
Lectures_1-2_monopoly
.pdfMicroeconomics, Lectures 1-2
Monopoly
Elena Paltseva
HSE, Perm
December 9, 2013
1
Introduction
I Teacher: Elena Paltseva, elena.paltseva@nes.ru
IWorks at SITE, Stockholm School of Economics, visiting professor at NES, Moscow
IInterests: applied microeconomics, political economy, industrial organization etc.
IO¢ ce hours: by appointment
I Course: part of your Microeconomics: Theory of Oligopoly
I6 lectures, exercise classes in January
Iwe will cover
Imonopoly and monopolistic price discrimination
Ibasics of game theory
Ioligopolies: Cournot, Bertrand, Stackelberg
IIf we have time: linear city model + monopolistic competition
2
Practicalities (cont.)
I Lecture notes will be uploaded to
Ieither your course page
Ior a specially made page at paltseva.com
Iwill tell you more later
I Textbooks:
IVarian, Intermediate Microeconomics
IPindyck, Rubinfeld, Microeconomics
IJehly, Reny, Advanced Microeconomics Theory
Isome material from
ITirole, Jean: The Theory of Industrial Organization
IShy, Oz: Industrial Organization
I see syllabus
3
Plan for today (lectures 1 and 2)
I Monopoly
Isingle-product monopolist
Imonopoly and social e¢ ciency; regulation of monopoly
Inatural monopoly
I Monopolistic price discrimination
I1st degree
I3rd degree
I2nd degree
Ifully non-linear tari¤
Itwo-part tari¤
Itying (if time permits)
4
What is a monopoly?
I Monopoly - a single price-making player/seller in the market
I a sole supplier of a good for which there is no close substitute
I not a price taker, unlike in perfect competition
I“Monopolistic” buyer is called monopsony
I Example: city-enterprises
IUsually “monopoly” is an extreme/an abstract concept – opposite to “perfect competition”
I In real life, most often oligopoly or monopolistic competition
5

Russian banking industry: Monopoly? Oligopoly?
6
Sources of monopolistic power
I Barriers to entry
I Legal
I patents
I Technological
Iaccess to critical resource
Inatural monopoly (e¢ cient size of a …rm is too large, only one …rm survives on the market)
Iknow-how, technological advantage
I Regulatory
Inatural monopoly (e¢ cient size of a …rm is too large, only one …rm survives on the market)
7
Problem of the monopoly
I Assume
Imonopolist produces only one good, which is given
Iits quality is known to the consumer
I Monopolist solves
max pD(p) C (D(p))
p
I or
max qP(q) C (q)
q
I Let’s look at the second formulation:
I FOC
P(q) + qP0(q) = C 0(q)
IUnlike competitive …rms, monopoly accounts for changes in demand due to its own price change
8

Problem of the monopoly (cont.)
I Let us analyze this …rst order condition
P(q) + qP0(q) = C 0(q)
ILHS - marginal revenue (MR) = how does the total revenue change if the monopolist increases the output by one unit
MR = ¶TR = P(q) + qP0(q)
¶q
IRHS - marginal cost (MC) = how does the total cost change if output is increased by one unit
9
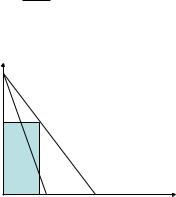
Marginal revenue
IHow is marginal revenue curve positioned relative to the inverse demand curve P(q)?
MR = ¶TR = P(q) + qP0(q)
¶q
I Since P0(q) < 0, MR(q) < P(q)
p
p(q)
TR
MR(q) |
q |
I Btw, what is marginal revenue in case of perfect competition?
10
