- •Endocrine disorders
- •Syndromes in endocrinology
- •Feedback control of target endocrine organs
- •Thyroid gland: anatomy
- •Palpation of the thyroid gland
- •Goiter
- •Classification of goiter
- •Laboratory evaluation in thyroid gland diseases
- •Relation between target hormone level and trophic hormones level in normal and disease
- •Imaging of the thyroid gland
- •Scintigraphy of thyroid gland
- •Syndrome of hyperthyroidism
- •Thyrotoxicosis
- •Causes of thyrotoxicosis
- •Causes of primary thyrotoxicosis
- •Proptosis (exophthalmos)
- •Palmar erythema
- •Plummer’s nails (onychomycosis and onycholysis) in thyrotoxicosis
- •Pretibial myxedema
- •Thyroid acropathy
- •Difference in thyrotoxicosis presentation
- •Diagnostic evaluation in thyrotoxicosis
- •Autoantibody tests for hyperthyroidism
- •Scintigraphy in thyrotoxicosis
- •Grave`s disease
- •Clinical presentation of Grave`s disease
- •Goiter in Grave`s disease
- •Grave`s ophtalmopathy
- •Presentation of Grave`s ophtalmopathy
- •Periorbital edema
- •Eye symptoms in Graves disease
- •Treatment of thyrotoxicosis
- •Hypothyroidism
- •Hypothyroidism
- •Clinical presentation of hypothyroidism
- •Signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism
- •Myxedema
- •Rheumatologic:
- •Laboratory findings
- •Treatment
- •Syndrome of hypercorticism (Cushing`s syndrome)
- •Иценко Николай Михайлович
- •Clinical presentation of Cushing`s syndrome
- •Steps of laboratory evaluation
- •Imaging. Pituitary gland
- •Imaging. Adrenal glands
- •Adrenal adenocarcinoma with metastases in the liver
- •Treatment
- •Adrenal insufficiency
- •Signs and symptoms of adrenal insufficiency
- •Diagnostic evaluation
- •Treatment of chronic adrenal insufficiency
- •Acute adrenal insufficiency (adrenal crisis)
- •Clinical presentation of acute adrenal crisis
- •Treatment of adrenal crisis

Pretibial myxedema

Thyroid acropathy
Difference in thyrotoxicosis presentation
•Younger patients tend to exhibit symptoms of sympathetic activation (eg, anxiety, hyperactivity, tremor)
•Older patients have more cardiovascular symptoms (eg, dyspnea, atrial fibrillation) and unexplained weight loss
•Patients with Graves disease often have more marked symptoms than patients with thyrotoxicosis from other causes
•Ophthalmopathy (eg, periorbital edema, diplopia, or proptosis) suggests Graves disease
Diagnostic evaluation in thyrotoxicosis
Laboratory tests
•Low TSH
•High T3 and T4
•Patients with milder thyrotoxicosis may have elevation of T3 levels only
•Subclinical hyperthyroidism presents with decreased TSH and normal T3 and T4levels
•Anemia, elevated ESR
•Low TC and TG
•High ALT, AST, AP
•Hyperglycemia
Instrumental methods
•Thyroid ultrasound:
–Diffuse enlargement
–Increased blood flow
–Nodules
•Scintigraphy
–Diffuse uptake increase
–Hot nodules
•Aspiration biopsy
Autoantibody tests for hyperthyroidism
•Anti–thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) antibody - Nonspecific elevation with autoimmune thyroid disease found in 8% of Graves patients
•Thyroid-stimulating antibody (TSab) - Also known as thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI), long-acting thyroid stimulator (LATS), or TSH-receptor antibody (TRab); found in 63-81% of Graves disease; a positive test is diagnostic and specific for Graves disease
Autoantibody titers in hyperthyroidism
•Graves disease - Significantly elevated anti-TPO, elevated TSab
•Toxic multinodular goiter - Low or absent anti-TPO and TSab
•Toxic adenoma - Low or absent anti-TPO and TSab
•Patients without active thyroid disease may have mildly positive anti-TPO and TSab
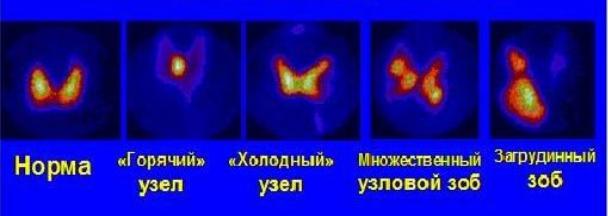
Scintigraphy in thyrotoxicosis
The degree and pattern of isotope uptake indicates the type of thyroid disorder
•Graves disease – Diffuse enlargement of both thyroid lobes, with uniform uptake of isotope and elevated radioactive iodine uptake
•Toxic multinodular goiter -- Irregular areas of relatively diminished and occasionally increased uptake; overall radioactive iodine uptake is mildly to moderately increased
•Subacute thyroiditis –Very low radioactive iodine uptake
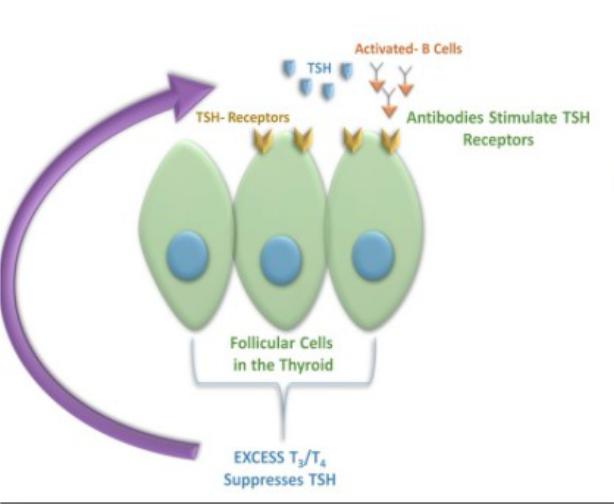
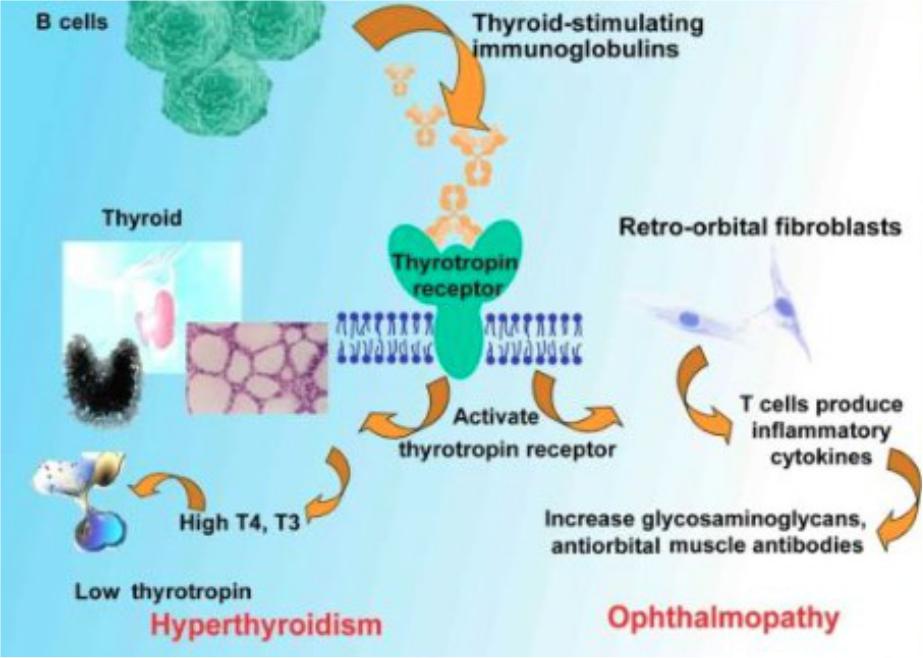
Grave`s disease
•The most common cause of endogenous hyperthyroidism
•Prevalence 1%
•Peak incidence in women 20-40 years old
•Etiology:
•Autoimmune
•Associated with other autoimmune diseases
•Stimulating immunoglobulins
•Hereditary
•Infections
•Trauma
Clinical presentation of Grave`s disease
•Thyrotoxicosis
•Diffuse goiter
•Ophtalmopathy
•Dermopathy
•Lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, enlargement of the thymus
•High incidence of other autoimmune diseases

Goiter in Grave`s disease