
учебник 3 курс ICT
.pdf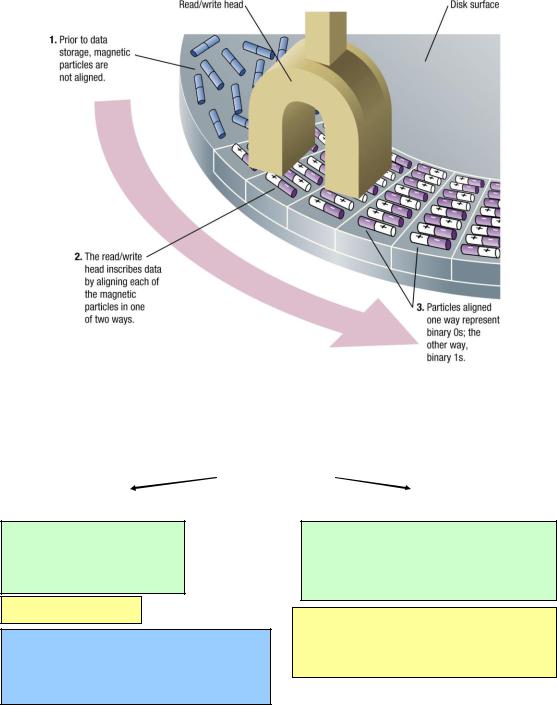
4. Summarize the information you learned about different forms and types of storage.
MEMORY |
|
DATA |
|
STORAGE |
PRIMARY STORAGE |
|
RETENTION |
|
SECONDARY STORAGE |
MAIN STORAGE |
|
|
|
MASS STORAGE |
INTERNAL STORAGE |
|
|
|
EXTERNAL STORAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
fast
temporary
volatile
directly accessible by CPU
Semiconductor - RAM
data to be processed;
intermediate & final results of processing;
instructions required for ongoing process.
slow
permanent
non-volatile
accessible through input/output channels
Semiconductor –flash memory devices Magnetic – hard disks, floppy disks, magnetic tape
Optical – CDs, DVDs, BDs - ROM, R, RW
5. Make a report on one of the following topics.
Evolution of storage technologies.
|
Use of online storage in different spheres of life (medicine, police, business, libraries, etc.). |
|
The most functional storage devices and technologies (everyday life and different spheres). |
|
Storage devices and technologies that have become obsolete and reasons for this. |
|
The future of storage technologies. |
|
An ideal imaginary storage medium. |
|
101 |
FUN AND GAMES SECTION |
|
||
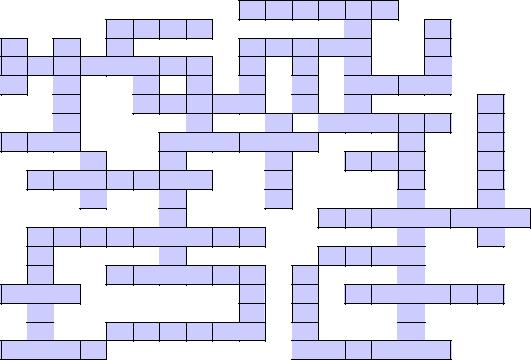
Complete the crossword using terms related to data storage. |
|
||
ACROSS |
|
|
|
1. |
– a segment of a disk; a subdivision of a track on a magnetic |
disk or optical disc. |
|
2. |
– (abbreviation) the basic system; a de facto standard defining |
a firmware interface; boot |
|
|
firmware, designed to be the first code run by a PC when powered on. |
||
3. |
–one of the written signs that represent the numbers 0 to 9 |
|
|
4. |
– memory that won‘t retain the stored information unless constantly supplied with electricity |
||
5. |
– a system of signals that represent words or letters when they are sent by machine |
||
6. |
– one of concentric circles into which the surface of a disk is divided |
||
7. |
– small storage devices connected to a USB port of a computer that let you save and transfer |
||
|
data quickly |
and easily |
|
8. |
Blue-……. - |
an optical disc storage medium for high-definition video and data storage |
|
9. |
– the part of a computer where information can be stored; the amount of space that can be used |
||
|
for storing information on a computer |
|
|
10. |
– (abbr.) part of a computer acting as a temporary storage area for data to be used immediately |
||
|
|
1 |
|
30 |
|
2 |
|
|
32 |
21 |
22 |
3 |
28 |
|
4 |
24 |
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
6 |
|
|
33 |
|
|
27 |
7 |
31 |
8 |
|
9 |
|
|
|
23 |
|
|
10 |
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
15 |
26 |
29 |
|
16 |
|
|
|
17 |
|
18 |
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
20 |
|
11.– the way data is kept; retaining data used for computing for some interval of time
12.– a thousand bytes
13.– a place in a computer where files or programs are organized
14.– a stiff disk inside a computer that is used for storing information
15.– a copy of a computer document, program etc, made in case the original is lost or damaged
102
16.– (abbr.) a way of connecting equipment to a computer using wires so that it can work together
17.……. time – the time taken by a computer to find and use a piece of information in its memory
18.– used to talk about video, CD, tape etc when saying what type of equipment it can be played on
19.– a unit for measuring computer information, equal to eight bits
20.– information about something stored on computer so that it can be looked at in the future DOWN
21.– (abbr.) a type of computer disc that can store a large amount of information
13. |
– the compactness of stored information; the storage capacity of a medium |
divided with a unit |
|
of length, area or volume |
|
|
|
22. |
– a square piece of plastic you can store information on, which you can remove from and put |
||
into a computer |
|
|
|
23. |
– (abbr.) the part of a computer where permanent instructions and information are stored |
||
2. |
– (abb.) the smallest unit on which information |
is stored on a computer |
|
24. |
– (abbr.) the study of processes and equipment |
for storing data and making |
it available |
9. |
– a disk on which data is encoded as microscopic magnetized needles on its surface |
||
25.– to remove information from a computer memory
3.– a round plate on which data can be encoded
26.– a part of a computer where you can connect another piece of equipment, such as a printer
27. – a piece of equipment in a computer that is used to get information from a disk or to store it
28.– one thousand million
29.– (acronym) a piece of equipment that produces a powerful narrow beam of light that can be used in recording and reading data
30. – disks that record data by burning microscopic holes in the surface of the disk with a laser
31.……. memory – memory which uses integrated circuits to store information
32.– information on a computer that you store under a particular name
33.– the total amount of stored information that a storage device or medium can hold
HUMOR SECTION
What does each of the cartoons imply? Why is it funny, in your opinion? Explain its humour.
103

OPERATING SYSTEMS & GUI |
KEY INFORMATION SECTION 1
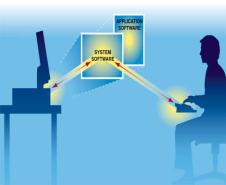
An operating system (OS or O/S) is an interface (connection) between hardware and user - it determines how the user interacts with the computer; it is responsible for the management and coordination of activities and the sharing of the resources of the computer. The operating system acts as a host for applications that are run on the machine, handling the details of the operation of the hardware. This relieves application programs from having to manage these details and makes it easier to write applications. The purpose of an operating system is to organize and control hardware and software so that the device it lives in behaves in a flexible but predictable way. The operating system is started automatically when a computer is switched on, it is the first thing loaded onto the computer - without the operating system, a computer is useless. It is then used to start up and control other programs.
PERIPHERALS |
|
|
|
COMPUTER |
|
|
|
|
|
(CPU, |
|
|
|
OPERATING |
|||
|
|
|
MAIN MEMORY) |
||
|
|
SYSTEM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
APPLICATIONS/PROGRAMS |
|
|
|
USER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common contemporary operating systems include Microsoft Windows (designed by Microsoft and used on most PCs), Mac OS (created by Apple and used on Macintosh computers). Microsoft Windows has a significant majority of market share in the desktop and notebook computer markets, while servers generally run on Unix or Unix-like systems (found on mainframes and workstations in corporate installations, as it supports multi-users). From the very first, it was designed to be a multi-tasking system. Written in C language, Unix is the most commonly used system for advanced
CAD programs. Linux is a generic term referring to Unix-like multi-tasking computer operating
104
systems based on the Linux kernel. Their development is one of the most prominent examples of free and open source software collaboration; typically all the underlying source code can be used, freely modified, and redistributed by anyone under the terms of the GNU General Public License (GPL) and other free licenses. Linux is predominantly known for its use in servers, although it is installed on a wide variety of computer hardware, ranging from embedded devices and mobile phones to supercomputers.
System software helps to run the computer hardware and computer system. It includes operating systems, device drivers, diagnostic tools, servers, windowing systems, utilities, language translator, data communication programs, data management programs and more. The purpose of systems software is to insulate the applications programmer as much as possible from the details of the particular computer complex being used, especially memory and other hardware features, and such accessory devices as communications, printers, readers, displays, keyboards, etc.
Application software is any tool that functions and is operated by means of a computer, with the purpose of supporting or improving the software user's work. In other words, it is the subclass of computer software that employs the
capabilities |
of a computer directly and |
|
||
thoroughly to a task that the user wishes to |
|
|||
perform. |
This should be contrasted with |
|
||
system |
software |
(infrastructure) |
or |
|
middleware (computer services/ processes |
|
|||
integrators), which is involved in integrating a |
|
|||
computer's |
various capabilities, but typically |
|
|
|
does not directly apply them in the |
|
|
||
|
performance of tasks that benefit the user. In this context the term application |
|||
|
refers to both the application software |
and its implementation. |
||
|
Utility software (also known as service program, service routine, tool, utility |
|||
|
routine or system utilities) is computer software designed to help manage and |
|||
|
tune the computer hardware, operating |
system or application software by |
||
performing a single task or a small range of tasks which improve a system's performance and help users take advantage of the computer's capabilities. Utility software has long been integrated into most major operating systems. Utilities are often desk accessories that can be called up while you're working in another application. They can also be system extensions which are activated when you turn on the computer, control devices which you adjust in the control panel, or even stand-alone programs that run when you need them.
105
Utilities are available for back-up, file search, virus protection, disaster recovery, and so on. Accessibility program makes a PC easier for disabled users to use.
Anti-virus utilities scan for computer viruses.
Crashed dick rescuer utility is used to restore disks and corrupted files.
Disk checkers can scan the contents of a hard disk to find files or areas that are corrupted in some way, or were not correctly saved, and eliminate them for a more efficiently operating hard drive.
Disk cleaners can find files |
that unnecessary to computer operation, or take up considerable |
||||
amounts of space. Disk cleaner |
helps the user to decide what to delete |
when their hard disk is full. |
|||
Disk |
compression |
utilities |
can transparently compress/uncompress the contents of a disk, |
||
increasing the capacity of the disk. |
|
||||
File |
managers provide a convenient method of performing routine data management tasks, such as |
||||
deleting, renaming, cataloging, moving, copying, merging, generating and modifying data sets. |
|||||
Launcher applications provide a convenient access point for application software. |
|||||
Media player lets you watch DVDs, play music and listen to |
|
||||
the radio on the Web. |
|
|
|||
Network managers check the computer's network, log events |
|
||||
and check data transfer. |
|
|
|||
Registry cleaners |
clean and |
optimize the Windows registry |
|
||
by removing old registry keys that are no longer in use. |
|
||||
System profilers |
provide detailed information about the |
|
|||
software installed |
and hardware attached to the computer. |
|
|||
Text and Hex Editors modify |
text or data of a file. These files could |
be data or an actual program. |
|||
VOCABULARY PRACTICE SECTION 1
1. Read the Key Information Section and find the following.
1. the difference between system software and application software
2. software that enables users and programs to communicate with hardware
3.the meaning of 'multitasking'
4.a multi-user OS used on large, powerful computer systems
5.the operating system that is freely distributed
6.the operating system designed by Apple
7.the OS created by Microsoft
8.the text-based operating system used in older PCs
9.the OS written in C language and used on minicomputers and workstations
106

2. Read the text below and complete it with the phrases in the box.
|
|
applications software |
operating |
system |
software |
system software |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Information provided by programs |
and data is known as (1) ….. Programs are sets of instructions |
||||||
that make the computer execute operations and tasks. |
|
|
|||||
There are two main types of software: |
|
|
|
|
|||
The (2) ….. refers to all the programs which control the |
|
|
|||||
basic functions of a computer. They include operating |
|
|
|||||
systems, system utilities (e.g. an |
anti-virus program, a |
|
|
||||
back-up utility) and language |
translators |
(e.g. |
a |
|
|
||
compiler- |
|
the software that translates instructions into |
|
|
|||
machine |
code). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
The (3) ….. refers to all those applications - such as
word processors and spreadsheets - which are used for specific purposes. Applications are usually stored on disks loaded into the RAM memory when activated by the user.
The (4) ….. is the most important type of system software. It is usually supplied by the manufacturers and comprises a set of programs and files that control the hardware and software resources of a computer system. It controls all the elements that the user sees, and it communicates directly with the computer. In most configurations, the OS is automatically loaded into the RAM section when the computer is started up.
3. Which utility would you use to do these tasks?
1. to play and organize multimedia on your PC
2.to diagnose and repair damaged disks
3.to help computer users with sight, hearing or mobility difficulties
4.to make files smaller, so you can send them with emails
5.to help the user delete unnecessary files
6.to manage your network activity
7.to protect your system against computer viruses
8.to automatically blank out the screen after a specific interval of inactive time (so that the image does not burn into the screen)
107

KEY INFORMATION SECTION 2
An operating system is a master control program which controls the functions of the computer system as a whole and the running of application programs. Typical functions of the OS are
handling input/output operations, |
running programs and organizing files on disks. The OS also |
|
gives access |
to networks and |
allows multitasking. All computers do not use the same operating |
systems and some software is only designed to run under the control of specific operating systems. Mainframe computers usually process several application programs concurrently, switching from one to the other, for the purpose of increasing processing productivity. This is known as multiprogramming (multi-tasking in the context of microcomputers), which requires a powerful operating system incorporating work scheduling facilities to control the switching between programs. This entails reading in data for one program while the processor is performing computations on another and printing out results on yet another.
In multi-user environments an operating system is required to control terminal operations on a shared access basis as only one user can access the system at any moment of time. The operating system allocates control to each terminal in turn. Such systems also require a system for record locking and unlocking, to prevent one user attempting to read a record whilst another user is updating it, for instance. The first user is allocated control to write to a record (or file in some instances) and other users are denied access until the record is updated and unlocked.
Some environments operate in concurrent batch and real-time mode. This means that a 'background' job deals with routine batch processing whilst the 'foreground' job deals with real-time operations such as airline seat reservations, on-line booking of hotel accommodation, or control of warehouse stocks, etc. The real-time operation has priority, and the operating system
interrupts batch processing operations to deal with real-time enquiries or file updates. The stage of batch processing attained at the time of the interrupt is temporarily transferred to backing storage. After the real-time operation has been dealt with, the interrupted program is transferred back to internal memory from backing storage, and processing recommences from a 'restart' point. The
108

operating system also copies to disk backing storage the state of the real-time system every few minutes (periodic check points) to provide a means of ‗recovering' the system in the event of a malfunction.
An operating system is stored on disk and has to be booted into the internal memory (RAM) where it must reside throughout processing so that commands are instantly available. The operating system commands may exceed the internal memory capacity of the computer in which case only that portion of the OS which is frequently used is retained internally; other modules being read in from disk as required.
Previously many microcomputers functioned under the control of a disk operating system known as DOS. This operating system was developed by Microsoft in 1981 for all IBM PC compatibles.
Today it's only used in old PCs. In this text-based OS, you communicate with the computer by typing commands that exist within its library.
Here is a partial list of the most common commands for Microsoft's MSDOS operating system.
APPAND - displays or sets the search path for data files. DOS will search the specified path(s) if the file is not found in the current path. This had some creative uses, such as running non-CD based games from the CD, with configuration/save files stored on the HD.
CHDIR or CD - change current directory. Displays the current working directory when used without path.
CHKDSK - verifies a hard disk or a floppy disk for file system integrity.
Displays the full path and name of every file on the disk and forces full disk verification.
CHOICE - allows for batch files to prompt the user to select one item from a set of single-character choices.
CLS - Clears the screen. It is the equivalent to the Unix – CLEAR.
COPY - copies files from one location to another. The destination defaults to the current directory. EXIT - exits the current command processor. If the exit is used at the primary command, it has no effect unless in a DOS window under Microsoft Windows, in which case the window is closed and the user returns to the desktop.
FC or COMP - compares two files or sets of files and displays the differences between them. MEM - displays memory usage. It is the equivalent to the Unix command – FREE.
REN - renames a file. Unlike the MOVE command, this command cannot be used to rename subdirectories, or rename files across drives.
TREE - shows the directory tree of the current directory. DEL or ERASE – deletes a directory or file.
TYPE – displays the text of the current directory on the screen.
109
VOCABULARY PRACTICE SECTION 2
1. Here is a list of typical tasks performed by an operating system. In each case the main verb has been omitted. Fill in the blanks from the words given (sometimes more than one may apply).
execute monitor format diagnose
A typical operating system will:
1.…… input and output devices.
2.…… the status of hardware devices.
3.…… hardware interrupts.
4.…… new disks.
5.…… disk directories.
6.…… disk reading and writing operations.
7.…… disk errors.
8.…… disk commands relating to the deletion, copying, renaming, and dumping of files.
2. |
Match these common DOS commands with the appropriate explanation. |
|
||
1. |
BACKUP |
a. searches for a specific string of text in a file. |
|
|
2. |
CHDIR or CD |
b. allows |
a text file from the current directory to be displayed |
on screen. |
3. |
CHKDSK |
c. allows |
the user to change the name of a file. |
|
4. |
CLS |
d. saves the contents of the hard disk to a floppy disk for security purposes. |
||
5. |
DEL |
e. is used when it is necessary to change the current directory. |
|
|
6. |
DIR:SORT |
f. clears data from the screen. |
|
|
7. |
REN |
g. alphabetically sorts and lists a disk directory. |
|
|
8. |
TYPE |
h. makes back-up copies of the contents of one disk to another. |
||
9. |
FIND |
i. deletes |
a specified file from the current directory, specified |
drive or path. |
10. DISKCOPY |
j. produces a status report of the currently logged-on disk, indicating the |
|
|
amount |
of disk space used, the available capacity (in bytes), and the number |
|
of files |
on disk. |
110
