
- •3. Read the text and do the exercises.
- •The entire oil industry is often divided into three major sectors: upstream, midstream and downstream.
- •Downstream (oil industry)
- •Upstream (oil industry)
- •Midstream (oil industry)
- •The Seven Sisters of the petroleum industry is a term coined by an Italian entrepreneur, Enrico Mattei, that refers to seven oil companies that dominated mid-20th century oil production, refinement, and distribution.
- •ROYAL DUTCH SHELL
- •Founded: 1907
- •Products: oil, natural gas, petrochemicals
- •Products: natural gas, petroleum
- •Headquarters: the Netherlands, principal offices in Houston, Paris and the Hague
- •Pronunciation of the name
- •12. Translate into English.
- •12. http://www.fourmilab.ch/gravitation/foobar/
- •15. http://www.fe.doe.gov/education/energylessons/oil/oil2.html
- •Exploration Methods
- •Elements of a petroleum prospect
- •Terms used in petroleum evaluation
- •Drill Stem Tests
- •A. Electric, Radioactivity and Acoustic (Sonic) Logging
- •2. ______ _______ invades the rock surrounding the wellbore, affects the logging of the hole and must be accounted for.
- •3. ______ _______ measure formation radioactivity.
- •Acidizing
- •2. Pay attention to the underlined stress in the following words.
- •Completion
- •Production
- •Abandonment
- •3. Pay attention to the underlined stress in the following words.
- •4. Read the following text and do the exercises.
- •2. Pay attention to the underlined stress in the following words.
- •5. Fill in the gaps with the most suitable words or terms from the text.
- •6. Match the two parts of the sentences.
- •Terms and Vocabulary
- •People
- •9. Read the text “Drilling Rig” and fill in the missing words from the box. There is one extra word.
- •Drilling Rig
- •Drilling Rig Classification
- •4. Read the text “Hoisting system components” and do the exercises.
- •16. Read the text “PIPE (MATERIAL)” and fill in the missing information. The first sentence is done for you.
- •2. Pay attention to the stress in the following words. □ shows the position of stress.
- •2. Pay attention to the stress in the following words. □ shows the position of stress.
- •2. Pay attention to the underlined stress in the following words.
- •6. Fill in the gaps with the correct term.
- •Example: 7. relies upon
- •7. Scan through the following short definitions and do the after – task exercises.
- •Corrosion types
- •Crack characteristics can vary greatly depending on the cause of the crack, the materials being cracked, and the environment causing the cracking. The following photos show examples of crack profiles.
- •Applied coatings
- •15. Match the questions about “Cathodic protection” on the left with the answers on the right.
- •STEEL TANKS WITH FIXED ROOFS
- •STEEL TANKS WITH FLOATING ROOF
- •METHODS OF ERECTION OF CYLINDRICAL STEEL TANKS
- •APPENDIX 5
- •Dictionary of Pipeliner's Terms (SLANGS)
- •A. подаваемый ток
- •1. weakening
- •B. коррозионный элемент
- •2. rust
- •C. выходное напряжение
- •3. discoloration
- •D. интенсивность
- •4. impressed current
- •E. (удельная) проводимость
- •5. direct current
- •F. ослабление
- •6. corrosion cell
- •G. обезвоживание
- •7. output voltage
- •H. постоянный ток
- •8. severity
- •9. water removal
- •10. conductivity
- •K. толщина стенки
- •11. operating pressure
- •12. yield strength
- •L. ухудшения характеристик
- •M. рабочее давление
- •13. allowance
- •N. предел текучести
- •14. wall thickness
- •O. допуск
- •fracture
- •трещина
- •gradient
- •угол наклона, склон
- •circuitous
- •окольный, обходной
- •Reynolds number
- •число Рейнольда
- •interplay
- •взаимодействие
- •facet
- •сторона
- •aquifer
- •водоносный слой
- •porous media
- •пористая среда
- •pertinent
- •имеющий отношение
- •civil engineering
- •гражданское строительство
- •soil science
- •почвоведение
- •fluid mechanics
- •механика жидкости
- •inertia
- •инерция
- •Laplace equation
- •уравнение Лапласа
- •simulate
- •имитировать
- •heat conduction
- •теплопроводность
- •heat transfer
- •теплообмен
- •uncoupled processes
- •несвязанные процессы
- •soil moisture
- •влажность почвогрунта
- •viscous
- •вязкий
- •viscosity
- •вязкость ( жидкости, газа )
- •diffusion
- •диффузия
- •steady flow
- •transient flow
- •неустановившийся поток
- •15. deterioration
- •UNIT 1
- •Introduction to Economics and management
- •UNIT 2
- •Finance
- •UNIT 3
- •STOCK
- •UNIT 4
- •THE ECONOMY OF PETROLEUM INDUSTRY
- •UNIT 5
- •Taxation and audit
- •UNIT 6
- •Production and Costs
- •UNIT 7
- •BUSINESS PLAN
- •UNIT 8
- •International Business Etiquette AND ETHICS
- •References
- •3. Read the text “Hydrogeology: Key Terms and Concepts”, do the exercises
- •Hydrogeology
- •7. What are the subjects of the following sciences?
- •12. Fill in the chart with the necessary information from the text.
- •13. Pay attention to the pronunciation of the following terms.
- •14. Read the following short texts and fulfill the after-reading exercises. Pay attention to the diagrams and underlined words.
- •Ground Water Aquifer
- •Confined or Artesian Aquifer
- •Drawdown – the vertical drop of the water level in a well caused by ground water pumping; also, the difference between the water level before pumping and the water level during pumping.
- •Make your own sentences with two of the expressions.
- •UNIT 4
- •THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT
- •Compose your own sentences with two of the expressions.
- •5. Translate from Russian into English.
- •10. Answer the following questions.
- •1. What are the functions of atmosphere?
- •1. The phenomenon known as El Niňo
- •A) is confined to the Pacific Ocean.
- •D) caused the disappearance of the dinosaurs.
- •2. It was named after
- •3. It is caused by
- •A) the wind changing direction.
- •D) occurs every four or five years.
- •5. The effect of El Niňo
- •Make your own sentences with two of the expressions.

2.Буровой раствор готовят в виброситах и закачивают в скважину при помощи бурового насоса.
3.Ротор вращает квадрат, квадрат вращает бурильную колонну, которая в свою очередь вращает бурильное долото.
4.Буровой раствор, выходящий из ствола скважины, проходит через вибросито, где шлам отделяется от раствора.
5.Вертлюг позволяет колонне бурильных труб вращаться и представляет собой шарнирное соединение (swing joint).
6.Талевая система (tackle system) включает кронблок, талевый блок и буровой крюк.
7.При роторном бурении мощность от двигателей передается через лебедку к ротору.
8.Ротор вращает колонну бурильных труб и привинченное к ней долото, которое дробит породу.
8.Think of possible failures which can occur due to damages, breaks and other defects of the following rig components and fill in the fault-finding chart.
Rig component |
Failure/ fault |
Probable causes |
Remedy |
Drawworks |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kelly |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shale shaker |
|
|
|
Pump |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9. Read the text “Drilling Rig” and fill in the missing words from the box. There is one extra word.
|
|
Drilling Rig |
|
|
|
|
|
A drilling |
rig is a machine which creates 1. holes |
and/or shafts in the |
|||||
ground. Drilling rigs can be massive structures housing |
2. |
|
|
used to |
|||
drill 3. |
,4. |
wells, or 5. |
extraction wells |
or they |
can be |
||
small enough to be moved manually by one person. They sample sub-surface
mineral 6. |
|
|
|
, test rock, soil and groundwater physical properties, |
|
and to |
|
|
|
|
|
install |
|
sub-surface fabrications, such as underground utilities, |
|||
|
|
|
|
325 |
|
instrumentation, tunnels or wells. Drilling rigs can be 7. ________ mounted on trucks, tracks or trailers, or more permanent land or marine-based structures (such as oil platforms, commonly called 'offshore oil rigs'). The term "rig" therefore generally refers to the complex of equipment that is used to 8. __________ the surface of the earth's crust.
Drilling rigs can be:
• Small and portable, such as those used in mineral exploration drilling and environmental investigations.
• Huge, capable of drilling through thousands of meters of the Earth's crust. Large "mud pumps" circulate drilling 9. ________ through the drill bit and the casing, for cooling and removing the 10. "________ " while a well is drilled. Hoists in the rig can lift hundreds of tons of pipe. Other equipment can force acid or sand into reservoirs to facilitate extraction of the oil or mineral sample; and permanent living accommodation and catering for 11. __________ which may be more than a hundred. Marine rigs may operate many hundreds of miles or kilometres offshore with infrequent crew rotation. Oil and Natural Gas drilling rigs can be used not only to identify geologic reservoirs but also to create holes that allow the extraction of oil or natural gas from those reservoirs. An oil or gas pumping rig, sometimes called a derrick, is used to retrieve oil / gas from a reservoir.
|
mud; derrick; penetrate; water; crews; natural gas; mobile; cuttings; |
|
|
oil; holes; deposits; |
equipment |
|
|
|
|
(Baker R. “A Primer of Oil Well Drilling”, 2001, Austin, Texas) |
|
|
|
Terms and Vocabulary |
clutch |
муфта, соединять |
|
convential |
стандартный |
|
deviation |
отклонение |
|
grid |
батарея, энергетическая система |
|
pipe rack |
стеллаж для труб |
|
slant rig |
наклонная буровая установка |
|
torque converters |
гидротрансформатор |
|
326

10. Read the following information about foreign drilling rig classification. Fill in the second part of the table about domestic drilling rig classification.
Drilling Rig Classification
There are many types and designs of drilling rigs, with many drilling rigs capable of switching or combining different drilling technologies as needed. Drilling rigs can be described using any of the following attributes:
1. by power used |
1. by power used |
•electric – the rig is connected to a power grid usually produced by its own generators and uses electric motors to drive individual components such as drawworks, mud pumps and rotary tables.
•mechanical – the rig uses torque converters, clutches, and transmissions powered by its own engines, often diesel
•hydraulic – the rig primarily uses hydraulic power
•pneumatic – the rig is primarily powered by pressurized air
2. by pipe used |
2. by pipe used |
•cable – a cable is used to raise and drop the drill bit or drill string
•conventional – uses metal drill pipe of varying types
•coil tubing – uses a giant coil of tube and a downhole drilling motor
3. by height |
3. by height |
•single – can drill only single drill pipes, has no vertical pipe racks (most small drilling rigs)
•double – can store double pipe stands in pipe racks
•triple – can store stands composed of three pipes in the pipe rack (most large drilling rigs)
•quad – can store stands composed of four
pipes in the pipe rack |
4. by position of |
4. by position of derrick |
derrick |
|
327 |
•conventional – derrick is vertical
•slant – derrick is at an angle (this is used to achieve deviation without an expensive downhole motor)
11.Discuss the following points.
1.The most high-usage rigs.
2.Foreign drilling rig classification advantages.
3.Domestic drilling rig classification advantages.
4.Disadvantages of both classifications.
5.Modern tendencies in drilling rig development.
Rigging Up
Once the contractor gets the rig to the site, the next step is for the drilling crew to put the rig together, or rig up.
12. Put the following rig components and stages in the right rigging up order.
Rig floor
Mast
Substructures
Derrick
Raising the mast or derrick
328
13. Read the following texts and match them with above-mentioned rig components and rigging up stages. Fill in the chart.
1.
This drilling rig part allows the crew to drill several wells right next to each other on the platform. Crew members can drill one well, shift the crown block and the rotary, drill another well, shift the crown block and the rotary again, drill still another well, and so on, until they have drilled up to nine wells.
3.
One of the tallest drilling rig parts are about 200 feet, or 60 metres, high. The shortest are about 65 feet, or 20 metres, high.
5.
An important piece of equipment that is drawworks is placed on this drilling rig part.
7.
Its capacities for vertical loads run from 0.25 million up to 1.5 million pounds (over 0.5 million to about
3 million kilograms). In some cases, the drill string alone may weigh as much as a half million pounds, or over one million kilograms.
2.
It can be of two types: box-on box and the self-elevating, or slingshot.
4.
It is a framework that rests right over the hole. It raises the rig floor anywhere from about 10 to 40 feet (3 to 12 metres) above the ground. The exact height depends on the space needed to clear this equipment.
6.
Some of them fold, telescope, or even come apart into sections to make them shorter and easier to move. Nevertheless, they retain their integrity as a unitized component.
8.
If the rig has a mast, it is done mainly with the help of drawworks. If the rig has a derrick, crew members bolt it together, one piece at a time, on the substructure.
329
Rig component |
Description |
Function |
Additional |
|
|
|
information |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
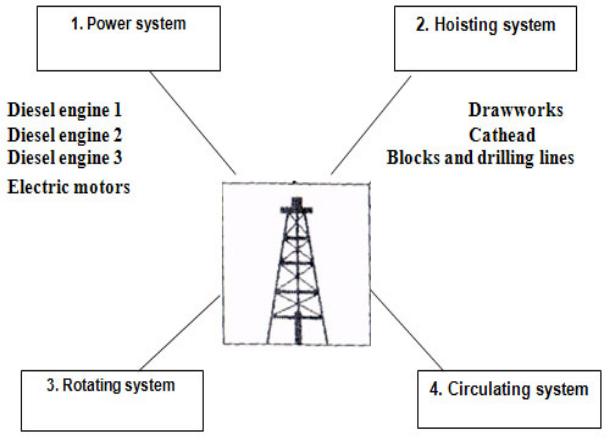
Rig Systems
A rotary rig's main job is to make hole. To make hole, the drilling crew places a bit on bottom, then the driller rotates it and pumps drilling mud to it. A rig needs a multitude of equipment to make these operations happen. A first look at all the gear on a drilling rig can overwhelm you. It is, however, easy to understand a rig's components if you divide them into systems: power, hoisting, rotating, and circulating.
Swivel |
Drilling mud |
Kelly |
Mud pits |
Rotary table |
Mud pumps |
Top drive |
Rotary hose |
Drill pipe |
Return line |
Drill bit |
Shale shaker |
|
330 |

1. Read the text “Power system” and fill in the missing words from the box. There is one extra word.
Power system
Without 1. power nothing on a rig operates. Machinery must have an energy source to make it go. On virtually every drilling rig, the power comes from internal-combustion engines, which are called prime movers. Further, they often use diesel 2. . Because of the way diesel engines operate, they
deliver more turning force, or torque, than gasoline engines. As a result,
many industries, including the 3. _ |
|
industry, use diesels. |
|
A 4. |
may need from two to four prime movers, depending on its size. |
||
The bigger the rig, the deeper it can drill and the more power it needs. Thus, big rigs have three or four prime movers. Together, they develop 4,500 horsepower (about 3,300 kilowatts) or more. In comparison, a powerful car engine may put out only 300 horsepower (220 kilowatts) or so; most develop even less.
This power must 5. to the rig's components to make them
work. For example, at the same time as the rotary table needs power to turn
the bit, the mud pump needs power to 6. |
|
drilling |
mud. What |
is more, to provide maximum power to a |
component, the |
7. |
must |
also be able to combine the power of two or more engines. Two common methods transfer power on today's rigs and allow the driller to combine engine power: mechanical transmission and electrical transmission.
be transferred; mix; drilling; fuel; circulate; driller; rig; power
(Baker R. “A Primer of Oil Well Drilling”, 2001, Austin, Texas)
331

2. Define whether the following sentences are true (T) or false (F).
T / F 1. Diesel engines are used in drilling industry mainly because of its operation regime.
T / F 2. In fact, power is generated by internal-combustion engines almost on all drilling rigs.
T / F 3. The rig height is in proportion to well depth.
T / F 4. There are two main ways of power transmission.
T / F 5. As a rule, big rigs have three prime movers.
3. Lab. Assignment:”Power Systems and Instrumentations”.
|
Terms and Vocabulary |
automatic cathead |
автоматическая шпилевая катушка |
auxiliary |
вспомогательный, дополнительный |
brake |
тормоз |
cathead |
шпилевая катушка |
catline |
канат для работ со шпилевой катушкой |
clutch |
муфта |
console |
пульт управления |
fast line |
ходовой конец (талевого каната) |
friction cathead |
фрикционная шпилевая катушка |
makeup cathead, |
шпилевая катушка для свинчивания |
breakout cathead |
бурильных труб |
reeve |
оснащать (талевую систему), продевать |
|
канат (через блок), надевать (на шкив) |
shaft |
вал, ось, шток |
sheave |
шкив; блок; ролик, каротажный ролик, |
|
колесо с желобчатым ободом |
slip |
скольжение, травить канат |
spool |
шпулька, бобина |
winch |
лебедка |
332
