
Angliyskiy
.pdf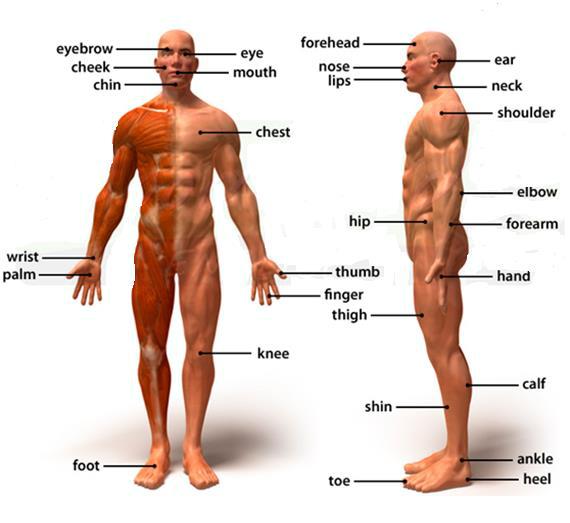
External parts of the Body
4. Read the text and complete it with the words.
body |
experience |
step |
canvas |
functions |
Knowing your body is the first (1) ___ in tackling any illness or disease. The more we know about our (2) ___, the more we can understand how our body (3) ___ and how diseases and illnesses interfere with natural body health. Even if you do not suffer from an illness or condition, learning about your body - inside and out - can be a rewarding and enlightening (4) ___. Our body is a miraculous (5) ___ of moving parts, liquids, electricity, and billions of living pieces all working together to make the Human Being.
151
5. Finish the health conversation below with your own words.
Doctor: Good ____________. What ________________? Patient: I‘ve got ___________ .
Doctor: That‘s ________. Let me ________. It is _________. Patient: Oh, ____________________.
Doctor: Do you have any other _______________ ? Patient: Yes. I __________ . What do I __________ to do? Doctor: You need to _________________.
Patient: Sure. _________________, doctor.
GRAMMAR
Phrasal Verbs
The term ―phrasal verb‖ is commonly applied to two or three distinct but related constructions in English: a verb and a particle and/or a preposition co-occur forming a single semantic unit. This semantic unit cannot be understood based upon the meanings of the individual parts in isolation, but rather it must be taken as a whole.
From Wikipedia
6. Read these statements and write the verbs down. Translate the verbs and then the statements.
1.Jane and I want to give up smoking.
2.Please put on your coat, it's cold outside.
3.I cannot go out tonight. I must look after my little brother.
4.I'm afraid the situation is getting out of hand.
5.All the hard work finally paid off.
1. to give up - ______________
2.
(see Appendix)
152

SELF-STUDY
Changing Your Habits
7. Read the text and complete it with the suitable words.
problems habits diabetes process routine
Old (1) ___ die hard. Changing your habits is a (2) ___
involving several stages. Sometimes it takes a while before changes turn into new habits. You may face challenges along the way. But adopting new, healthier habits may protect you from serious health (3) ___, such as (4) ___. New habits may also help you look better and feel more energetic. After a while, if you stick with these changes, they may become a part of your daily (5) ___.
Remember that eating healthy and being physically active are lifelong behaviors, not one-time events.
8. Ask yourself about the pros (benefits) and cons (things that get in the way) of changing your habits may be helpful. Look at the lists below. Feel free to add others that you think are important.
|
HEALTHY CHOICES |
Pros |
Cons |
•Am nervous about my health.
•Am not good at being active.
•Become stronger.
•Do not have enough money.
•Do not have time.
•Do not know what to do.
153
•Feel better about myself.
•Feel more energetic.
•Have some time alone.
•Improve my health.
•Lose weight.
•Lower my risk for health problems.
•Maintain a healthy weight.
•May need to cook more often at home.
•May need to give up foods I love.
•May spend more on food.
•Reduce my risk for serious health problems.
•Relax.
•Spend time with others.
•Try new, delicious foods.
QUICK CHECK
9.Write 8-10 rules for the healthy living. Complete the diagram. What should we do every day?
10.Write a short essay about your lifestyle.
What habits did you give up? What activities do you do? What food do you prefer?
Is your lifestyle healthy?
What do you do regularly for healthy living?
Min. -15 sentences.
154

UNIT 3 |
ENVIRONMENT |
|
|
Texts |
Environment |
|
Our Home – Planet Earth |
|
Earth Surface |
|
Tiger |
|
Environmental Protection |
|
|
Grammar |
Active Voice / Passive Voice |
|
|
Self-Study |
Soil and the Environment |
|
Pollution and its Negative Effects |
Quick Check |
Life in Color: Green - Essay |
|
|
1. Keep in mind. |
|
Environment: 1) external conditions or surroundings, those in which people live or work; 2) (ecology) the external surroundings in which a plant or animal lives, which tend to influence its development and behavior.
2. Do you know all continents and oceans of the Earth?
|
Our Home – Planet Earth |
|
|
|
|
Continents |
|
Oceans |
|
|
|
Africa |
|
Pacific Ocean |
Antarctica |
|
Atlantic Ocean |
Australia |
|
Indian Ocean |
Eurasia [juə'reɪʒə] |
|
Southern Ocean |
North America |
|
Arctic Ocean |
South America |
|
|
|
|
|
3. Look at the title of the article and answer the questions. Then read the text and check your answers.
155
What is the most of the Earth surface covered with?
When was the Earth‘s surface formed?
Is the Earth‘s surface fixed and permanent?
|
Earth Surface |
by Jerry Coffey |
on March 26, 2010 |
Most of the Earth surface, about 70%, is covered with water. The remaining 30% is made up of the six continental landmasses. Underneath the water that fills the oceans, and the dirt and plants that cover the continents, the Earth‘s surface layer is made of rock.
This outer layer formed a hard, rocky crust as lava cooled about 4.5 billion years ago. This crust is broken into many large plates (tectonic plates) that move slowly relative to each other. The mountain ranges around the world formed when two plates collided and their edges are forced up. Many other surface features are the result of the movement of these tectonic plates. The plates move anywhere from 25 to 100 mm per year. About 250 million years ago most of the land was connected together.
The rocky layer under the soil of the Earth is called the crust. This comprises the continents and ocean basins. The crust has a variable thickness, being 35-70 km thick on the continents and 5- 10 km thick in the ocean basins. The crust is composed mainly of alumino-silicates. The entire crust occupies just 1% of the Earth‘s volume. The temperature of the crust increases as you go deeper into the Earth. It starts out cool, but can get up to 400 degrees C at the boundary between the crust and the mantle.
The tectonic plates are actually floating on the molten asthenosphere which is the lower mantle of the Earth. Earthquakes, volcanoes, mountains, and oceanic trench formation occur along plate boundaries. The plates are in constant motion. The reason that tectonic plates are able to move is the Earth‘s lithosphere has a higher strength and lower density than the underlying
156
asthenosphere. Their movement is dictated by heat dissipation from the Earth‘s mantle. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection, which is transferred into plate motion through some combination of frictional drag, downward suction at the subduction zones, and variations in topography and density of the crust that result in differences in gravitational forces.
The Earth‘s surface may seemed fixed and permanent to us, but underneath our feet there is constant motion and changes that we may not notice until there is an earthquake or a volcanic eruption.
Vocabulary
−environment [ɪn'vaɪər(ə)nmənt ] - окружающая среда
−surrounding [sə'raundɪŋ] - окружение
−surface ['sɜːfɪs] - поверхность, земная поверхность
−to cover ['kʌvə] - покрывать
−remaining - оставшаяся
−landmass ['lændˌmæs] - земля, континент
−underneath [ˌʌndə'niːθ] - внизу; ниже
−dirt [dɜːt] - земля, почва, грунт
−rock - горная порода
−crust [krʌst] - земная кора
−mountain ['mauntɪn] range - горный хребет
−to collide [kə'laɪd] - сталкиваться
−to force up - вытеснять вверх
−feature ['fiːʧə] - особенность, деталь, признак
−to comprise [kəm'praɪz] - включать, содержать
−ocean basin ['beɪsn] - океанический бассейн
−to compose [kəm'pəuz] - составлять
−alumino-silicate - глиноземистый силикат (соль кремниевой или поликремниевой кислоты)
−volume ['vɔljuːm] - объѐм, масса
157
−mantle - (земная) мантия
−to float [fləut] - плавать; держаться на поверхности
−molten ['məult(ə)n] - расплавленный
−asthenosphere [əsˈθɛnəsfɪə] - астеносфера (Земли)
−earthquake ['ɜːθkweɪk] - землетрясение
−trench [tren(t)ʃ] - океанская впадина
−reason ['riːz(ə)n] - причина
−strength [streŋθ] - прочность, крепость
−density ['den(t)sɪtɪ] - плотность, удельная масса
−dissipation [ˌdɪsɪ'peɪʃ(ə)n] - рассеяние, рассеивание
−eruption [ɪ'rʌpʃ(ə)n] - извержение (вулкана)
4.Read each sentence. Then read the text again and choose the correct answer.
1. |
Most of the Earth surface, about 70%, is covered with ___. |
||
a) water |
b) landmass |
c) dirt |
|
2. |
The Earth‘s surface layer is made of ___. |
||
a) clay |
b) rock |
c) sand |
|
3. |
The outer layer was formed as lava___. |
||
a) cooled |
b) heated |
c) erupted |
|
4. |
The crust is broken into many large ___. |
||
a) mantles |
b) basins |
c) plates |
|
5. |
The mountain ranges were formed when ___. |
||
a) two plates were collided |
b) the plate was broken in two |
||
6. |
The crust has a ___ thickness. |
||
a) constant |
b) fixed |
c) variable |
|
7. Earthquakes, volcanoes occur ___. |
|||
a) along plate boundaries |
b) underneath the water |
||
8. The movement of plates |
is dictated by ___ dissipation from the |
||
Earth‘s mantle. |
|
||
a) light |
b) power c) heat |
||
158

5.Find Phrasal Verbs in the text and define their meaning.
6.Find the opposites of these words in the text.
overhead |
fast |
to decrease |
soft |
to divide |
identical |
7. Complete the table with the words below.
stream |
mountain |
waterfall |
sea |
plant |
river |
forest |
rock |
plain |
drop |
island |
field |
pool |
jungle |
desert |
8. Divide the words below into: domestic animals, poultry, wild animals, birds and insects.
Domestic |
|
Wild Animal |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Poultry |
Herbivorous |
Carnivorous |
Bird |
Insect |
||
Animal |
||||||
|
Animal |
Animal |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
bear [bɛə] |
camel ['kæm(ə)l] |
butterfly ['bʌtəflaɪ] |
cat [kæt] |
|
159 |

chicken ['ʧɪkɪn] cock [kɔk] cow [kau]
crocodile ['krɔkədaɪl] cuckoo ['kukuː]
deer [dɪə] dog [dɔg]
dragonfly ['dræg(ə)nflaɪ] duck [dʌk]
eagle ['iːgl] elephant ['elɪfənt] fly [flaɪ]
fox [fɔks]
giraffe [ʤɪ'rɑːf] goat [gəut] hamster ['hæmstə] horse [hɔːs]
lion ['laɪən] monkey ['mʌŋkɪ] pig [pɪg]
seagull ['siːgʌl] sheep [ʃiːp] spider ['spaɪdə] wolf [wulf]
woodpecker ['wudˌpekə]
9. Look at the website. What is this site about? Why are tigers in danger?
1. Wild tiger numbers are at an all-time low. We have lost 97% of wild tigers in just over a century. Tigers may be one of the most revered animals, but they are also vulnerable to extinction. As few as 3,200 exist in the wild today.
160
