
учебник 3 курс ICT
.pdf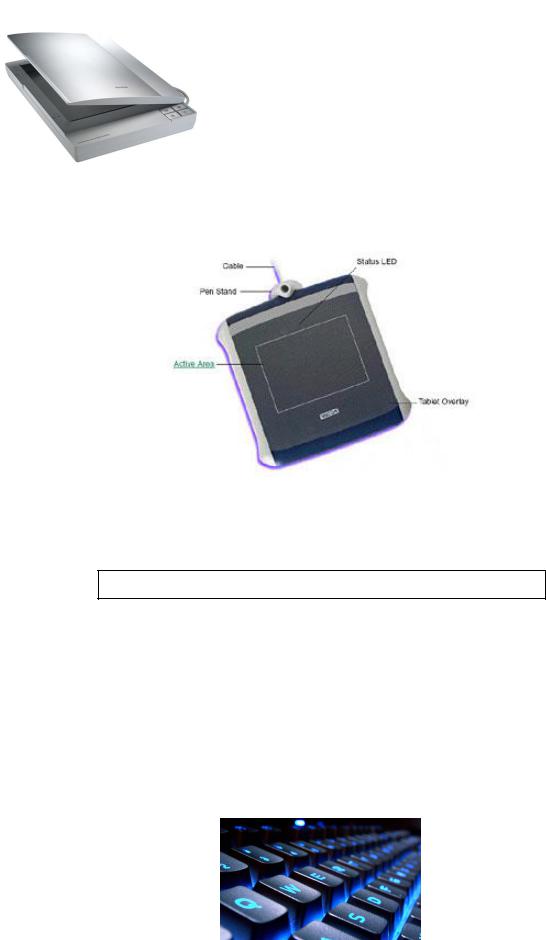
5. Read the notes about two input devices. Then describe them to your partner. He/she has to guess what you are describing.
a)It scans text and pictures and sends digitized image to computer.
b)It allows you to control computer vocally and spoken commands do what is normally done with keyboard/mouse.
c)It controls the cursor and selects items on the screen, works like upside-down mouse and ball on top turned round with figures.
d)It lets you interact with computer. You move pressure-stylus across the surface of a tablet and create graphics.
6. Complete this review of a digital camcorder using words from the box.
additional processing player optimized controller powerful
The DF201 benefits from a (1) … optical zoom lens and a video image (2) … designed for High Definition (HD) recording. Features include a ‗Quick Start‘ button and an intuitive menu system, easily navigated using a joystick (3) ... The camcorder is (4) … for high-resolution true widescreen recording and offers (5) … features such as a 2.7‖ LCD and a 0.27‖ 16:9 colour EVF (Electronic
Viewfinder), which allow users to compose and play back video in the same dimensions that it will be displayed on a widescreen TV set. It is then a simple process to finalize the DVD in-camera before playing it back in a compatible home DVD (6) ...
41

GRAMMAR PRACTICE SECTION
Conditionals
1. |
Match the sentences with the explanations. |
|
|
|
1. |
When you buy a computer |
in the shop |
a. future |
events that will happen, or likely to happen |
you always get an operating |
manual. |
- 1st conditional |
||
2. |
If you increase your order of CDs and |
b. If or When can be used where the meaning is |
||
DVDs, we‘ll give you a bigger discount. |
―every time‖ - 0 conditional |
|||
3. |
If you surfed the Internet yesterday, |
c. imaginary past event, but the result refers to the |
||
you probably learnt the news. |
present - mixed conditional |
|||
4. |
If the program were better, we |
d. things |
that are always or generally true |
|
wouldn‘t be doing it for such a long time. |
- 0 conditional |
|||
5. |
When anyone rings my mobile, I get |
e. events that are different to what really happened |
||
a photograph of the person on the screen. |
with a |
suggestion of criticism or regret (imaginary |
||
|
|
|
past) - 3rd conditional |
|
6. |
If I had reinstalled the operating system, |
f. imaginary, unlikely, impossible future events |
||
my computer wouldn‘t have crashed. |
- 2nd conditional |
|||
7. |
If I had upgraded my computer, I |
g. past events which possibly happened |
||
wouldn‘t have these problems now. |
|
|
||
2. |
Put the verbs into the correct form in the conditional sentences. |
|||
A. If your mobile phone (1) … (can/ talk), it (2) … (can/ reveal) a great deal. If it (3) … (be) privy to your calls and text messages, and possibly your e-mail and diary, obviously it (4) … (know) many of your innermost secrets.
B. Some years ago if your phone (5) … (know) where you were, how you got to work, where you liked to go for lunch, what time you got home, it (6) … (be) a great surprise. But it couldn‘t.
C. Now imagine! If it (7) … (be) possible to aggregate this sort of information from large numbers of phones. It (8) … (be) possible to determine and analyse how people move around cities, how social groups interact, how quickly traffic is moving and even how diseases might spread. The world‘s 4 billion mobile
phones (9) … (be) turned into sensors on a global data-collection network.
42

D. Phones (10) … also (be) used to collect data in more direct ways. Sensors inside phones, or attached to them, (11) … (gather) information about temperature, humidity, noise level and so on. E. More straightforwardly if it (12) … (be) necessary, people (13) … (send) information from their phones, by voice or text message, to a central repository. This can be a useful way to gather data quickly during a disaster-relief operation, for example, or when tracking the outbreak of a disease.
READING PRACTICE SECTION
Speech-recognition
Mobile phones and the Internet have changed the way we communicate. However, we still need to use the keyboard and the mouse to communicate with computers. When shall we be able to interact with PCs by voice? Speech recognition systems can make this possible soon in fact, speech companies claim that their programs let you dictate, control your PC by voice command, and convert text into speech.
The most popular voice recognition packages are IBM ViaVoice, Dragon NaturallySpeaking and L&H Voice Xpress. If you decide to buy one speech program, look for these features:
1. All the programs let you dictate text directly onto your word processor, spreadsheet or email. They claim an accuracy rate of around 98 percent. The technology is particularly useful to dictate notes, business memos, letters and e-mail.
2. Speech programs are usually more accurate if you train the software by reading aloud for about
20 minutes. This process involves reading sample text and teaches the program to recognize words that are not in its built-in dictionary (e.g. proper names, acronyms, unusual words). Most products let multiple users personalise their vocabulary and pronunciation.
3. They offer useful voice commands for editing and formatting (e.g. setting font size and style, text alignment etc.). However, it‘s a bit difficult to make corrections by voice; using the keyboard may be faster and more accurate.
4. Speech software allows you to use commands to launch programs or to navigate around windows and menus. You can also tell your programs to open a file, save it in a particular format or print it. 5. Some systems let you search the Web by voice. The Web version of IBM ViaVoice enables chat room users to chat using their voices rather than keyboards. Dragon NaturallySpeaking lets you browse the Web by speaking URLs and links, and dictate into online forms and fields in Microsoft Internet Explorer.
43

Speech recognition requires a powerful processor (500 MHz Pentium recommended), 64 MB of RAM, a good sound card, and a high-quality headset microphone.
Speech recognition technology has improved a lot and its potential is enormous, but some experts consider that it is not ready for common use yet. Some day, however, we‘ll be talking to our PC naturally, like a friend.
1. Tick the features mentioned in the article and give details from the text.
1. |
Activate |
menus by saying the words on the screen |
8. |
Take dictation with accuracy |
2. |
Execute |
applications by voice |
9. |
Design graphics |
3. |
Manage |
databases |
10. Accept spoken commands |
|
4.Configure multiple voice profiles
5.Read documents to you using a text-to-speech system.
6.Surf the web by speaking
7. Create and compile a computer program |
Speech-recognition icon |
|
2. With the help of the text, fill in the gaps in these sentences.
software dictate (2) package microphone interact voice recognition
1.With many ……. programs, the user must first train the software to recognise individual pronunciations.
2.You can ……. into the program‘s text screen, or you can ……. directly into any Windows application.
3. |
If you intend to do a lot of dictation, |
you should get a high-quality headset ……. |
|
4. |
Speech-recognition ……. could help |
children with special educational |
needs. |
5. |
In a few years‘ time, everyone will use voice commands to ……. with |
computers. |
|
6. |
If I could afford it, I would buy a new PC and a speech-recognition ……. |
||
3. What do you think of the idea from the text: “Some day we‟ll be talking to our PC naturally, like a friend”? Express your opinion.
44

SPEAKING/WRITING PRACTICE SECTION
1.Find a funny picture of an input device and give comments.
2.Find the information on the topics and make a report:
1.The evolution of input devices.
2.Classification of input devices.
3.Early input devices.
4.The most attractive input devices.
5.Some more functions of alphanumeric keys.
6.Wide usage of different kinds of scanners.
7.New technologies and touch screens.
8.Is it just a mouse?
9.Cameras – from history to the future.
10.Future of input devices.
3.Look through the text and make an instruction how to take care of any computer input device.
Our guide to cleaning and maintaining your keyboard.
Computer Keyboards can get dirty very easily, to clean the surface of a keyboard is very straight forward.
What you will need: lint free cloth, dry cloth or duster, suitable cleaning fluid (isopropyl alcohol), cotton buds, can of compressed air or vacuum cleaner, flat tip screwdriver (optional for thorough clean).
Shutdown your PC and remove the main plug, unplug the keyboard (remember where it was plugged in) and hold it upside down to release any debris from in-between the keys. This is where the patience comes in, make a note of the position of
all the keys or you will have trouble putting them back correctly, alternatively just remove the letter keys A - Z from the keyboard (which is where the most of the dust/debris will be) and refer to fig. 2 as a reference to put them back. All the keys can be removed although the larger keys
(space bar, enter key, shift keys, backspace, caps lock, etc) can be difficult to put back so you might avoid removing them. Remove the keys using the screwdriver, ease the screwdriver under the key and gently lift the key top off (see fig. 1). Note: don't forget to make a note of their position!!
45

When you have removed all the keys (except any keys you wish to avoid) use the compressed air (or vacuum cleaner) to remove any dust and debris from inside the keyboard.
|
Now is a good |
time to give the |
keys a proper clean, for best results |
|
|
clean each |
one |
individually (the |
patience thing again) with the cloth |
|
and cleaning |
fluid, when clean, wipe them over with the dry cloth. |
||
|
Before replacing the keys, take your lint free cloth and dampen it |
|||
Fig.1 |
with your cleaning fluid (don't put the liquid directly on the |
|||
keyboard), give the surface of the keyboard a good wipe over ensuring to clean as much as possible any keys that you haven't removed. When the keyboard is nice and clean replace the keys according to your notes or if you have just removed the letter keys
use fig. 2 as a guide, to put the keys back on position the key in place and press gently but firmly until it clicks home.
After replacing all the keys give the keyboard a quick wipe over with your dry cloth and you have a nice clean keyboard.
4. Make an advertisement for a real or imaginary input computer device.
FUN AND GAMES SECTION
1.In each of the sets of words below, one term is the odd one out: different from the others. Find it and explain why it is different.
1.keyboard……..……..………modem………....…………..mouse……..………………trackball
2.function key……………….screen………………….….shift……..………………….space bar
3.click…………….…………drag…………………..…….point…………………………….type
2.Word association: missing links.
The sets of words below can be linked by one other word. What is the missing word? What other collocations with this word do you know?
OPTICAL |
|
|
|
POINTER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CORDLESS |
|
|
|
MAT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MECHANICAL |
|
|
|
DRIVE |
|
|
|
|
|
46
3. |
Solve the clues and complete the puzzle with words |
|||||
1. |
Scanners and cameras are … devices used to transfer images into a format that can be |
|||||
understood by computers. |
|
|
|
|
||
2. |
A … lets you copy photos and printed documents |
into your PC. |
||||
3. |
It has become one of life's most familiar sounds |
– the beep of the supermarket till whenever a |
||||
… is scanned. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
If you need to scan 35mm … you should go for a dedicated 35mm film scanner which |
|||||
concentrates all its dots into a tiny area. |
|
|||||
5. |
This scanner |
has a resolution |
of 600 … . |
|
||
6. |
A … scanner |
is small enough |
to hold in your hand. |
|||
7. |
A … scanner |
is used to capture |
lines of text, barcodes and numbers. |
|||
8. |
Most digital |
cameras use flash |
|
… cards to store photos. |
||
9. |
… scanners |
have a flat |
surface |
and take at least A4-sized documents. |
||
10. To scan photographic |
negatives or slides you will need a …scanner. |
|||||
1 |
p |
2 |
e |
3 |
r |
4 |
i |
5 |
p |
6 |
h |
7 |
e |
8 |
r |
9 |
a |
10 |
l |
HUMOR SECTION
What does each of the cartoons imply? Why is it funny, in your opinion? Explain its humour.
47
DATA PROCESSING
KEY INFORMATION SECTION 1
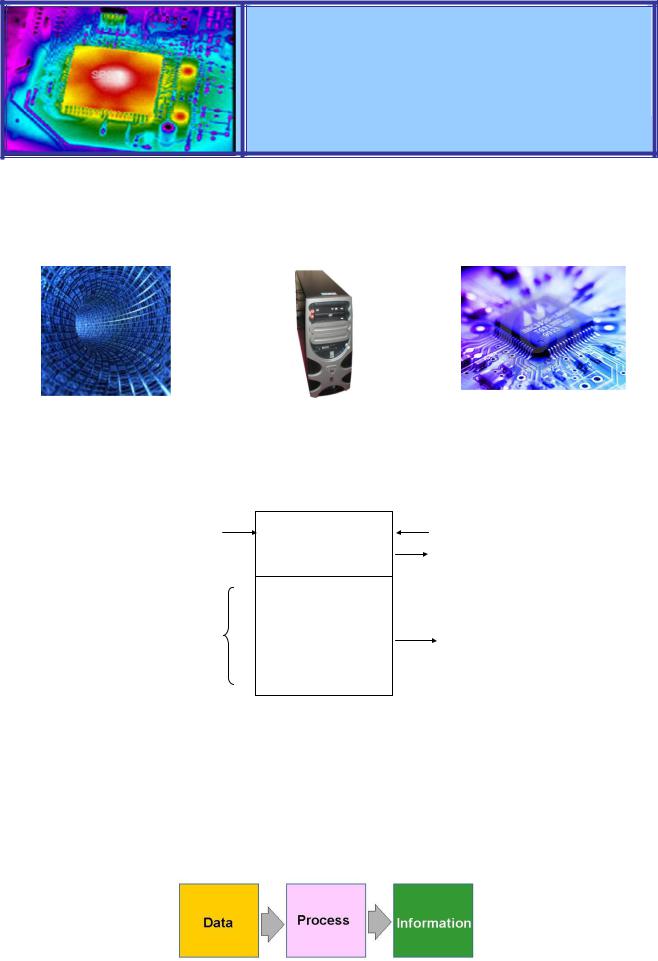
Computer data processing is any computering process that converts data into information or knowledge. Data-processing systems are often referred to as information systems to emphasize their practicality.
Data instructions |
|
Internal storage |
|
|
External storage |
||
|
|
unit |
|
|
unit |
||
Input |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Control unit |
|
|
|
|
|
Central |
|
|
|
|
Useful |
|
|
|
|
||||||
processing |
|
Arithmetic |
|
|
information |
|
|
unit |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
and logic unit |
|
|
Output |
|||
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Computer data processing system
Data-processing systems typically manipulate raw data into information, and likewise information systems typically take raw data as input to produce information as output. In order to be processed by a computer, the data needs first to be converted into a machine readable format. Once data is in digital format, various procedures can be applied on the data to get useful information.
Five basic operations characteristic of all data processing systems are defined as follows.
48

Inputting is the process of entering data, which are collected facts, into a data processing system.
Storing is saving data or information so that they are available for initial or for additional processing.
Processing represents performing arithmetic or logical operations on data in order to convert them into useful information.
Outputting is the process of producing useful information, such as a printed report or visual display.
Controlling is directing the manner and sequence in which all of the above operations are
performed.
Computer data processing systems have four main advantages:
Accuracy. Once data have been entered correctly into the computer component of a data
processing system, the need for further manipulation by humans is eliminated, and the possibility of error is reduced. Computers, when properly programmed, are also unlikely to make computational errors.
Ease of communications. Data, once entered, can be transmitted wherever needed by
communications networks. These may be either earth or satellite-based systems.
Capacity of storage. Computers are able to store vast amounts of information, to organize it, and to retrieve it in ways that are far beyond the capabilities of humans. The amount of data that can be stored on devices such as magnetic discs is constantly increasing. All the while, the cost per character of data stored is decreasing.
Speed. The speed, at which computer data processing systems can respond, adds to their value. The response required might be a fraction of a second.
VOCABULARY PRACTICE SECTION 1
1. |
Find in the right column the definitions for the terms in the left column. |
|
1. |
Data |
a) a part of a computer, entering data into the device; |
2. |
Data processing |
b) facts unorganized but able to be organized; |
3. |
Input |
c) the output of a data processing system; |
4. |
Output |
d) a series of operations that results system in the conversion of data |
5. |
Useful information |
system into useful information; |
|
|
e) an electronic device accepting the data processing results from the |
|
|
computer and displaying them; |
49

KEY INFORMATION SECTION 2
The nerve centre, the brain and the heart of a PC is the central processing unit or CPU. This unit is built into a single microprocessor chip - an integrated circuit - which executes program instructions and supervises the computer's overall operation. In electronics, an integrated circuit (also known as IC, microcircuit, microchip, silicon chip, or chip) is a miniaturized electronic circuit (consisting mainly of semiconductor devices, as well as passive components) that has been
manufactured in the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor |
material. Integrated |
circuits |
are |
|
used in almost all electronic equipment in use |
today and have revolutionized the |
world |
of |
|
electronics. |
|
|
|
|
A multi-core processor is simply a single chip |
containing more |
than one microprocessor core, |
||
effectively multiplying the potential performance with the number of cores (as long as the operating system and software is designed to take advantage of more than one processor). Because the cores are physically very close they interface at much faster clock rates, improving overall system performance.
The unit consists of three main parts:
1. The control unit, which examines the instructions in the user's program, interprets each
instruction and causes the circuits and the rest of the components |
-disk drives, monitor, etc. - to be |
|
activated |
to execute the functions specified, selects instructions and data from memory, and |
|
controls |
the flow between main storage and the arithmetic-logical |
unit. |
The control unit has the following components:
a counter that selects the instructions, one at a time, from memory;
a register that temporarily holds the instructions read from memory while they are being executed;
a decoder that takes the coded instruction and breaks it down into individual commands necessary to carry it out;
a clock, which produces marks at regular intervals.
The sequence of control unit operations is as follows:
The next instruction to be executed is read out from primary storage into the storage register.The instruction is passed from the storage register to the instruction register.
50
