
Angliyskiy
.pdf• If something is tiring, you feel ___.
7. Match the positive and negative adjectives.
Positive |
|
Negative |
bad-tempered |
hard-working |
stingy |
boring |
impatient |
unfriendly |
cheerful |
lazy |
unintelligent |
friendly |
patient |
|
generous |
smart |
|
GRAMMAR
Verbal Nouns
A verbal noun is a noun that has no verb-like properties despite being derived from a verb. This means that a verbal noun can be modified by adjectives, be pluralized (if the sense allows), and be followed by a prepositional phrase.
8.Pay attention to the verbal nouns. Define their meaning.
1.There are very old historic buildings in the street.
2.Some ceremonies are rather formal, such as the changing of the Guard at Buckingham Palace, Trooping the Colour, the State opening of Parliament.
3.You may arrange an outing in a park if you wish.
4.I do not want another repetition of yesterday.
5.That was an awful decision by the referee.
6.He is an artist and can't live without painting.
7.People move according to growing or falling of their wellbeing.
8.The housekeeping was perfect.
9.Are there the twins' drawings on the wall?
10.We were shocked by her terrible crying.
101
SELF-STUDY
9. Read the text and match the paragraphs 1-4 with their describing.
How to study
When you sit down to study, how do you transfer that massive amount of information from the books and notes in front of you to a reliable spot in your mind? You need to develop good study habits as outlined below. At first, it'll take a good deal of conscious effort to change your studying ways, but after a while, it'll become second nature, and studying will be easier to do.
1Make things interesting. |
3 |
Study in 20-50 minute chunks. |
|
|
|
2 Manage your time. |
4 |
Rewrite your notes at home. |
|
|
|
a)It takes time for your brain to form new long-term memories, and you can't just keep studying flat out. Write notes to the side, or write questions about the text you just read. Take 5-10 minute breaks minimum and do something physically active to get your blood flowing and make you more alert.
b)Make a weekly schedule and devote a certain amount of time per day to studying. This will also improve your grades. That amount will vary depending on whether you're in high school or college, and also varies by field of study.
c)When you're in class, emphasize recording over understanding or neatness when you take notes. That doesn't mean you shouldn't try to understand or organize your notes at all; just don't waste time doing something in class that you can figure out or neaten up at home. Consider your in-class notes a "rough draft" of sorts. Rewrite your notes as soon after the class as possible, while the material is fresh in your mind so that you can fill in any gaps completely from memory.
102
d) Logical arguments will not give you motivation to study. Thinking that if I study hard and get into a good university and get a good job, etc., will not interest you. Love what you do. Try to find the beauty of every subject, and most importantly try to link it with the events of your life and things that interest you.
QUICK CHECK
10. Choose the correct options.
Student1: ―How do you pronounce this word?‖
Student1: ―___________________________‖
a)I‘m afraid, I don‘t know. Why don‘t you ask the teacher?
b)Ask the teacher.
c)And what about you?
d)No idea.
Student: ―What additional literature can you advise?‖ Teacher: ―____________________________‖
a)Oh, dear, you can look up in the library yourself.
b)There are two new text-books in our reading hall and a technical encyclopedia.
c)I have one technical booklet.
d)Your list of literature is available at the laboratory.
Teacher: ―Read the passage and match the names with …‖ Student: ―____________________________‖
a)What does this mean?
b)Could you repeat that, please?
c)What?
d)Slow down!
Student: ―I‘d like to fix an appointment with the principal for tomorrow.‖
Secretary: ―____________________________‖
103
a)You can come earlier if he is free.
b)Would nine tomorrow be all right?
c)I‘m afraid not. He‘s got rather a full day today.
d)How about Tuesday then?
Student: ―How much time do we have to complete our tests?‖ Teacher: ―Your time is up! ______________‖
a)Hand in your papers, please!
b)Stop talking!
c)You may continue reading.
d)Who is on duty today?
Student: ― ____________________________‖ Tutor: ―Certainly, you have four credits this term.‖
a)Have we got any credits this term?
b)Have we got four or five credits this term?
c)Have we got any terms for our credits?
d)How many credits have we got this term?
Student1: ―Let‘s go to the library and take the necessary books.‖ Student1: ―___________________________‖
a)Are you all right?
b)I think, we‘d better do it after the break.
c)My idea doesn‘t coincide with yours.
d)I am not ready for my English class.
Student: ―Have you had time to mark my composition?‖ Teacher: ― ___________________________‖
a)Oh, dear, you look awful, what‘s the matter with you?
b)Yes, it was quite good, and I‘ve underlined the mistakes you‘ve made.
c)Yes, and I do hope you don‘t mind my saying this but you‘ve made one or two tiny mistakes.
d)Yes, I have.
104
UNIT 4 |
|
AGRICULTURE |
|
|
|
Texts |
|
Agriculture in the World Today |
|
|
Food Processing |
|
|
Soil Basics |
|
|
|
Grammar |
|
Sequence of Tenses |
|
|
|
Self-Study |
|
Soil Formation |
|
|
History of Agriculture |
|
|
|
Quick Check |
|
Agriculture in General |
|
|
|
|
Agriculture in the World Today |
|
―The discovery of agriculture was the first big step toward a civilized life.” Arthur Keith That means that agriculture played a vital role in the
economy of every nation. It was the key development that led to the rise of human civilization, creating food. The word
―agriculture‖ means ―in fields‖ and is the sector of an economy concerned with the production of food, consumption, and for the export of the goods to external markets and trades. It is divided in branches like agronomy, horticulture that is the growing of fruits and flowers etc.
Agriculture developed over the centuries and each innovation caused changes in the human life. The primary agricultural products consisted of crop plants for the people food, animal feed, and domestic animal which were kept for sale.
Agriculture is still a basic part of economy in the world of today. It has the main contribution to the Gross Domestic Production (GDP) that is declining over the years. At the same time, the productivity has been increasing. Also it has impact in other branches. It stimulates trades, industry and tourism other sectors in the economy can be even more successful. About half the world's workers are employed in agriculture more than in any other industry.
105

Sir Arthur Keith (5 February 1866 – 7 January 1955) was a famous Scottish anatomist and anthropologist.
Vocabulary
−a vital role - жизненно-важная роль
−the rise - возвышение, подъѐм
−civilization [ˌsɪvɪlaɪ'zeɪʃ(ə)n]
−agriculture ['ægrɪkʌlʧə]
−concerned with [kən'sɜːnd] - связанный с чем-л.
−consumption [kən'sʌm(p)ʃ(ə)n] - потребление
−an external market - внешний рынок
−trade - торговля; коммерческая деятельность
−horticulture ['hɔːtɪkʌlʧə] - садоводство
−crop plants ['krɔpˌplɑːnts] - хлебные злаки
−domestic animal - домашнее животное
−contribution [ˌkɔntrɪ'bjuːʃ(ə)n] - вклад
− the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) - валовой внутренний продукт, ВВП
−to decline [dɪ'klaɪn] - спадать; снижаться; уменьшаться
−impact ['ɪmpækt] - удар, толчок; импульс
−branch [brɑːnʧ] - 1) ветвь, ветка (растений) 2) отрасль, подразделение
−to employ [ɪm'plɔɪ ] - держать на службе, иметь в штате
1.Answer the questions.
1.What role did agriculture play in the economy?
2.What does the word ―agriculture‖ mean?
3.What is agriculture concerned with?
4.What branches of agriculture are there?
5.What does agriculture stimulate?
106
2. Write down the branches of agriculture.
Agriculture
Agronomy
3. Complete the sentences with the words from the text.
1.Agriculture plays a ___ role in the economy.
2.It developed the ___ civilization.
3.The word ―agriculture‖ means ―in ___‖.
4.Today it is the sector of an economy concerned with the ___
of food, consumption.
5.It is divided in ___ like agronomy, horticulture that is the growing of fruits and flowers.
6.The agricultural products consist of ___ plants, animal feed, and domestic animal.
7.Agriculture is still a basic ___ of economy.
8.It has the main ___ to the Gross Domestic Production.
9.It stimulates trades, industry and tourism.
10.About half the world's ___ are employed in agriculture.
4. Complete the table with the words below.
CROPS VEGETABLES FRUITS ANIMALS MACHINERY
apple |
broccoli |
game |
poultry |
apricot |
carrot |
hoe |
roller |
artichoke |
cattle |
hog |
rye |
banana |
corn |
millet |
sheep |
barley |
cucumber |
oats |
|
beet |
digger |
orange |
|
binder |
drill |
plum |
|
|
|
107 |
|
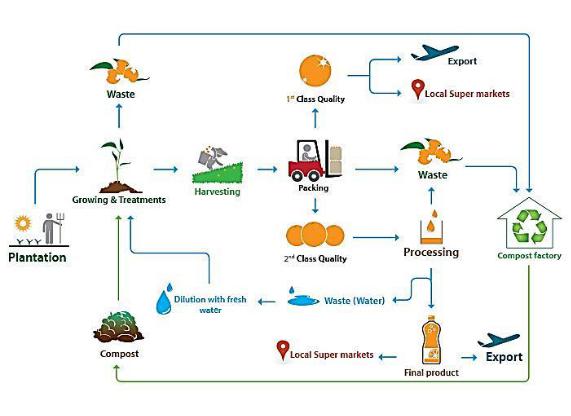
Food Processing
5. Write the stages of agricultural products.
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Harvesting |
Planting |
Processing and storage |
||||
|
|
|
Cultivating |
Preparing the soil |
|
||
6. Read the text and complete it with the words. Soil Basics
biofuels complex civilization surface |
life |
words |
Soil has been a defining component of cultures since the beginning of (1) ___. Some of the first written (2) ___ were recorded on clay tablets and water was carried in clay pitchers. It provides the base for our food, fiber, feed, and even some (3) ___.
108

Soils are (4) ___ mixtures of minerals, water, air, organic matter, and countless organisms that are the decaying remains of once-living things. It forms at the (5) ___ of land – it is the ―skin of the earth.‖ Soil is capable of supporting plant life and is vital to (6)
___ on earth.
GRAMMAR
Sequence of Tenses
Simple Tenses
|
(is) |
was |
|
Present |
Past |
|
|
|
He said (Past) that he |
(was) |
was |
|
Past |
Past |
|
|
|
|
(will be) |
would be |
|
Future |
Future in the Past |
|
|
|
7. Pay attention to Sequence of Tenses.
1.The results of a British holiday survey showed that children would rather travel then stay in Britain.
2.Queen Victoria said it was dangerous to have a link with France.
3.We knew that he was going in London.
4.I was sure that I had seen Tom.
5.He thought that the teachers and older students parked their cars near the Institute.
6.Newton found that white light was made up of rays of different colours.
7.In a survey done, 89% of those asked said that they still had traditional English Sunday lunch.
8.The Romans noted that the Britains regularly met in their taverns to drink ale and discuss problems.
109
SELF-STUDY
Soil Formation
Soils differ from one part of the world to another, even from one part of a backyard to another. They differ because of where and how they formed. Five major factors interact to create different types of soils:
Climate, Temperature and moisture influence the speed of chemical reactions, which in turn help control how fast rocks weather and dead organisms decompose. Soils develop faster in warm, moist climates and slowest in cold or arid ones.
Organisms - Plants root, animals burrow, and bacteria eat - these and other organisms speed up the breakdown of large soil particles into smaller ones. For instance, roots produce carbon dioxide that mixes with water and forms an acid that wears away rock.
Relief (landscape) - The shape of the land and the direction it faces make a difference in how much sunlight the soils gets and how much water it keeps. Deeper soils form at the bottom of a hill because gravity and water move soil particles down the slope.
Parent material - Every soil ―inherits‖ traits from the parent material from which it formed. For example, soils that form from limestone are rich in calcium and soils that form from materials at the bottom of lakes are high in clay. Every soil formed from parent material deposited at the Earth's surface. The material could have been bedrock that weathered in place or smaller materials carried by flooding rivers, moving glaciers, or blowing winds. Parent material is changed through biological, chemical and environmental processes, such as weathering and erosion.
Time - All of these factors work together over time. Older soils differ from younger soils because they have had longer to develop. As soil ages, it starts to look different from its parent material. That is because soil is dynamic. Its components - minerals, water, air, organic matter, and organisms - constantly
110
