
- •Liver
- •Liver and detoxification
- •The first way of intoxication
- •The second way of intoxication
- •Liver and carbohydrate metabolism
- •Liver and protein metabolism
- •Liver and fat metabolism
- •Liver and blood coagulation
- •Liver and hormone inactivation
- •Liver and Vitamins
- •Depot and excretory role of a liver
- •Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
- •Cellular Defense Against ROS
- •Thymol test
- •Quantitative determination of serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity
- •Role of kidneys in water-salt metabolism
- •Regulation of sodium excretion. Renin
- •Regulation of sodium excretion. Renin
- •Antinatriuretic system
- •Natriuretic system
- •Urine
- •Physico-chemical properties of urine
- •Proteinuria
- •Functional proteinuria
- •Organic proteinuria
- •Prerenal proteinuria
- •Renal proteinuria
- •Postrenal proteinuria
- •False proteinuria
- •Qualitative determination of protein in urine
- •Glucosuria
- •Causes of Glycosuria
- •Extrainsular glucosuria
- •Hepatic and renal glucosuria
- •Primary and secondary glucosuria
- •Insular glucosuria
- •Clinical diagnostic value
- •Fructosuria
- •Ketonuria
- •Detection of ketone bodies in urine
- •Bilirubinuria
- •Qualitative detection of bile pigments in urine
- •Saliva
- •Chemical composition of saliva
- •Saliva proteins
- •Biological role of saliva
- •Mucins
- •Lysozyme
- •Saliva Whey Proteins
- •Ferrous enzymes
Saliva proteins
Let’s write!
Proteins of saliva are represented by: enzymes, albumin, immunoglobulins (A, M), glycoproteins. In saliva there are special proteins that induce the deposition of potassium salts on the teeth; calcium binding protein and a protein with high affinity for hydroxyapatite. These proteins contribute to the formation of plaque and tartar.
Biological role of saliva
1.Wetting food and making swallowing easier.
2.Dissolution of food components, which ensures their effect on digestive analyzers.
3.The initial chemical processing of carbohydrates by amylase.
4.Chemical protection of the oral cavity from the toxic effects of microbes (due to lysozyme).
5.Mechanical protection of the oral cavity (mucins, liquid part).
6.Bilateral transport of substances between the oral mucosa, teeth and saliva.
7.Saliva is the main source of Ca, P, and other minerals entering the tooth enamel.
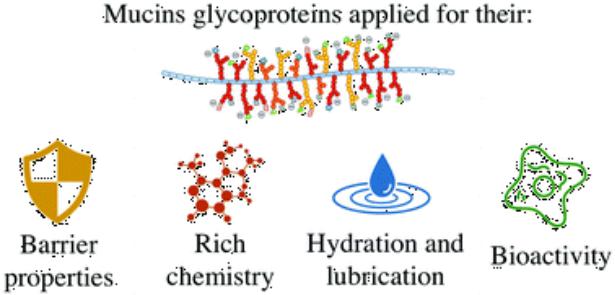
Mucins
•This is a large group of proteins, glycoproteins, many of which are membrane proteins, but their highly dominant region can be cleaved, becoming a component of the mucus proper.
•Enveloping the epithelial integument, mucins protect them from dehydration, from bacteria sticking, and also serve as a good lubricant when swallowing.
•Due to the peculiarities of its structure, mucins complicate the bacterial colonization of the oral cavity and tooth enamel. Composing a physical barrier on the path of macromolecules and microorganisms, mucins at the same time easily pass water, ions and low molecular weight substances.
•The mucin protein network is resistant to proteolytic enzymes due to the protective effect of carbohydrates.

Lysozyme
The protein composition of the pure secrets of various salivary glands is significantly different from each other. The parotid salivary gland produces secretory immunoglobulin, as well as the lysozyme enzyme, which has an antibacterial effect. It is associated with the ability of lysozyme to hydrolyze glycosidic bonds of glycosaminoglycans and glycoproteins of the cell membranes of certain types of bacteria.
