
2247
.pdf
The last three years of Leonardo’s life were spent in Cloux (now ClosLucé), near the king's summer palace at Amboise on the Loire. Leonardo spent most of his time working on scientific manuscripts and studying anatomy. In a final work, Visions of the End of the World, or Deluge, he depicts the primal forces that rule nature with a growing pessimism. Leonardo died at Cloux and was buried in the church of Saint-Florentin
Leonardo da Vinci had an unlimited desire for knowledge, and visual perception was the main tool he used in pursuit of that knowledge. Leonardo believed that only the faculty of sight allowed you to take in experience immediately, correctly, and with certainty.
Seeing was paramount for Leonardo, which is why he excelled in the visual arts. But his penetrating vision was used to further many other branches of knowledge, including anatomy and engineering. He had over 100 drawings that illustrated his theories on flight. The ornithopter flying machine was never actually created. It was a design that Leonardo DaVinci made to illustrate how man could fly. Some experts feel that the modern day helicopter was inspired by DaVinci's concept.
Design for a flying machine
211
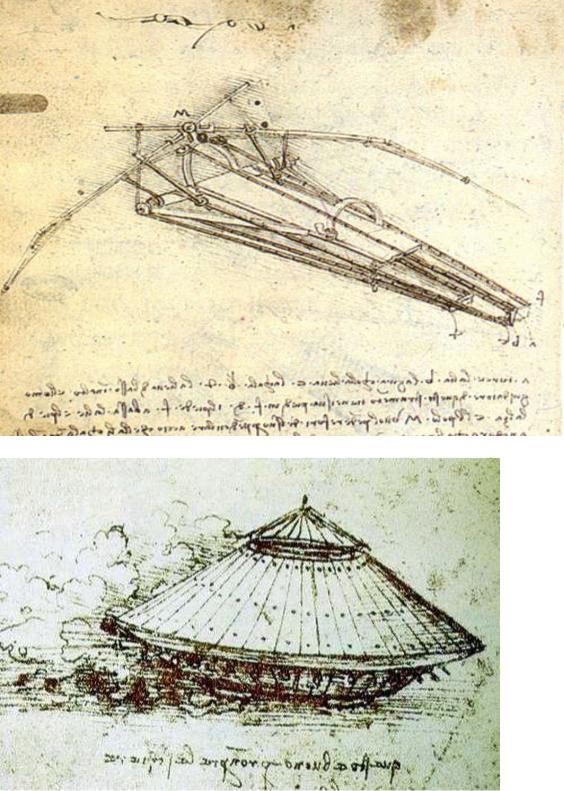
Design for a flying machine drawn by Leonardo Da Vinci in 1488
Armoured Car drawn by Leonardo Da Vinci in 1488
5.Find in the text
A)Supporting factual data
B)Analytical findings
212
C)Solutions ( or conclusion)
D)Recommendations or predictions
6.Find the terms which are in need to be explained. Explain it.
7.Changing the aim should we change the style of the report?
8.Changing the audience should we change the style of the report?
9.Does your aim demand changing of the style? What about audience?
10.What kind of visual illustration does your report need?
11.What kind of presentation do you prefer?
12.What kind of presentation does your report need? 13. Type of presentation. What does it depend on?
Speaking
1.Look through the text. Compare it with the report devoted to Leonardo Da Vinci. Find common and distinguishing features in its
a)Titles
b)Themes
c)Ideas
d)Structures (composition)
e)The scope of the report
f)Primary, secondary and immediate audience
g)Style of the report
2.What text have you found more
a)Informative
b)Illustrative
c)Emotional
d)Complete
e)Creative and why? Prove your answer.
213

Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton was born in 1642 in a manor house in Lincolnshire, England. His father had died two months before his birth. When Isaac was three his mother remarried, and Isaac remained with his grandmother. He was not interested in the family farm, so he was sent to Cambridge University to study.
Isaac was born just a short time after the death of Galileo, one of the greatest scientists of all time. Galileo had proved that the planets revolve around the sun, not the earth as people thought at the time. Isaac Newton was very interested in the discoveries of Galileo and others. Isaac thought the universe worked like a machine and that a few simple laws governed it. Like Galileo, he realized that mathematics was the way to explain and prove those laws. Isaac Newton was one of the world’s great scientists because he took his ideas, and the ideas of earlier scientists, and combined them into a unified picture of how the universe works.
Isaac Newton explained the workings of the universe through mathematics. He formulated laws of motion and gravitation. These laws are math formulas that explain how objects move when a force acts on them. Isaac published his most famous book, Principia, in 1687 while he was a mathematics professor at Trinity College, Cambridge. In the Principia, Isaac explained three basic laws that govern the way objects move. He then described his idea, or theory, about gravity. Gravity is the force that causes things to fall down. If a pencil falls off a desk, it will land on the floor, not the ceiling. In his book Isaac also used his laws to show that the planets revolve around the suns in orbits that are oval, not round.
Isaac Newton used three laws to explain the way objects move. They are often call Newton’s Laws. The First Law states that an object that is not being pushed or pulled by some force will stay still, or will keep moving in a straight line at a steady speed. It is easy to understand that a bike will not move unless something pushes or pulls it. It is harder to understand that an object will continue to move without help. Think of the bike again. If someone is riding a bike and jumps off before the bike is stopped what happens? The bike continues on until it falls over. The tendency of an object to remain still, or keep moving in a straight line at a steady speed is called inertia.
214
The Second Law explains how a force acts on an object. An object accelerates in the direction the force is moving it. If someone gets on a bike and pushes the pedals forward the bike will begin to move. If someone gives the bike a push from behind, the bike will speed up. If the rider pushes back on the pedals the bike will slow down. If the rider turns the handlebars, the bike will change direction.
The Third Law states that if an object is pushed or pulled, it will push or pull equally in the opposite direction. If someone lifts a heavy box, they use force to push it up. The box is heavy because it is producing an equal force downward on the lifter’s arms. The weight is transferred through the lifter’s legs to the floor. The floor presses upward with an equal force. If the floor pushed back with less force, the person lifting the box would fall through the floor. If it pushed back with more force the lifter would fly into the air.
When most people think of Isaac Newton, they think of him sitting under an apple tree observing an apple fall to the ground. When he saw the apple fall, Newton began to think about a specific kind of motion—gravity. Newton understood that gravity was the force of attraction between two objects. He also understood that an object with more matter –mass- exerted the greater force, or pulled smaller object toward it. That meant that the large mass of the earth pulled objects toward it. That is why the apple fell down instead of up, and why people don’t float in the air.
Isaac Newton thought about gravity and the apple. He thought that maybe gravity was not just limited to the earth and the objects on it. What if gravity extended to the moon and beyond? Isaac calculated the force needed to keep the moon moving around the earth. Then he compared it with the force the made the apple fall downward. After allowing for the fact that the moon is much farther from the earth, and has a much greater mass, he discovered that the forces were the same. The moon in held in an orbit around earth by the pull of earth’s gravity.
Isaac Newton’s calculations changed the way people understood the universe. No one had been able to explain why the planets stayed in their orbits. What held them up? Less than 50 years before Isaac Newton was born it was thought that the planets were held in place by an invisible shield. Isaac proved that they were held in place by the sun’s gravity. He also showed that the force of gravity was affected by distance and by mass. He was not the first to understand that the orbit of a planet was not circular, but more elongated, like an oval. What he did was to explain how it worked.
3. Give a summary of this text using these word structures:
the text is about... ; the text deals with the problem...; the main problem of the text is...; I know that...; it is a well-known fact...; it is worth mentioning...; as for
215
the problem of...; it should be noted that... .
Discussing
1. Fill in the table. Add the lines if it is in need.
№ |
NAME |
SPHERE |
ACHIEVEMENTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.Discuss the role of each scientist in the
a)World’s history
b)In art’s history
c)History of science
d)In the history of automobile construction.
Language practice
1.Examine the phrases and try to translate it. A) Put someone on
B) Put someone up C) Put something away
D) Put the bite on someone E) Put the finger on someone
2.Match these phrases with the definitions given below
1)eat or drink something
2)fool, tease someone
3)identify someone
4)try to get money from someone
5)provide accommodation
3.Fill in the gaps in the sentences
216
Could you … me .. for the night?
We … …. six beers.
I don't believe anything you say. You're ……. me ...!
We … them … last week as they couldn't find a hotel.
The victim … the finger .. the criminal.
She … the bite .. me for $50.
He …the whole pizza …. in fifteen minutes!
5. Match the words in two columns
enforce |
a car or vehicle |
|
|
drive a car |
a lay |
|
|
exit |
defensively |
|
|
hit |
a road |
|
|
injure |
a law |
|
|
merge |
a person |
|
|
obtain |
a vehicle or car |
|
|
follow |
onto a road |
|
|
insure |
a permit or license |
|
|
obey |
an object |
|
|
Writing
217
1.Using phrases and word structures from section “Language practice” describe a situation which could happen with Leonardo Da Vinci or Isaac Newton.
2.Write down your report connected with one of the automobile inventors.
3.In written form describe your report (the theme, the idea of it (the aim), the scope of the report, primary, secondary and immediate audience, style of the report).
Unit 3.
Section A. Gather and organize the supporting information
Theory
Now that the report’s author has a clear understanding of the purpose and scope of the business report and who the target audience is, he is now ready to gather and organize the research and data collection. Business research and analysis provide information to facilitate operational planning, production planning, supply chain management, quality systems and investment strategy development. The research issues that are most decisive in this area include customer activity and behavior, market and economic conditions, competitive considerations and business strategies in response to the market place.
Market research always involves some from data collection. This can occur from a primary data level, whereby the researcher collects data first hand from customers, or from secondary data through investigative research. Primary research data refers to data obtained from the original source regardless of whether that data was gathered in a laboratory or out in the field. Secondary research data is considered the type that would present information that is obtained largely from historical information sources or data which has been gathered from other studies or business process. Unlike academic research, which is more conceptual, business market research is highly purposeful in providing reliable and valid data on consumer behavior in a specific product category or area within a specific target market.
To enable a business report audience to make business decisions based on research data, it is important to explain the procedures or methods that were used in the research process. This supports the data’s credibility and in turn allows the decision makes to weight the significance of the market information. The data that is collected is critical to any primary business market research
218
findings. It is important to present the data in various tables, charts and graphs to facilitate effective communication with intended readers. This findings, or extract of the business market data, can go directly into the Body of your business feasibility study or business plan, or included as appendices.
As you are gathering information it is critical to generate a methodology on how to record and organize (quality control) the information. Immense volumes of information are difficult to analyze if they are not organized.
Questions:
1.What is the aim of the included information in business report?
2.What are the ways of data collection?
3.What is the difference between Primary and Secondary data?
4.What should be taken into consideration in gathering information?
5.What demands should the data correspond to?
6.How can we use business report’s findings?
Section B. Car Manufacturing
Reading
1.Read the text and find two ways of presentation.
2.Find common and distinguishing features in organization of supporting information.
3.What is the aim of each type of presentation?
4.What kind of visual illustration can be used for each of them?
5.How does the organization of supporting information depend on the target audience? Prove your answers with the examples.
6.Write down the introduction and conclusion to this text in accordance with your target audience.
HISTORY OF THE CAR MANUFACTURING
Ferdinand Verbiest, a member of a Jesuit mission in China, built the first steam-powered vehicle around 1672 which was of small scale and designed as a toy for the Chinese Emperor that was unable to carry a driver or a passenger, but quite possibly, was the first working steam-powered vehicle ('auto-mobile').
Although Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot is often credited with building the first self-propelled mechanical vehicle or automobile in about 1769 by adapting an existing horse-drawn vehicle, this claim is disputed by some, who doubt Cugnot's three-wheeler ever ran or was stable. What is not in doubt is that
219
Richard Trevithick built and demonstrated his Puffing Devil road locomotive in 1801, believed by many to be the first demonstration of a steam-powered road vehicle although it was unable to maintain sufficient steam pressure for long periods, and would have been of little practical use.
In Russia, in the 1780s, Ivan Kulibin developed a human-pedalled, threewheeled carriage with modern features such as a flywheel, brake, gear box, and bearings; however, it was not developed further.
François Isaac de Rivaz, a Swiss inventor, designed the first internal combustion engine, in 1806, which was fueled by a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen and used it to develop the world's first vehicle, albeit rudimentary, to be powered by such an engine. The design was not very successful, as was the case with others such as Samuel Brown, Samuel Morey, and Etienne Lenoir with his hippomobile, who each produced vehicles (usually adapted carriages or carts) powered by clumsy internal combustion engines.
In November 1881 French inventor Gustave Trouvé demonstrated a working three-wheeled automobile that was powered by electricity. This was at the International Exhibition of Electricity in Paris. Although several other German engineers (including Gottlieb Daimler, Wilhelm Maybach, and Siegfried Marcus) were working on the problem at about the same time, Karl Benz generally is acknowledged as the inventor of the modern automobile.
An automobile powered by his own four-stroke cycle gasoline engine was built in Mannheim, Germany by Karl Benz in 1885 and granted a patent in January of the following year under the auspices of his major company, Benz & Cie., which was founded in 1883. It was an integral design, without the adaptation of other existing components and including several new technological elements to create a new concept. This is what made it worthy of a patent. He began to sell his production vehicles in 1888.
220
