- •Kidney:
- •Kidney functions
- •Nephron - functional unit of the kidney
- •Electronic microscopy: glomerular capillary loops
- •Scheme of glomerulus structur
- •Investigation methods of kidneys and urinary tract
- •Complains
- •Anamnesis
- •Anamnesis
- •Laboratory methods
- •Laboratory methods
- •Proteinuria
- •erythrocytes in 1 ml
- •Haematuria
- •Haematuria
- •CAUSES OF RED OR DARK URINE
- •Dysmorphic erythrocytes on electronic microscopy (A – normal erythrocyte)
- •Leucocyturia - more then 2000 cells in 1 ml
- •Crystalluria
- •Measurement of the glomerular filtration rate
- •Markers of renal functional state
- •Calculation of GFR with Cokroft- Gault formula
- •MDRD formula
- •Image investigations of kidney and urinary tract
- •Эхоангиография правой почки
- •Пиелоуретероэктазии справа (экскреторная урография)
- •Аплазия правой почки (КТ)
- •Нефрокальциноз
- •Опухоль почки (ангиография)
- •Проходимость артерии восстановлена после стентирования
- •Scintigraphy of female patient of
- •Female patient of 67
- •RENAL BIOPSY
- •Normal glomerulus
- •Electronic microscopy
- •Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis: immunofluorecent staining of deposits
- •Creschendic nephritis with “demilunes” of proliferating cells with rapture of Bowman capsule
- •Creschendic nephritis: immunofluorecent staining shows the lineal deposition of antibodies to basal membrane
- •RENAL SYNDROMS
- •Urinary syndrome
- •Nephritic syndrome
- •Clinical case 1
- •Nephrotic syndrome
- •Edema (nephrotic syndrome)
- •COMMOM CAUSES OF NEPHROTIC SYNDROME
- •CONSEQUENCES AND COMPLICATIONS
- •Hypertensive syndrome
- •Hypertensive syndrome
- •Tubular abnormalitis
- •Incidence of AKI*
- •Staging of AKI
- •Conceptual model for AKI
- •Causes of AKI and diagnostic tests
- •Exposure and susceptibility risk factors for non-specific AKI
- •Classification of AKI
- •Intrinsic Renal Damage
- •Post-renal
- •Natural history of AKI
- •Principles of AKI
- •Management of AKI
- •Chronic renal failure
- •Causes of chronic renal failure
- •Signs of chronic renal failure
- •Mechanisms of progression
- •REVERSIBLE FACTORS IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE
- •Markers of activity of renal disease

Tubular abnormalitis
Etiology : kidney congenital diseases, pyelonephritis, interstitial nephritis, autoimmune diseases, tumors.
•Polyuria
•Nocturia
•< of urine density
•Nephrogenic osteopathy
•Electrolytes disorders
•Glucosuria
•Acidosis
•Normal GFR



Incidence of AKI*
•500 ppm/year – UK ( up to 38,000/yr)
•Incidence of AKI needing dialysis 200 ppm/year
•Pre renal and acute tubular necrosis (ATN) accounts for 75% of the cases of AKI
•7% of all hospital admissions( 65% of intensive care admission)
•Mortality:
•5-10% in uncomplicated AKI
•50-70% in AKI secondary to other organ failure( intensive care)
•> 50% in dialysis requiring AKI
*Xue JL, Daniels F, Star RA et al. Incidence and mortality of acute renal failure in Medicare beneficiaries, 1992 to 2001. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006; 17: 1135–1142.

Staging of AKI
The cause of AKI should be determined whenever possible

Conceptual model for AKI
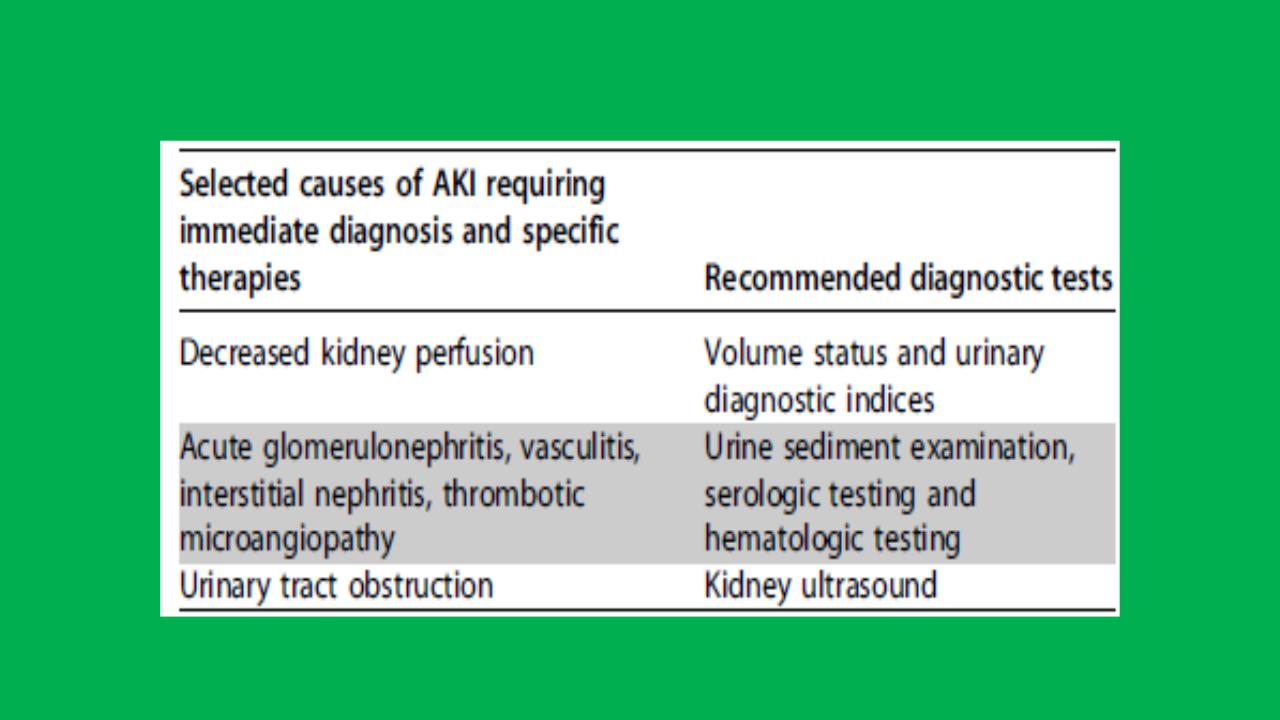
Causes of AKI and diagnostic tests

Exposure and susceptibility risk factors for non-specific AKI

Classification of AKI
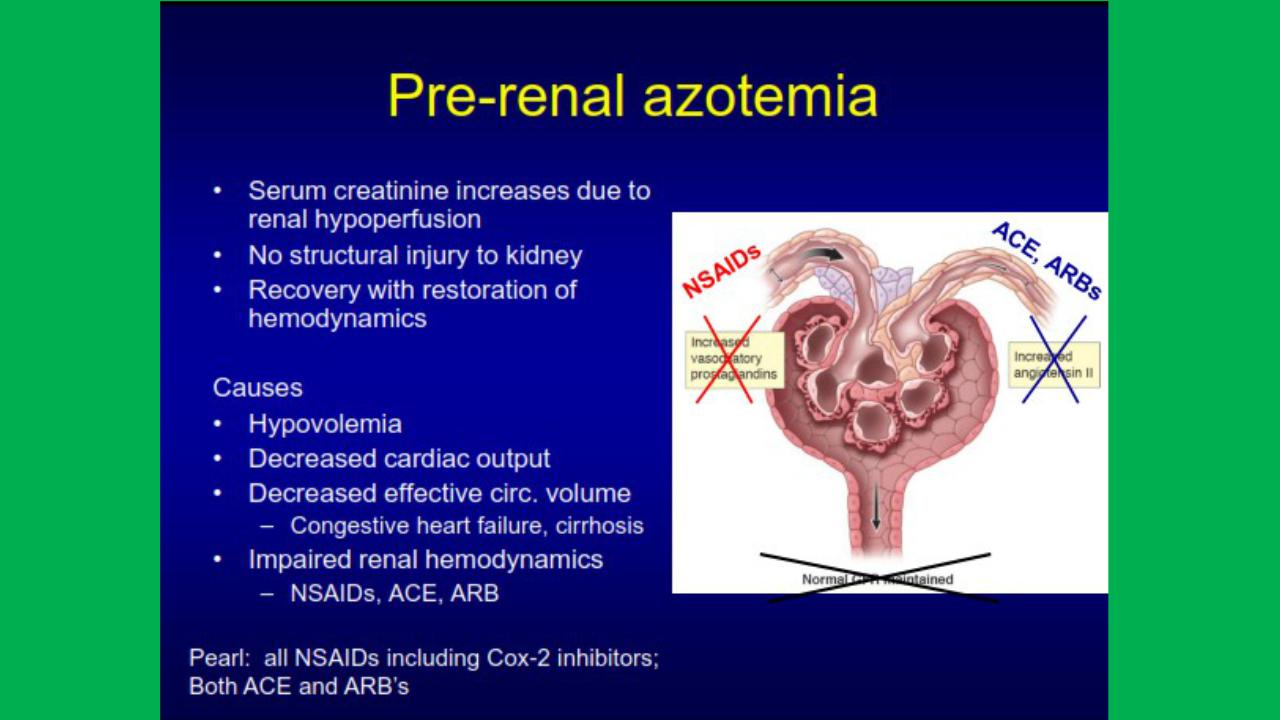
•Pre-renal
•Intrisic renal damage
•Post-renal
•Anuric
•< 50 cc / 24 hrs
•Oliguric
•< 500 cc / 24 hrs
•Non-olguric
•Normal urine output, but inadequate clearance
•GFR 2 ml/min will produce ~3L of urine/day if there is no tubular reabsorption