
- •Section b gasoline (petrol) engines
- •Section c diesel engines
- •Section b water and its boiling point
- •C) molecules in motion
- •Section d engine-cooling system
- •Section b lubrication
- •Section c engine lubricating system
- •Section d filters
- •Unit four electricity Section a electrolysis
- •Uses of Electrolysis
- •Section b batteries
- •Section c automobile electric system
- •Section d battery-powered automobiles
- •Section b ferrous metals
- •Tensile strength and hardness section c
- •Section d aluminium bronze
- •Grammar exercises
- •Unit 1 advantages and disadvantages of diesel engines
- •Unit 2 comparative characteristics diesel and gasoline engines
- •Unit 3 basic parts of the automobile
- •Unit 4 where diesel engines are used
- •Unit 5 Temperature Regulators of Cooling System
- •In machihes and machinery.
- •Unit 8 the instruments in a car
- •Unit 9 Battery chargers
- •Vocabulary Список сокращений
- •Literature used
- •Contents
Section c automobile electric system
All automobiles are provided with a certain number of electric devices. These devices serve the purpose of starting the engines, igniting the compressed mixture in the cylinders, lighting, controlling different systems of the car and some others.
Storage batteries and generators are the two sources of electric current used in all modern automobiles. The lead-acid storage battery is an electro-chemical device capable to generate and accumulate electric current due to chemical reactions taking place in it. When needed, the current is supplied to various systems of the car.
The basic purpose of the storage battery is feeding the cranking motor with electric energy. When the cranking motor switch is put in a closed position, cranking, motor is connected with the battery, the crankshaft rotates and starts the engine. The current being withdrawn from the battery, chemical compounds in it continue their work and produce electric energy. A certain amount of current having been withdrawn from the battery, it becomes partly discharged. To recharge the .battery an electric current should be forced through it in the opposite direction. In practice, the storage battery service life is about five-six years, then it has to be replaced by a new one.
All storage batteries in use in automobiles today are of the three or six cell, six or twelve volt type. There are some positively and negatively charged plates in each cell. The plates are put into the solution of a chemically pure sulphuric acid and distilled water. To secure the reliable operation of the storage battery, it is necessary that the density of the electrolyte should be constantly controlled.
So, the battery is considered to be a source of initial electric .energy. Besides, it supplies the electric energy for various systems of the car when the engine operates idly.
Another important source of electric energy is the generator. This is a device converting mechanical energy from the automobile engine into a flow of electric current. The current supplied by the generator restores the battery to a charged condition when it has become discharged and also operates electrical devices, such as the ignition system, lights, radio and others when the engine operates and the car moves.
It should be noted in conclusion that the electric current passing through the wires from one electrically operated device to another performs the work absolutely for the successful operation of the car.
Exercise 11 Answer the following questions.
What purposes do the electric devices of all automobiles serve?
What electric device serves the source of initial electric current?
When does the storage battery become discharged?
In what way can the storage battery be recharged?
5. What functions of the generator can you enumerate?
Section d battery-powered automobiles
It is safe to predict that in the near future most cars will use the internal combustion engine and burn petrol. But at the present rate of production development oil supplies will run out in about fifty years, and we will have to look for other sources of energy. That is one of the most important aspects of the problem, another being the damage that exhaust fumes do to the environment and health, especially in the towns.
What kind of vehicle will eventually dominate? At present there is a lot of talking about electric cars, for they have the advantage of giving off no exhaust gases. The electric car has a long history. The first electric cars were built at the end of the 19-th century, but they could not compete against the internal combustion engine automobiles.
The electric cars have several disadvantages. First, we have no really suitable batteries—they are too heavy, take a long time to charge, have too small a capacity and a relatively short life.
For a while the fuel cell looked very hopeful. This does not have to be charged, it generates its own energy from a chemical reaction. But this, too, proved to be too large and expensive.
An electric car have to run 200-250 km on one charge to compete with the conventional car which can do about 200 km on a full tank. Nowadays scientists and engineers are looking for better storage batteries or cells, and ways of using energy more economically.
There are about 120 different electric cars around the world. Some can run 100 km and longer on one charge. This is quite sufficient for town traffic, where cars do not cover such long distances. Electric vans can have their storage batteries recharged while being loaded or unloaded.
The first electric cars have already been used in Moscow and in several other cities. So far there are few of them. They are used for local deliveries, post offices and the services. Specialists think that in future these cars will be used for urban transportation.
Exercise 12. Complete the sentences.
Present oil resources will be exhausted in (...).
1) half a century; 2) a century; 3) fifty thousand years.
Electric cars appeared (...).
1) in the 18th century; 2) in the 19th century; 3) in the 20th century.
The weak point of the electric car is (...). 1) the body; 2) the battery; 3) the brakes.
Electric cars cover over 100 kilometers on one charge and that makes them suitable for (...)
1) city passenger transport; 2) town goods transport; 3) highway passenger transport.
5. For the electric cars to become universally used it is necessary (...).
1) to increase their production; 2) to perfect their design;
3) to generate more electricity.
UNIT FIVE
PROPERTIES of ENGINEERING MATERIALS
SECTION A
FOUR PROPERTIES of ENGINEERING MATERIALS
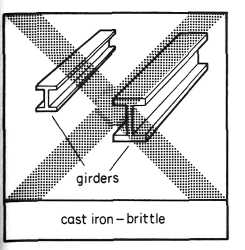
It is important to know the properties of engineering materials. For example, steel is used for making girders because it is an elastic metal. Cast iron is never used for making girders because it is brittle. The properties of a material determine its use.
Malleability: It is easy to roll a malleable material into a new shape. A malleable material does not fracture easily under pressure. Gold is extremely malleable. It is possible to roll gold into very thin sheets. Copper is very malleable and so is lead. Glass is not at all malleable and nor is cast iron. It is very easy to fracture glass with a hammer. Cast iron also fractures easily.
Ductility: It is easy to draw a ductile material. It does not fracture and it retains its new shape. Copper is extremely ductile. Tin is very ductile and so is aluminium. Steel is not very ductile and nor is lead. It is very difficult to draw lead into thin wire because it fractures easily.
Elasticity: An elastic material stretches easily under stress. However, remove the stress and it does not retain its new shape. It regains its original shape. Rubber is extremely elastic. Some steels are quite elastic. Glass is not at all elastic and nor is cast iron.
Durability: A durable material does not corrode easily. Under normal conditions, glass is very durable and so are plastics. Among the metals, chromium is extremely durable and so is platinum. Gold is quite durable and so is aluminium. Cast iron is not very durable and nor is steel.
Exercise 1 Complete this table from the text.
MATERIAL |
malleability |
ductility |
durability |
|
||
Copper |
|
|
**** |
|
||
aluminum |
*** |
|
|
|
||
gold |
|
**** |
|
|
||
glass |
|
* |
|
|
||
extremely = |
***** |
|
||||
very = |
**** |
|
||||
quite = |
*** |
|
||||
not very = |
** |
|
||||
not at all = |
* |
|
||||
Now make questions from this table and answer them.

Look at these examples. 1.Copper is very malleable and very durable and it is extremely ductile. 2 .Aluminium is quite malleable and quite durable and it is very ductile. 3. Gold is extremely malleable and very ductile and it is quite durable. 4. Glass is not at all malleable and not at all ductile, but it is very durable.
Exercise 2 Now look at this table of other metals. Make sentences about these metals in the same way. Use the words and or but.
METAL |
MALLEABILITY |
DUCTILITY |
DURABILITY |
tin |
**** |
**** |
**** |
nickel |
*** |
**** |
*** |
cast iron |
* |
* |
** |
lead |
**** |
** |
*** |
steel |
*** |
** |
** |
chromium |
*** |
*** |
***** |
zinc |
**** |
*** |
**** |
brass |
*** |
*** |
**** |
bronze |
*** |
*** |
***** |
Exercise 3 Look at the examples.
Copper is very malleable and so is lead.
Glass is not at all ductile and nor is cast iron.
Now make sentences in the same way from these words.
1. Aluminum, tin - ductile |
2. steel, lead - ductile |
3. Steel cast iron - durable |
4. bronze, brass - malleable |
5. cast iron, glass - malleable |
6. plastic, gold - durable |
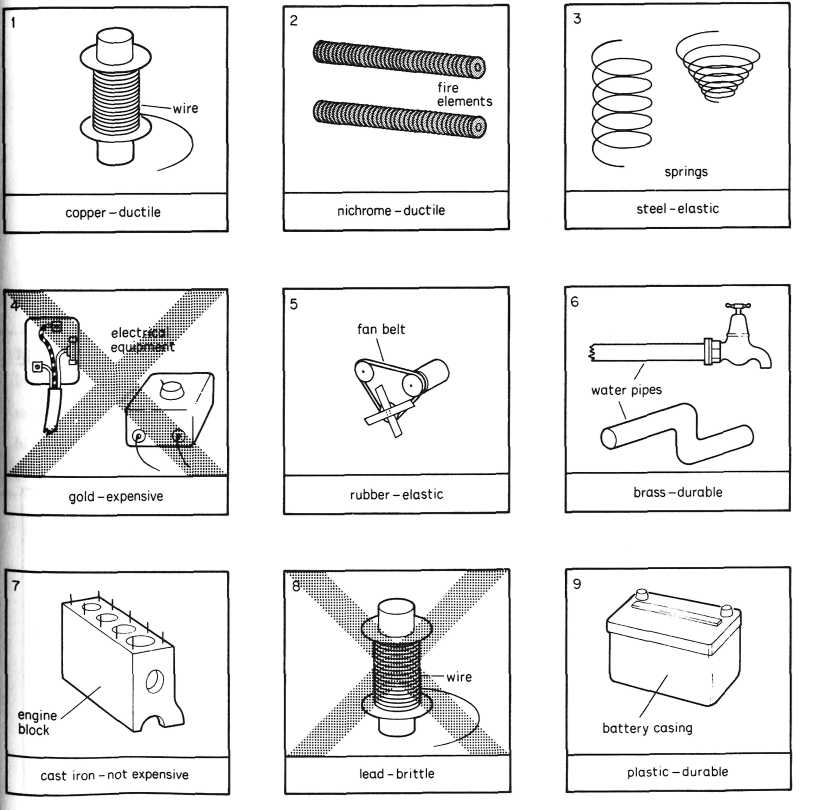
Exercise 4 Look at the example. Then make sentences from the pictures below in the same way.
Cast iron is not used for making girders because it is brittle.
Exercise 5 Check up whether you know the following words and expressions:
a property, malleability, ductility, elasticity, durability, a girder, spring, a belt, fracture, engineering, stress, roll, draw, know, determine, retain, retain, regain, stretch, (and) so, (and) nor, its, extremely, very, brittle, important, quite, easy (—ily), not very, difficult, not at all, original, thin.
Terminology: a property, malleability, ductility, elasticity, durability, brittle, stress, roll, fracture, draw.
