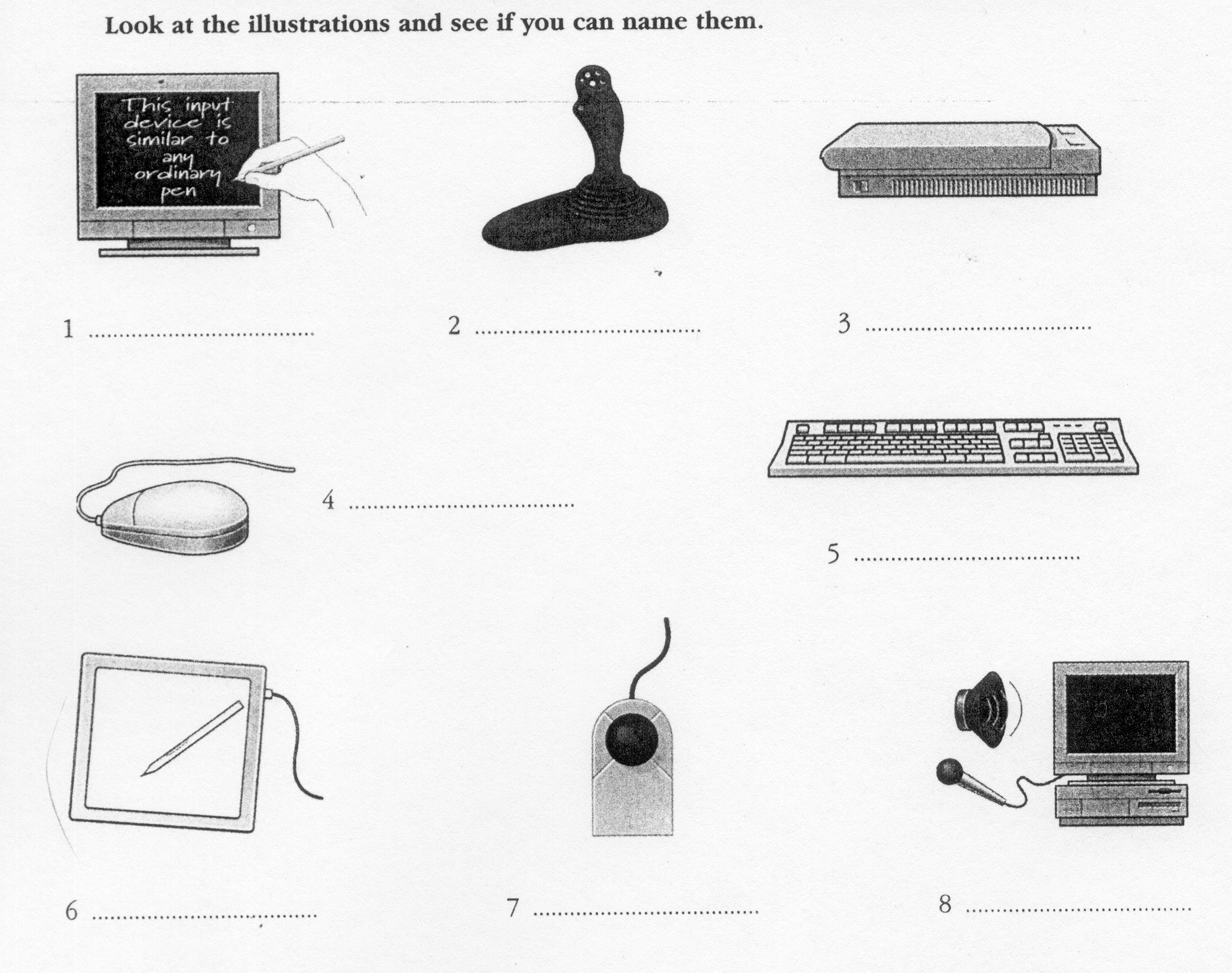
8
Exercise 2. About the keyboard.
A Look at the picture of a PC-compatible keyboard and identify these groups of keys.
Alphanumeric keys: arranged in the same order as a typewriter.
Function keys: used by various programs to instruct the PC to perform specific tasks, such as Save, Copy; Cut, Paste, Help, etc.
Numeric keypad: set of numeric or editing keys. The Num Lock key is used to switch from numbers to editing functions.
Editing keys: cursor and other keys usually used within word processors to page up and down in a long document or to edit text (using Insert or Delete keys).
S
 pecial
keys:
used to issue commands or to produce alternative characters in key
combinations, for example, the Alt key.
pecial
keys:
used to issue commands or to produce alternative characters in key
combinations, for example, the Alt key.
B Match these descriptions with the names of keys on the right. Then find them on the keyboard.
|
|
arrow keys |
|
|
return |
|
|
caps lock |
|
|
shift |
|
|
tab |
|
|
escape |
|
|
space bar |
|
|
backspace |
|
|
alt |
Exercise 3. Mouse actions.
Read the passage about a computer mouse. Fill in the gaps with verbs from the box.
|
click double-click drag grab select move control |
A mouse allows you to 1_____ the cursor and move around the screen very quickly. Making the same movements with the arrow keys on the keyboard would take much longer. As you 2_____ the mouse on your desk, the pointer on the screen moves the same direction. The pointer usually looks like an I-bar, an arrow or a pointing hand, depending on what you are doing.
A mouse has one or more buttons to communicate with the computer. For example, if you want to place the insertion point or choose a menu option, you just 3_____ (press and release) on the mouse button, and the option is chosen.
The mouse is used to 4_____ text and items on the screen. You can highlight text to be deleted, or you can select an item from a check-box or questionnaire.
The mouse is widely used in graphics and designs. When you want to move an image, you position the pointer on the object you want to move, press the mouse button, and 5_____ the image to a new location on the screen. Similarly, the mouse is used to change the shape of a graphic object. For example, if you want to convert a square into a rectangle, you 6_____ one corner of the square and stretch it into rectangle.
The mouse is also used to start a program or open a document^ you put the pointer on the file name and 7_____ on the name – that is, you rapidly press and release mouse button twice.
