
учебник 3 курс ICT
.pdf
6. Describe how a printer works using the pictures below.
7. Describe how a VDU (LCD, plasma, CRT) works using the pictures below.
Plasma technology
CRT
81

8. Summarise the information about output devices using the scheme below to help you.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IMPACT |
|
|
DOT-MATRIX |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PRINTER |
|
|
|
HARD |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
COPY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INK-JET PRINTER |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NON-IMPACT |
|
|
LASER PRINTER |
||||
COMPUTER |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PLOTTER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CRT/LCD |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
SOFT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
COPY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOICE |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FUN AND GAMES SECTION
1. Each of the sets of four words below can be linked by one other word. What are the missing words?
LASER |
|
BUFFER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INK-JET |
|
QUALITY |
|
DATA |
|
INTERFACE |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GRAPHICS |
|
DEVICE |
TOUCH |
|
SAVER |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TEXT |
|
CAPTURE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Word search
Find the terms and expressions hidden in the letters below; you can read across (any direction), down or up. The clues below will help you to find all the words.
1. The smallest single unit or point of a display whose colour or brightness can be displayed.
2.A device that prints your texts or graphics on paper.
3.A group of pins a printer uses to create precise dots.
4. |
A substance a printer sprays onto the paper to generate an image. |
5. |
A beam a printer uses to fix the ink to the paper. |
6. |
The output quality, the clarity of the image. |
7. |
A hard copy. |
8. |
The powder attracted to paper by an electrostatic charge and then fused on by a hot roller. |
9. |
A type of printer using ink & fine pens held in a carriage to draw detailed designs on paper. |
10. |
A visual unit of a computer (2 different words). |
82

11.An unsteady light that goes on and off quickly.
12.The part of a television or computer where the picture or information appears.
13.A type of television or computer screen that has special gas inside.
14.A small container that you put inside a printer to make it work.
15.The part of a television that produces the picture on the screen.
16.Liquid ……. displays are currently the most popular display device for computers.
17.……. rate is the number of times in a second that a display is illuminated.
18.A small round mark or spot.
19.A picture on the screen of a television, cinema, or computer.
20.The information produced by a computer.
|
A |
|
C |
|
Q |
|
|
A |
|
M |
|
S |
|
A |
|
L |
|
|
P |
|
V |
|
M |
|
|
M |
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
R |
|
E |
|
F |
|
|
R |
|
E |
|
S |
|
H |
|
F |
|
|
R |
|
P |
|
H |
|
|
A |
|
|
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
J |
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Y |
|
T |
|
U |
|
|
|
F |
|
|
Z |
|
D |
|
|
I |
|
R |
|
E |
|
|
T |
|
|
J |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Q |
|
W |
|
E |
|
|
N |
|
L |
|
B |
|
Q |
|
E |
|
|
N |
|
E |
|
G |
|
|
R |
|
|
P |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
F |
|
E |
|
G |
|
|
E |
|
I |
|
D |
|
W |
|
O |
|
|
T |
|
N |
|
A |
|
|
I |
|
|
R |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
O |
|
G |
|
R |
|
|
E |
|
K |
|
I |
|
N |
|
K |
|
|
O |
|
O |
|
M |
|
|
X |
|
I |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
D |
|
O |
|
|
R |
|
E |
|
S |
|
O |
|
L |
|
|
U |
|
T |
|
I |
|
|
O |
|
|
N |
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
P |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
A |
|
I |
|
T |
|
|
|
R |
|
|
U |
|
O |
|
|
T |
|
P |
|
D |
|
|
O |
|
|
T |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
T |
|
R |
|
I |
|
|
S |
|
Y |
|
L |
|
A |
|
S |
|
|
E |
|
R |
|
L |
|
|
K |
|
|
E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
X |
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
S |
|
T |
|
N |
|
|
|
Z |
|
|
P |
|
L |
|
|
O |
|
T |
|
T |
|
|
E |
|
|
R |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Y |
|
R |
|
O |
|
|
A |
|
D |
|
Y |
|
F |
|
R |
|
|
Y |
|
U |
|
G |
|
|
F |
|
|
T |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
R |
|
A |
|
M |
|
|
O |
|
U |
|
T |
|
P |
|
U |
|
|
T |
|
B |
|
V |
|
|
R |
|
|
T |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
C |
|
C |
|
T |
|
|
P |
|
I |
|
X |
|
E |
|
L |
|
|
V |
|
E |
|
G |
|
|
H |
|
|
Y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HUMOR SECTION
What does each of the cartoons imply? Why is it funny, in your opinion? Explain its humour.
Dangerous laser printers
83

DATA STORAGE |
KEY INFORMATION SECTION 1
Computer data storage, often called storage or memory, refers to computer components, devices, and recording media that retain digital data used for computing for some interval of time. It provides one of the core functions of the modern computer, that of information retention.
Hierarchy of storage
CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT |
PRIMARY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
REGISTERS |
STORAGE |
MAIN MEMORY |
LOGIC |
|
MEMORY BUS |
RAM |
UNIT |
CASHE |
|
|
|
|
||
|
MEMORY |
|
|
INPUT-OUTPUT
CHANNELS
SECONDARY STORAGE
MASS STORAGE DEVICE
HARD DISK
OFF-LINE STORAGE
REMOVABLE MEDIA DRIVE
REMOVABLE MEDIUM
(CD, DVD)
Memory usually refers to a form of semiconductor storage known as random access memory (RAM) and sometimes other forms of fast but temporary storage.
Storage more commonly refers to mass storage - optical discs, forms of magnetic storage like hard disks, and other types slower than RAM, but of a more permanent nature.
Primary storage is the only one directly accessible to the CPU which continuously reads instructions stored there and executes them as required. Any data actively operated on is also stored there in uniform manner. Primary storage is also called main storage or internal storage.
84

The specific functions of internal storage are to hold (store): all data to be processed; intermediate results of processing; final results of processing; all the instructions required for ongoing process. Another name for primary storage is memory, because of its similarity to a function of the human brain. But computer storage differs from human memory in important respects: it must be able to retain very large numbers of symbol combinations, without forgetting or changing any details and locate all its contents quickly upon demand.
Information in computer memory is stored in the form of coded characters. The codes are based upon a binary number system that has only two possible values, 0 and 1. Each binary digit is called a bit. As the information capacity of a single bit is limited to 2 alternatives, codes are based upon combinations of bits, called binary codes. A fixed number of consecutive bits that represent a character is called a byte. The most common byte size is 8-bit byte.
Secondary storage, or storage is not directly accessible by the CPU. The computer usually uses its input/output channels to access secondary storage and transfers the desired data using intermediate area in primary storage. Secondary storage does not lose the data when the device is powered down—it is non-volatile.
In modern computers, hard disks are usually used as secondary storage. A very significant accesstime difference distinguishes solid-state memory from rotating magnetic storage devices: hard disks are typically about a million times slower than memory. Some other examples of secondary storage technologies are: flash memory (e.g. USB sticks or keys), floppy disks, magnetic tape, paper tape, punch cards, standalone RAM disks, and Zip drives.
The secondary storage is often formatted according to a file system format to organize data into
files and directories, providing |
also additional information (called metadata) |
describing the owner |
of a certain file, the access time, |
the access permissions, and other information. |
|
Most computer operating systems use the concept of virtual memory, allowing utilization of more primary storage capacity than is physically available in the system. As the primary memory fills up, the system moves the least-used chunks (pages) to secondary storage devices (to a swap file or page file), retrieving them later when they are needed.
85

VOCABULARY PRACTICE SECTION 1
1. Match the terms with the definitions.
1. primary |
a. one of the performance |
characteristics of storage measured in binary digits; |
|
2. secondary |
b. memory that has random access to the information; |
||
3. binary codes |
c. combination of units of information; |
||
4. RAM |
d. area of memory where protected programs can be read from, not written on; |
||
5. bit |
e. a fixed number of consecutive bits representing a character; |
||
6. byte |
f. initializing; |
setting tracks and sectors on magnetic disks |
|
7. ROM |
g. additional |
information |
about a certain file |
8. capacity |
h. part of memory having |
lower speed but greater capacity; |
|
9. backing store |
i. a unit of information or binary digit; |
||
10. formatting |
j. the most expensive part of memory having the least capacity and the fastest |
||
|
access time. |
|
|
11. directory |
k. a catalogue |
of where each piece of data is stored and how to find it |
|
12. metadata |
l. secondary memory |
|
|
2. Complete the gaps with the words from the box.
primary permanent processing secondary CPU memories location data storage
Computers are used widely for storage of data. Like us, computers have 1….. too. There are two types of 2….. in a computer, primary and secondary.
3….. storage is where the computer holds 4….. that it is currently using. This place is also known as computer memory or temporary storage. For example, you tell your computer to store two numbers
after 5….. them. The computer will get these two numbers from specified location in its memory. After the ALU adds the two numbers, the result will be stored to another 6….. in the memory.
7….. storage is used to store 8….. data. For example, you are working on a word document and are planning to continue tomorrow. You cannot store the document in the primary storage because it is temporary. The document will be lost if you turn off the computer and so, it has to be saved in the secondary storage which is separated from the 9…..
86

KEY INFORMATION SECTION 2
Many different forms of storage have been invented. So far, no practical universal storage medium exists, and all forms of storage have some drawbacks. Therefore a computer system usually contains several kinds of storage, each with an individual purpose. The most commonly used storage technologies are semiconductor, magnetic, and optical.
The most important performance characteristics of a storage unit are:
Speed, measured in cycle time.
Capacity, measured by the number of machine words or binary digits.
Reliability, measured by the number of failures per unit of time.
Semiconductor memory uses semiconductor-based integrated circuits to store information. A semiconductor memory chip may contain millions of tiny transistors or capacitors. Both volatile and non-volatile forms of semiconductor memory exist. In modern computers, primary storage almost exclusively consists of dynamic volatile semiconductor memory or dynamic random access memory. Since the turn of the century, a type of non-volatile semiconductor memory known as flash memory has steadily gained share as off-line storage for home computers. Removable flash memory is solid-state, rewritable memory; it is non-volatile, so it retains data when the power is turned off. This explains its popularity in small devices.
Flash memory cards are found in cameras, PDAs and music players.
Flash drives, also known as thumb or pen drives, are connected to a USB port of the computer. They let you save and transfer data easily.
Magnetic storage uses different patterns of magnetization on a magnetically coated surface to store information. It is non-volatile. The information is accessed using one or more read/write heads which may contain one or more recording transducers. A disk drive spins the disk at high speed and reads its data or writes new data onto it. Magnetic storage takes these forms:
Floppy disk, used for off-line storage. A floppy disk drive uses 3.5 inch diskettes which can
only hold 1.44 MB of data; it's often called A: drive and is relatively slow.
Hard disk, used for secondary storage. Most PCs have one or two internal hard disks, usually called C: or D: drive, which can hold gigabytes of data. It's used to keep the operating system, the programs and the files easily available for use. When you format a disk, or prepare it for use, its surface is divided into concentric circles called tracks. Each track is further divided into
87
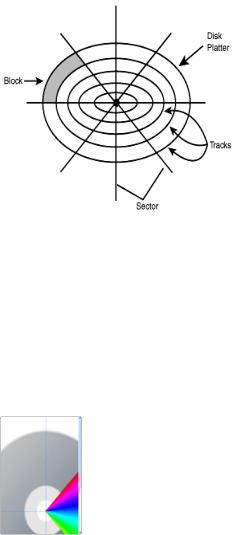
a number of sectors. The computer remembers where information is stored by noting the track and sector numbers in a directory.
A portable hard drive is an external unit with the drive mechanism and the media all in one sealed case. You can use it to make a backup, a spare copy of your files, or to transport data between computers.
Magnetic tape data storage, used for tertiary and off-line storage.
The average time required for the read/write heads to move and find data is called access time; it is measured in
milliseconds (ms). Don't confuse 'access time' with 'transfer rate', the rate of transmission of data from the disk to the CPU (e.g. 15 Mb per second).
VOCABULARY PRACTICE SECTION 2
1.Complete these sentences by choosing the correct phrase from the given options.
1.The average time it takes the read/write heads to move and find data on a disk is
|
called the seek time /transfer rate |
2. |
Access time/ Transfer rate is another way of saying seek time. |
3. |
Transfer rate /Seek time is the average speed required to transmit data to the |
|
CPU from the disk; it is measured in megabytes per second. |
4.Once formatted, a disk's surface is organized into circular tracks/ sectors. Each of these is then divided into tracks/ sectors.
5.When a disk is formatted, a directory/ partition is created by the operating system to record the location of files.
6.If you have more than one directory/ partition on your hard drive, you can install more than one operating system.
2.Choose a term from the box to complete the sentences below.
|
|
hard disk access time |
magnetic |
storage |
floppy disk drive |
|
|
transfer rate portable hard drive |
backup |
sectors tracks |
|
|
|
|
|||
1. |
The first rule of data storage is to make a ……. of all important files. |
||||
2. |
A ……. is slower than a hard drive and can only hold 1.44 MB disks. |
||||
88

3. |
The ……. inside your PC is made of aluminium alloy covered with a magnetic coating. This |
||
|
makes the disk itself |
a rigid plate, hence its name. |
|
4. |
The ……. are circles |
around a disk and the ……. are segments |
within each circle. |
5. |
This hard drive is a 60 GB IBM model with a fast ……. of 8 ms. |
||
6. |
The ……. is the rate of transmission of data from the disk to the CPU. |
||
7. |
This is usually described in megabytes per second. |
|
|
8. |
Apple's iPod music player can double as a ……. for transporting |
computer data. |
|
3. Complete this conversation in a computer shop using words or phrases from the box.
|
storage |
head crash |
holds |
read/write |
back up hard |
||
|
portable |
platters |
external |
capacity |
formatted |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Sales assistant: Can I help you with anything? |
|
|
|
||||
Anna: - Yes, please. I need a new (1) ……. drive. |
|
|
|
||||
SA: - OK. Are you looking |
for an internal |
drive or an (2) …. one? |
|
||||
Anna: - Well, I need it for moving |
files between home and work. |
|
|||||
SA: - Sure. Well, you've basically |
got two options. If you need a |
|
|||||
lot of (3) ……. for secondary (4) ……. , then you could try this Freecom drive. It (5) ……. 750GB. That's probably enough to (6) ……. your whole computer many times оvеr. You'd probably have lots of space left for archiving any files that you don't need on a day-to-day basis. This one's £140.
Anna: - That's a little expensive, to be honest. And I probably don't need 750GB. My home computer only has a 120GB drive! And it looks a bit heavy to carry around.
SA: - In that case, you need something more (7) ……..This might be what you're looking for: the ATMTHD160 Ultra-Portable. It's only 20GB, but it's light and relatively cheap - only £80.
Anna: - That sounds perfect. I'll take it. Is it already (8) …….?
SA: - Yes, it's all ready to use. Just bear a couple of things in mind if you're carrying it between home and work a lot. Inside the drive there is a stack of metal (9) ……. that are used to store the
information. Don‘t move the disk while the platters are spinning - you'll be able to hear them - |
or |
|
the drive could suffer |
a (10) …. That's when the (11) …. head touches the disk surface. |
|
Anna: - Right, OK. Anything else I need to know? |
|
|
SA: - Just a couple |
of things. You shouldn't unplug the drive without using the 'Remove hardware' |
|
command first. And |
you should check the drive regularly for viruses, especially if you're moving |
it |
between machines. |
|
|
Anna: - OK, well thanks for all your help. Now where do I go to pay?
89

4. Complete these technical specs from an MP4 player by choosing the correct words from the given options. Use a dictionary if necessary.
1.1GB of solid-state flash memory storable/store/storage.
2.1.5"true coloured/colour/colourful LCD display.
3.Screen unprotected/protector/protect for avoiding scratches.
4.View digitized/digital/digit photos as well as videos.
5. Decoding/decodes/decoder video AMV files as well as audio AAС files.
6.Supportive/unsupported/supports multi music format: MP1, MP2, MP3, WMA, WMV, ASF and WAV.
7. Includes |
digital |
voice |
recording/recorder/record |
with |
up |
to |
36 |
hours |
recorder/recording/record time. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
8.Building/built-in/builts FM radio.
9.Offload/upload/download files direct from the Internet.
10.Standby modular/mode/modal for power saving.
5. Complete the sentences with the right word from the group.
magnet |
magnetic |
magnetically magnetism |
magnetize |
magnetized |
1. ……. is the science of magnetic phenomena and properties.
2.Floppy and hard disks are considered as ……. storage devices.
3.Data is recorded on a disk in the form of …… spots called bits.
90
