
- •G.A. Kozlova, a.M. Kozlova
- •Preparation course
- •Содержание
- •Предисловие
- •4 Уровню знаний соответствуют следующие навыки:
- •Vocabulary:
- •Раздел I. Фразеология икао (стандартная фразеология)-icao phraseology;
- •Как пользоваться пособием?
- •Exam overview
- •Part I. Vocabulary review
- •Flight operation. Hazardous conditions in flight.
- •Part II. Grammar review
- •Present meaning
- •Past meaning
- •Future meaning
- •Active & Passive Voices
- •V-смысловой глагол
- •V1,v2,v3 - 1-ая, 2-ая, 3-я формы глаголов
- •V-ing - смыловой глагол с окончанием - ing
- •Степени сравнения прилагательных
- •Reported speech
- •Согласование времен*:
- •Possibility. Probability. Necessity
- •Part III. Speaking
- •Part IV. Listening
- •Recommendations:
- •Unruly passengers
- •Recommendations:
- •Effects of weather
- •Flight hazards
- •Collision course
- •Truck collapse leads to delay
- •Plane’s mayday call missed due to pilot’s poor English
- •Part V. Video clips
- •Video film 1 an approach and landing accident (ala):
- •It could happen to you
- •Video film 2 cfit
- •Part VI. Radiotelephony Communication
- •What communication skills mean
- •Советы психолога: Вам предстоит тестирование по авиационному английскому языку…
- •Work-related topics
- •Introduce yourself, tell about yourself
- •3. Your job
- •4. Your working day
- •5. Hazards and hazardous conditions for flight.
- •6. Weather, natural disasters
- •9. Dangerous goods
- •11. Pilot-controller communication
- •12. Air traffic management (atm)
- •13. The aircompany you are working for
- •14. Passengers behaviour
- •15. Health. Medicine
- •Список литературы
Video film 2 cfit
Watch the film and answer the following questions:
1. What is the main idea of this film?
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
2.What accidents are discussed?
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
3. What were the main reasons for those accidents?
The first accident
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
The second accident
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
The third accident
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
4. What is CFIT checklist? What do you need it for?
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
Part VI. Radiotelephony Communication
Ability tested
Questions test your ability to use appropriate communicative strategies
-to exchange messages,
-to recognize and resolve misunderstandings (e.g. to check, confirm, or clarify information) in a work-related context;
-to handle successfully and with relative ease the linguistic challenges presented by a complication or unexpected turn of events during flight;
-in other words questions test your ability to communicate effectively with an air traffic controller in any situation: standard, abnormal or emergency.
Basic skills necessary
You must be able to demonstrate radio-telephony communication skills in routine and non-routine situations. You must be able to describe your problem, clarify the situation, paraphrase if necessary, and understand air traffic controller instructions.
This section also requires the strong professional vocabulary.
How to prepare for RTC section.
1, For standard phraseology use and follow strictly the rules of Doc. 4444 RAC/501 (ICAO. Rules of the Air traffic services) and Doc. 9432-AN/925 (Manual of radiotelephony)
2. In non-routine situations use plain language to describe the problem. Comply with the recommendations of Doc.9835 AN/453 (Manual on the implementation of ICAO language proficiency requirements)
Communications shall be concise and unambiguous, using standard phraseology for all situations for which it is specified. Only when standard phraseology can not serve an intended transmission, shall PLAIN language be used.
From CAP 413R/T Manual
Exercise 1
Listen to the first part of the tape and fill in the missing words:
What communication skills mean
Aviate, navigate, …………………. That is the traditional order of ………….…..for pilots. Today it is the ……………….…, but different. Aviation and ……………………. have changed. The aviate/navigate part is very nearly synonymous in …………………. aircraft operating in precision area navigation airspace.
……………….. is the least-changed part of the job. It is not …………………... at all, but with increasing traffic densities demanding more accurate …..……… ………………, communication is becoming more important. In the future ……..communications will take over all the routine work that ………………… communications must do today. But it will take at least …………………… to 10 years to achieve this, so voice communication is going to be the …………………………. for air/ground and air/air co-operation for a long time.
2. Listen to the second part of the tape and answer the questions:
What will voice communication do in the datalinked future? What will voice contact deal with?
Why have fatal accidents happened?
How did ICAO define tests of English communications skills? What should pilots and air traffic controllers demonstrate?
What is workable English, in your opinion?
Exercise 2 (A, B, C)
Listen to the pilot-controller communications. What is the problem in each situation? What are pilots’ intentions and controllers’ instructions?
Exercise 3
How would you describe these situations to ATC?
Your departure is delayed due to:
baggage identification. You have one piece of extra baggage on board;
catering (the catering truck has not brought the food);
damage caused by vehicles ( i.e. a baggage vehicle damaged your aircraft);
vehicle obstructing RWY
Loose debris is observed on the TWY (You are advised to have a look out).
There has been a fuel spillage beneath your starboard (port side) wing.
You have had a tyre puncture while taxiing into position
You are unable to continue taxiing into position. The nose wheel steering seems to be jammed.
There are injuries among passengers after severe turbulence
As a result of evasive action (danger of collision) some passengers have been injured (bruised).
You are hijacked. Terrorists demand to change your route of flight. They threaten to explode the aircraft.
You are informed of a bomb scare on board.
You have fire warning indication. You are going to make an emergency landing and prepare for an emergency evacuation.
You have had explosive decompression.
You have had a dangerous near miss with converging traffic. The safety separation has not been provided.
You have made several attempts to extend gears but failed.
You have missed the necessary intersection while taxiing to the stand after landing. You are not familiar with taxi procedures at the airport.
You slid off the RWY, right gear is sunk (bogged down), you are unable to vacate the RWY under own power.
Your TWY is blocked by a disabled aircraft.
Exercise 4
Discuss a situation with a partner:
1 Have you ever had a bird strike (bird ingestion)? With what results?
Imagine that you have encountered a flock of birds. There is an engine problem.
2. You have a passenger with health problems (with an acute pain, suspected heart attack, loss of consciousness, breath difficulties, bleeding, food poisoning etc.). Give advice what would you do in these situations:
A: Passenger has got ........... (health problem)
B: If you have a passenger with ...............you should.........................
If I were you....................................
3. You have an aggressive behaviour./unruly/intoxicated passenger on board. He refuses to fulfil the requirements of the crew members. What would you do and what would you say in these situations?
Exercise 5
What could cause take-off incidents and problems on landing?
How can these conditions (phenomena) affect the operation of the flight?
wind gusts
microburst
sudden (abrupt) wind shear
up/down draughts
jet stream activity
aircraft icing
lightning strike
Exercise 6
Discuss the following word map: what reasons could be for these situations?
For example: in what kinds of situations do pilots need to dump (burn out) fuel?
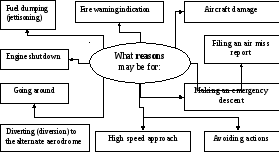
Exercise 7
Listen to the tape, read back and translate the phrases causing difficulties in controller-pilot communications.
To have more practice of all phases of the flight, refer to “Bonus RTC” section.
Exercise 8
Before listening. Answer the following questions:
What are the reasons for pilot-controller misunderstanding?
What are the main linguistic problems?
How to prevent linguistic problems?
What changes have occurred in controller-pilot communication?
What can you say about controller-pilot communication problems at present?
How do you think the controller-pilot communication will change in the future?
2. Listen to the tape and match the questions with the answers.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exercise 9
Listen to the tape and complete the recommendations below.
1. Pilots and controllers should make a conscious effort to use…………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………….
2. Controllers need to provide……………………………………………………., and pilots need to ………………………. if there is any confusion or opportunity for misinterpretation.
3. Do not make………………………………………………………………………
4. Watch out ……………………….. Include key words …………………………. in any message containing a number to indicate what the number refers to.
5. Never assume. Ensure ……………………………………………………………
6. Keep communication …………………………………………………………….
