
учебник 3 курс ICT
.pdf
record |
|
recorder |
recording |
recorded |
|
1. |
All disks must |
be initialized |
before information can be ……. onto them. |
||
2. |
The ……. heads follow |
the tracks and magnetize the coating along each track. |
|||
3. |
A disk drive works very much like a tape ……. that can both play and record. |
||||
fragment |
fragmentation |
defragmented fragmented defragmenter |
|||
1.In a .……. disk, a file is stored in noncontiguous sectors. In a …… disk a file is stored in neighbouring sectors.
2.After you create, delete and modify a lot of files, the hard disk becomes ……. with bits and pieces spread all over the disk.
3.………. slows down the speed at which data is accessed because the disk drive has to work
harder to find the parts of a file stored in many different locations.
4.To reorganize your hard disk, you can use a disk optimizer or …….; this will reorder your files into contiguous clusters.
6.Choose words from each line to make terms related to flash technology.
flash |
smart |
memory |
based |
state |
LAN |
card |
player |
drive |
technology |
card |
drive |
1. flash … 2. solid-… 3. wireless … 4. USB … 5. flash- … 6. U3 …
7. Complete these product descriptions using the terms from the exercise above.
1.With the 4GB Gridfire ……. , you can back up, store, carry and offload large files with one affordable, convenient device. What's more, ……. means no moving parts, and therefore less chance of damage if the device is dropped.
2.The 2GB One-Tech ……. is the best choice for high-performance results from your digital camera and other handheld devices.
3.The STM ……. gives you the ability to carry your files and your software on a secure USB drive, by using separate partitions to.
4.The Airlink ……. connects your desktop PC to a network, using the latest advanced silicon chip technology.
5.With 80GB of storage capacity, the iSing ……. is the only device you'll need for audio and video playback on the move.
91

KEY INFORMATION SECTION 3
Optical storage, the typical optical disc, stores information in deformities on the surface of a circular disc and reads this information by illuminating the surface with a laser diode and observing the reflection. The deformities may be permanent (read only media ), formed once (write once media) or reversible (recordable or read/write media). Optical disc storage is non-volatile.
Optical disks can store information at much higher densities than magnetic disks. Thus, they are ideal for multimedia applications where images, animation and sound occupy a lot of disk space. Besides, they are not affected by magnetic fields. This means that they are secure and stable, e.g. they can be transported through airport metal detectors without damaging the data. However, optical drives are slower than hard drives. While there are hard drives with an average access time of 8 ms, most CD-ROM drives have an access time of 150 to 200 ms.
The following forms of optical storage are currently in common use:
CD, CD-ROM, DVD, BD-ROM (read only memory): Read only storage, used for mass distribution of digital information (music, video, computer programs), you cannot change data stored on them.
CD-R, DVD-R, DVD+R BD-R (recordable): Write once
storage, used for tertiary and off-line storage; write-once devices which let you duplicate CDs.
CD-RW, DVD-RW, DVD+RW, DVD-RAM, BD-RE (Blue Ray) (rewritable): Slow write,
fast read storage, used for tertiary and off-line storage, the disks enable you to write onto them in multiple sessions, like a hard disk and can be erased and reused many times.
DVDs (digital versatile discs) are similar in size to CDs (both are 1.2 mm thick), but they differ in structure and capacity. DVDs have more tracks and more pits (tiny holes) per track, and can store from 4.7 GB to 17 GB of data, movies, high-definition sound, etc.,; so they will probably replace CDs.
Ultra Density Optical or UDO is similar in capacity to BD-R or BD-RE and is slow write, fast read storage used for tertiary and off-line storage.
92
Magneto-optical disc storage is optical disc storage where |
the magnetic state on a ferromagnetic |
|||||
surface stores information. The information is read optically |
and written by combining magnetic |
|||||
and optical methods. Magneto-optical |
disc storage is non-volatile, sequential |
access, slow write, |
||||
|
fast read storage used for tertiary and off-line |
|||||
|
storage. |
Consequently, |
MO |
disks |
are |
|
|
rewritable, |
i.e. they can be written to, erased, |
||||
|
and |
then |
written again. They usually come in |
|||
|
two formats: 5.25" cartridges can |
hold |
more |
|||
|
than |
5.2 |
GB; 3.5" floptical disks have a |
|||
|
capacity of 230 MB to 1.3 GB. They are ideal |
|||||
for back-up and portable mass storage. |
3D optical data storage has also been proposed. |
|
|
|||
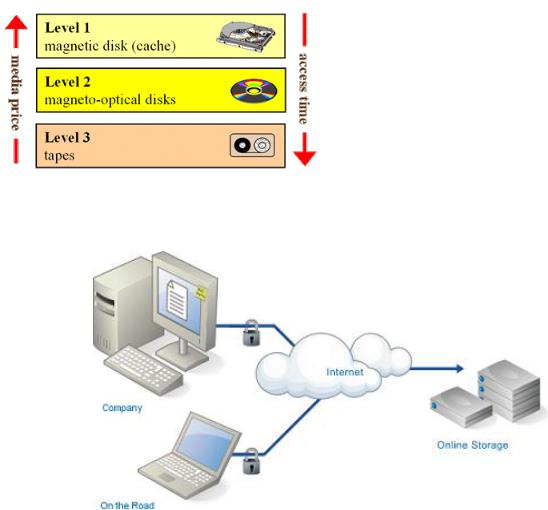
Online data storage |
|
|
|
|
|
|

 Recent developments have enabled users to store their data on the internet. This is precisely what online data storage is all about. The rapid technological advancements taking place have brought the price of broadband internet down. This has been coupled with better service and better speed which has driven many people to purchase online data storage.
Recent developments have enabled users to store their data on the internet. This is precisely what online data storage is all about. The rapid technological advancements taking place have brought the price of broadband internet down. This has been coupled with better service and better speed which has driven many people to purchase online data storage.
Online data storage benefits the user in more than one way.
Primarily, it is an additional and flexible source for storing data.
Secondly, it also serves as a backup mechanism.
Thirdly, it serves as an effective method through which users can share their data with others on the internet.
Another advantage is the opportunity to expand when you need to. Once you reach the maximum limit of storage you can expand your storage capacity by purchasing additional space. This will give you more space without you being required to install any additional storage hardware.
Online data storage allows the users to access their data from any location whatsoever. They can easily access their storage space wherever they find a computer and an internet connection.
93

VOCABULARY PRACTICE SECTION 1
1. Decide if the sentences are true or false.
1. Besides CDs and DVDs, there are other types of optical storage; e.g. Blu-ray and HD-DVD.
2.CDs are 120 mm in diameter and 12 mm thick. DVDs are 122 mm in diameter and 12.5 mm thick.
3.DVDs have more tracks, and the pits used to store data are smaller; they have a greater storage capacity than CDs.
4. DVDs can be played on CD players, so there's no need to invest in new hardware.
5. Blu-ray may soon become the dominant optical storage technology, although Toshiba, Microsoft and the DVD Forum are supporting HD-DVD technology instead.
2. Look back into the Key Information Section and find:
1. |
the CD and DVD formats that can be rewritten many times |
2. |
the CD and DVD formats that can be written to by the user only once |
3. |
the CD and DVD formats that can be read by a computer but not written to |
4. |
the type of cards used in digital cameras |
5. |
a type of drive that plugs into a USB port and lets you share photos and music with friends |
6. |
the memory without moving parts; it is erasable, non-volatile and used in small devices |
7. |
the expression that means to 'initialize a disk and prepare it to receive data' |
3. Complete this product description with the words from the text in the box.
Portable DVD players let you watch movies or TV, play games and listen to music,  wherever you are. They usually run on batteries, have a widescreen (rectangular 16:9
wherever you are. They usually run on batteries, have a widescreen (rectangular 16:9
format) LCD and support multi-format playback, allowing you access to many file formats including DVD video, JPEG pictures, MP3 music, etc. They have two built-in stereo speakers, or headphones if you don't want to disturb other people.
The Panasonic DVD-LS91 is a top-of-the-range ……., which provides pure entertainment wherever you go. It has a big 9 inch built-in ……. LCD, so you can really enjoy movies. The built-in stereo speakers allow you to listen along, or if you want to listen alone, just plug in a pair of ……. This portable machine provides ……. , so you can play DVD Audio/Video, CD-R/RW, DVD-RAM, DivX and MP3 files. Its compact design features a built-in rechargeable 6 hour battery pack.
94

The DVD-LS91 allows 6 hours of playback, and provides a perfect way to entertain yourself and your kids during long trips.
4. Fill in the missing letters to make a term related to optical storage. Complete these extracts from an ICT textbook using these terms. You may have to use the plural form.
optical d……. |
backward-с……. |
multi-f……. |
|
|
laser b…... |
double-s……. |
Blu-r……. |
dual l……. |
|
1. |
Portable DVD players usually support ……. playback; this means the user can watch a |
|||
|
wider variety of different file types (DivX, |
MP4, etc.). |
|
|
2. |
……. differ from magnetic ones, in terms of both internal structure |
and storage capacity. |
||
3. |
CDs and DVDs are read using a red …...... In ..….. discs it is blue-violet, hence the name. |
|||
4. |
Unlike |
a CD, a DVD can be ……. and ……., giving it a capacity of up to 17GB. |
||
5. |
DVD drives are ……. , meaning that they can play older technologies such as CD-ROMs. |
|||
5. Which device or format would be most suitable for storing these things and why?
the operating system and the programs on the home computer
an electronic encyclopedia
|
a movie in digital format, hold several movies in different languages |
|
the music tracks by your favourite artist |
|
all the files generated by a company in one day |
the photos taken with a digital camera
READING PRACTICE SECTION
Thanks for the memory
A mathematical trick may allow people to scatter their computer files across the world's hard disks
If you have lots of unused storage space on your hard disk, then why not share it with others on the internet? The benefit could be distributed storage for your own files, making them available any time via the web, even if you are nowhere near your computer—indeed, even if your computer is switched off. That desideratum* is what a Zurich-based firm called Caleido is aiming to provide, with a free online storage service known as Wuala that was recently introduced to the public.
Though the idea underlying is simple, Wuala requires some |
nifty* technology to make its |
distributed system work reliably. In particular, its developers, |
Dominik Grolimund and Luzius |
|
95 |

Meisser, have used a clever mathematical trick to compensate for the fact that the participating computers will come and go from the internet in an unpredictable way.
The challenge is how to minimise the number of copies of the same file that have to be distributed. Copying costs participants both storage space and bandwidth. Yet there have to be enough copies to ensure that there is at least one available most of the time. If, for example, each computer is online 25% of the time, then a quick calculation shows that you would have to copy each file to 100 different computers to ensure that 999,999 times out of a million there is at least one copy available when a user looks.
But copying every file a hundred times is hugely inefficient. Instead, Mr Grolimund and Mr Meisser plan to break each file into chunks, which can be scattered liberally around the hard disks
of participating computers, and then to use a mathematical trick to reconstruct the original file from those chunks.
This trick, known as Reed-Solomon error correction, is employed routinely to interpret the data on DVDs, but it has not been used before in the volatile world of private computers on the internet. The first step is to convert the file (which is, regardless of what it represents, simply a long string of ones and
zeros) into a mathematical function called a polynomial. This is done by splitting it into 100 fragments, which are smaller binary numbers. It is these numbers that are used to define the polynomial.
One of the characteristics of a polynomial is that a few numbers can nail* it down precisely. If a simple polynomial is plotted out on a graph it forms a line. A straight line (the simplest type of polynomial) is defined by any two points on its length. A parabola can be defined by three points. The polynomials that Wuala generates can be defined by 100 points—though, because the polynomials used are not simple ones, these points are complex mathematical constructs, rather than straightforward numbers.
All you have to do now, therefore, is select a suitable number of points from along the polynomial (these need not be the original ones) and convert their values into the appropriate mathematical constructs. Scatter these around the host computers and, when someone wants to look at the file, he need recover only 100 of them to have enough data to reconstruct the file from scratch. To have 100 points available 999,999 times out of a million it turns out that you need to scatter a total of 600 of them around. That is an amount of data equivalent to six versions of the original file, rather than the 100 that would be needed to achieve the same level of reliability if whole files were being stored. Moreover, the system needs the computers linked to it to be available for only 17% of the time, rather than 25%, for this to apply.
 Online storage is a growing market, especially for backing up data, where reliability is a big concern. Most commercial online-storage services use centralised servers. Although these are
Online storage is a growing market, especially for backing up data, where reliability is a big concern. Most commercial online-storage services use centralised servers. Although these are
96

generally reliable, they do sometimes fail. And when they do, the results are embarrassing—as Amazon, an online shopping company, learnt on two occasions this year when the servers for its commercial data-storage system went down for several hours at a time.
Though some people may feel squeamish* about scattering their data over hundreds of other
computers |
(even though it will be encrypted), or storing unknown file fragments on their own, Mr |
|||
Grolimund |
is adamant* that Caleido has learnt from other ―peer-to-peer‖ file-sharing |
systems, and |
||
that Wuala |
is built to handle concerns about the illegal distribution of copyrighted or |
|
||
―inappropriate‖ content. If he is right, Wuala may prove that, for online data storage, |
it is as good to |
|||
give as it is to receive. |
|
|
|
|
Notes. |
|
|
|
|
*Desideratum-things you need or want |
|
|
||
*Nifty-well-designed, |
effective, easy to use |
|
|
|
*Nail down-definitely |
decide, arrange or complete |
something |
|
|
*Squeamish-easily shocked or upset by something |
unpleasant |
|
||
*Adamant-determined |
not to change your belief or decision about something |
|
||
1. Answer the questions on the article
What do these numbers from the article refer to?
25 100 999,999 17 600
What do these names from the article refer to?
|
Caleido |
Wuala |
Dominik |
Grolimund |
Amazon |
|
Luzius |
Meisser |
Zurich |
Reed Solomon |
|
|
What type of storage does the article talk about? |
||||
|
What possible problems does the author talk about? |
||||
|
What benefits do the developers offer? |
|
|||
|
What clever trick to avoid copying each file |
many times did the creators of Wuala invent? |
|||
|
What are the differences between Wuala and most of the other on-line storage services? |
||||
What is a polynomial?
|
What might people using this service be worried about? How might they feel and why? |
|
Do you think there would be a market for such a service? What might that market be like? |
Would you agree to use Wuala? If yes, on what conditions?
Do you know any storage opportunities similar to the one described in the article? Do you use them? Why/why not?
97

2. Read the comments to the article. Which comments do you agree with? Why? What is your opinion on the article and on the service it talks about? What would you write to comment it?
Readers’ comments.
1. Storage as a Service ! Well, sounds promising. Is that safe enough?
2. Our company has also come up with some clever tricks that could greatly improve
the lives of our customers. They have all failed due the understandable security 
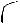 paranoia - not least within IT departments, that can be exceedingly technophobic.
paranoia - not least within IT departments, that can be exceedingly technophobic.  3. The model assumes that there is enough spare space available on hard disks, which I believe is not the case. Thanks to broadband connection and now HD content, many home computers are at their max capacity. That's the reason we go and buy external 300 Gig drives, right?
3. The model assumes that there is enough spare space available on hard disks, which I believe is not the case. Thanks to broadband connection and now HD content, many home computers are at their max capacity. That's the reason we go and buy external 300 Gig drives, right?
4. I can see some useful applications of this, but definitely not a complete shift from today‘s method. The issue for me is speed, the wait from pulling files from the net all the time would drive me crazy. No thanks, disk is cheap; I‘d rather just get a couple of disks and backup my own stuff.
5. Although it sounds unsecured when it splits our files in to small encrypted pieces into someone else‘s computer, we don‘t have that amount of secret personal files, right? Speed is still my main consideration. It would be great if I can upload quickly and my friend can download at the same speed. Hanging on line for four hours one day is a little forcing.
3. Find in the article all the words related to computers and IT. Try to explain their meaning with your own words (if necessary use a dictionary to help you).Use them to make your own sentences.
GRAMMAR PRACTICE SECTION
Passive.
1. Match the sentences with the explanations.
1. |
have something done |
a. |
The transistor that completely changed the vacuum tubes |
|
|
|
|
was invented in 1948. |
|
2. |
passive + infinitive |
b. |
All the computers |
have just been checked for viruses. |
3. |
passive + perfect infinitive |
c. |
By 2100 quantum |
computers will have been built. |
4. |
passive + continuous infinitive |
d. |
The new program is currently being tested for bugs. |
|
5. |
present simple passive |
e. |
Sooner or later computers that can see will be invented. |
|
6. |
past simple passive |
f. |
Computers are believed to perform thousands of |
|
|
|
computations per second. |
||
98

7. |
present continuous passive |
g. |
Steven Jobs and Stephen Wozniak are known to have set |
|
|
|
|
|
up the Apple Company. |
8. |
past continuous passive |
h. |
If you want to use your PC for artwork or video, you can |
|
|
|
|
|
have a powerful graphics card added to it. |
9. |
present perfect passive |
i. |
Computers are said to be getting smaller and more |
|
|
|
|
|
powerful. |
10. past perfect passive |
j. |
Before the invention of computers various devices had |
||
|
|
|
|
been used to make calculations. |
11. future |
simple passive |
k. |
Various terminals are connected to this workstation. |
|
12. future |
perfect passive |
l. |
They ordered these devices to be repaired as soon as |
|
|
|
|
|
possible. |
13. passive infinitive |
m. When the computer crashed a new program was being |
|||
|
|
|
|
installed on it. |
2. Put the verbs in brackets into the correct passive form.
1. |
As computers count quickly, they widely (use) in business data processing. |
2. |
Vacuum tubes to control and amplify electric signals (create) by Neumann. |
3.This program (write) to help people in the use of the computer system.
4.All the current files (lose) when the system crashed and we had no backup copies.
5.A new brand of LCD screen cleaner currently (develop) by our company.
6. |
The new version of this software (release) next July. |
7. |
We searched the database but your transaction (not/record). |
8. |
A lot of techniques (believe) to be used in the design of printers. |
9.These machines (not/service) for a year.
10.If you need a lot of storage, you can a bigger hard disk (fit).
11.When keyed the data (hold) in a small memory called buffer.
12. |
Information (put) into the computer for processing should be coded into ones and zeroes. |
|
13. |
An impact printer (consider) to produce a character by impacting |
a font against the paper. |
14. |
Before the computer (switch) off yesterday, all the necessary files |
(copy) onto a laser disc. |
15. |
At the moment the system (check) for any unnecessary file that make it work slower. |
|
16. |
The power failure occurred while the antivirus (update) – so the update process (interrupt). |
|
17. |
In the next century, computers (program) in natural languages like English or French. |
|
18.The technician (expect) to be searching our database for any invalid data.
19.Many different storage technologies (invent) by men since ancient times.
99
SPEAKING/WRITING PRACTICE SECTION
1. Identify the storage devices in the pictures and tell about their main features.
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
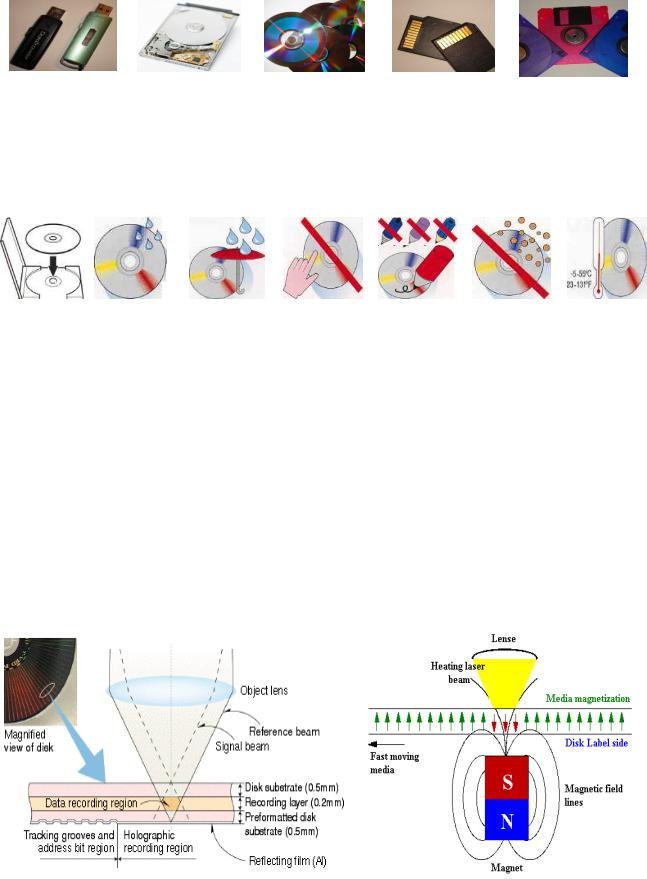
2. Make a list of things that you must or mustn‟t do to protect your data using the clues and pictures below. Add more recommendations to this list. Which of them do you personally follow?
1 |
2 |
3 |
10-90%
high temperatures
dust
special marker/pen
water and humidity
hold the disks around the edge
stack disks on top of each other
disks in a protective case
into the disk drive very carefully
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
near magnets; damage the information stored on
viruses before opening files you receive from the Web or via e-mail
update your anti-virus program regularly since new viruses are created everyday
back-ups (spare copies) of your data
passwords and security devices to protect confidential information
3. Describe the principles of magnetic and optical storage technologies using the diagrams below.
100
