
Lectures_1-2_monopoly
.pdf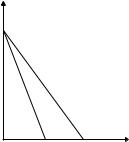
Marginal revenue, linear demand
I What is MR in case of linear (inverse) demand
P = a bq
I let’s calculate
MR = P(q) + qP0(q) = a 2bq
I How does it look on a graph?
I MR(q) is exactly halfway from P(q) towards the vertical axis!
p
p(q)
MR(q)
q
11

Marginal revenue, isoelastic demand
I What is MR in case of isoelastic (inverse) demand
P = aq 1/#
Icheck it is isoelastic
Ilet’s calculate
MR = aq 1/# + q ( 1/#) aq 1/# 1 = (1 1/#)aq 1/#
I MR(q) is lower than P(q) exactly by the factor (1 1/#) p
p(q)
MR(q)
q
I
12

Monopolist problem (cont.)
I Back to the monopolist’ problem
P(q) + qP0(q) = C 0(q)
I |
Notice that |
|
|
|
|
|
|
P(q) + qP0(q) = P(q) + P(q) |
q ¶P(q) |
= |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
P(q) ¶q |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||
I |
where # is the elasticity of demand, # = Pq |
¶q |
||||
¶P |
||||||
ISo, the FOCs of monopolist take the form
1 |
|
1 |
P(q) = C 0(q) |
|
# |
||||
|
|
1 |
1 |
P(q) |
# |
Imonopolist only operates on the elastic part of the demand curve # > 1
IIf elasticity is below 1 then MR is negative!
Iprice " 1% ) demand # by less than 1% ) revenue increases + cost falls (!)
IMonopoly wants to raise prices as high as possible and produce as little as possible, cannot be pro…t-maximizing
13

Monopolist problem (cont.)
IIntroduce mark-up= by how much the price is above the competitive one
IMonopolistic FOC can be rewritten as
P(q) |
1 |
|
|
|
= |
|
|
C 0(q) |
1 1# |
|
|
Ithe more elastic is the demand, the lower is the monopolistic mark-up!
I Alternatively, we can write
P(q) C 0(q) = 1
P(q) #
I LHS - Lerner Index= measure of market power
ILerner Index for perfectly competitive situation?
I=0!
IPositive ( 1) for monopoly
14
Solution of the monopoly
P
MR(qmon)=MC(qmon)
pmon
MR |
D |
|
MC=c
Q
qmon
15
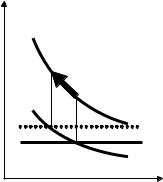
Comparative statics: tax incidence under monopoly
IWhat happens to the perfectly competitive market with constant MC, when the government introduces a tax on this market’s product?
IPrice goes up.
IBy how much?
I by exactly the tax size t!
I Consumers take all the tax burden!
I And under monopoly?
Iprice usually goes up as well
Ibut may go up by a more or less than t
I depends on the shape of the demand curve
16
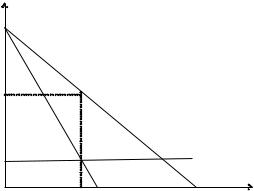
Taxation of monopoly, linear demand
The change in price is less than the tax increase
17
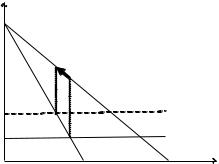
Taxation of monopoly, isoelastic demand
IWhat is the e¤ect of a tax increase by $1/unit ?
IThe price may go up by more or by less than $1!
18
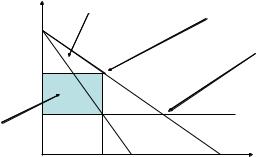
Ine¢ ciency of monopoly
I Is monopoly e¢ cient?
Ithere are people who are willing to buy the good at the price above the marginal cost, but below the monopoly price
Iserving them - Pareto improvement
IBut monopoly does not do so = Dead-weight loss (DWL)
IMonopoly is ine¢ cient!
p
Consumer surplus |
Monopoly equilibrium |
Competitive equilibrium
|
DWL |
MC |
|
|
|
Monopoly |
MR |
D |
profits |
|
|
q
19
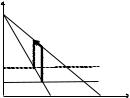
Regulation of monopoly
IMonopolistic price is too high!
IShall the government tax monopoly to restore e¢ ciency?
I
I No, subsidize!
I how much?
I Alternatively, the government can use price caps
Iwe will see later, that social e¢ ciency may be di¢ cult to restore
20
