
- •Liver
- •Liver and detoxification
- •The first way of intoxication
- •The second way of intoxication
- •Liver and carbohydrate metabolism
- •Liver and protein metabolism
- •Liver and fat metabolism
- •Liver and blood coagulation
- •Liver and hormone inactivation
- •Liver and Vitamins
- •Depot and excretory role of a liver
- •Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
- •Cellular Defense Against ROS
- •Thymol test
- •Quantitative determination of serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity
- •Role of kidneys in water-salt metabolism
- •Regulation of sodium excretion. Renin
- •Regulation of sodium excretion. Renin
- •Antinatriuretic system
- •Natriuretic system
- •Urine
- •Physico-chemical properties of urine
- •Proteinuria
- •Functional proteinuria
- •Organic proteinuria
- •Prerenal proteinuria
- •Renal proteinuria
- •Postrenal proteinuria
- •False proteinuria
- •Qualitative determination of protein in urine
- •Glucosuria
- •Causes of Glycosuria
- •Extrainsular glucosuria
- •Hepatic and renal glucosuria
- •Primary and secondary glucosuria
- •Insular glucosuria
- •Clinical diagnostic value
- •Fructosuria
- •Ketonuria
- •Detection of ketone bodies in urine
- •Bilirubinuria
- •Qualitative detection of bile pigments in urine
- •Saliva
- •Chemical composition of saliva
- •Saliva proteins
- •Biological role of saliva
- •Mucins
- •Lysozyme
- •Saliva Whey Proteins
- •Ferrous enzymes
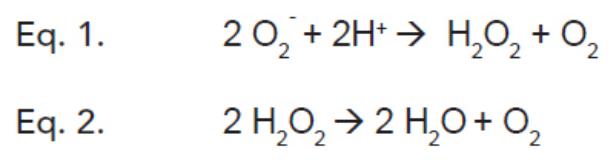
Cellular Defense Against ROS
•Superoxide dismutase (SOD) catalyzes the conversion of two superoxide anions into a molecule of hydrogen peroxide (H O ) and oxygen (O ) (Eq. 1).
•In the peroxisomes of eukaryotic cells, the enzyme catalase converts H O to water and oxygen, and thus completes the detoxification initiated by SOD (Eq. 2).
•Glutathione peroxidase is a group of enzymes containing selenium, which also catalyze the degradation of hydrogen peroxide, as well as organic peroxides to alcohols.

Thymol test |
Let’s write! |
|
The thymol test is a test that allows you to diagnose "inflammation syndrome" that accompanies many lesions of the hepatic parenchyma. The principle of the method is based on the ability of serum globulins to precipitate at pH 7.55 with a thymol reagent and cause clouding of the reaction mixture, the intensity of which depends on the stability of globulin proteins.
•Normally, a thymol sample is 0-5 units of turbidity, which is considered a negative thymol sample.
•The test in 90-100% of cases is positive for toxic, infectious, viral hepatitis, moreover, in the preicteric stage and in anicteric forms of the course of the disease. The more severe the liver damage, the higher the turbidity in a thymol sample.
•A positive thymol test is due to a quantitative change in the ratio of globulin fractions of plasma proteins or a decrease in the number of albumin. At the same time, due to liver damage, the colloidal stability of all types of plasma proteins also changes.

Quantitative determination of serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity
The principle of the method is based on the ability of the enzyme to hydrolyze p- nitrophenyl phosphate ether with the release of p-nitrophenol, which gives a yellow color in an alkaline medium, the intensity of which is proportional to the activity of the enzyme.
•Normally, alkaline phosphatase activity ranges from 100-120 units/L/min in adults.
•A sharp increase in activity occurs with cholestasis, cirrhosis, obstructive jaundice, primary and metastasized liver tumors, viral hepatitis, tuberculosis, and lymphogranulomatosis.
•The second group of diseases that cause an increase in enzyme activity is bone damage: rickets, decay of bone tissue, osteosarcoma, as well as with metastases of tumors in bone tissue.

Role of kidneys in water-salt metabolism |
Let’s write! |
In the kidneys, filtration, reabsorption, secretion of sodium, potassium occurs. Aldosterone, an antidiuretic hormone, has a regulatory effect on the kidneys. In the kidneys, renin is produced – the starting enzyme of the angiotensin system. The kidneys secrete protons, and thereby regulate the pH.
The main circuit with which the rest are connected is the content of Na in the body. Indeed, sodium ion, holding water molecules, determines the volume and osmolarity of the fluids of the internal environment and provides a number of vital functions.
