
- •Textbook Series
- •Contents
- •1 Properties of Radio Waves
- •Introduction
- •The Radio Navigation Syllabus
- •Electromagnetic (EM) Radiation
- •Polarization
- •Radio Waves
- •Wavelength
- •Frequency Bands
- •Phase Comparison
- •Practice Frequency (
- •Answers to Practice Frequency (
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •2 Radio Propagation Theory
- •Introduction
- •Factors Affecting Propagation
- •Propagation Paths
- •Non-ionospheric Propagation
- •Ionospheric Propagation
- •Sky Wave
- •HF Communications
- •Propagation Summary
- •Super-refraction
- •Sub-refraction
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •3 Modulation
- •Introduction
- •Keyed Modulation
- •Amplitude Modulation (AM)
- •Single Sideband (SSB)
- •Frequency Modulation (FM)
- •Phase Modulation
- •Pulse Modulation
- •Emission Designators
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •4 Antennae
- •Introduction
- •Basic Principles
- •Aerial Feeders
- •Polar Diagrams
- •Directivity
- •Radar Aerials
- •Modern Radar Antennae
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •5 Doppler Radar Systems
- •Introduction
- •The Doppler Principle
- •Airborne Doppler
- •Janus Array System
- •Doppler Operation
- •Doppler Navigation Systems
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •6 VHF Direction Finder (VDF)
- •Introduction
- •Procedures
- •Principle of Operation
- •Range of VDF
- •Factors Affecting Accuracy
- •Determination of Position
- •VDF Summary
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •7 Automatic Direction Finder (ADF)
- •Introduction
- •Non-directional Beacon (NDB)
- •Principle of Operation
- •Frequencies and Types of NDB
- •Aircraft Equipment
- •Emission Characteristics and Beat Frequency Oscillator (BFO)
- •Presentation of Information
- •Uses of the Non-directional Beacon
- •Plotting ADF Bearings
- •Track Maintenance Using the RBI
- •Homing
- •Tracking Inbound
- •Tracking Outbound
- •Drift Assessment and Regaining Inbound Track
- •Drift Assessment and Outbound Track Maintenance
- •Holding
- •Runway Instrument Approach Procedures
- •Factors Affecting ADF Accuracy
- •Factors Affecting ADF Range
- •Accuracy
- •ADF Summary
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •8 VHF Omni-directional Range (VOR)
- •Introduction
- •The Principle of Operation
- •Terminology
- •Transmission Details
- •Identification
- •Monitoring
- •Types of VOR
- •The Factors Affecting Operational Range of VOR
- •Factors Affecting VOR Beacon Accuracy
- •The Cone of Ambiguity
- •Doppler VOR (DVOR)
- •VOR Airborne Equipment
- •VOR Deviation Indicator
- •Radio Magnetic Indicator (RMI)
- •Questions
- •In-flight Procedures
- •VOR Summary
- •Questions
- •Annex A
- •Annex B
- •Annex C
- •Answers
- •Answers to Page 128
- •9 Instrument Landing System (ILS)
- •Introduction
- •ILS Components
- •ILS Frequencies
- •DME Paired with ILS Channels
- •ILS Identification
- •Marker Beacons
- •Ground Monitoring of ILS Transmissions
- •ILS Coverage
- •ILS Principle of Operation
- •ILS Presentation and Interpretation
- •ILS Categories (ICAO)
- •Errors and Accuracy
- •Factors Affecting Range and Accuracy
- •ILS Approach Chart
- •ILS Calculations
- •ILS Summary
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •10 Microwave Landing System (MLS)
- •Introduction
- •ILS Disadvantages
- •The MLS System
- •Principle of Operation
- •Airborne Equipment
- •Question
- •Answer
- •11 Radar Principles
- •Introduction
- •Types of Pulsed Radars
- •Radar Applications
- •Radar Frequencies
- •Pulse Technique
- •Theoretical Maximum Range
- •Primary Radars
- •The Range of Primary Radar
- •Radar Measurements
- •Radar Resolution
- •Moving Target Indication (MTI)
- •Radar Antennae
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •12 Ground Radar
- •Introduction
- •Area Surveillance Radars (ASR)
- •Terminal Surveillance Area Radars
- •Aerodrome Surveillance Approach Radars
- •Airport Surface Movement Radar (ASMR)
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •13 Airborne Weather Radar
- •Introduction
- •Component Parts
- •AWR Functions
- •Principle of Operation
- •Weather Depiction
- •Control Unit
- •Function Switch
- •Mapping Operation
- •Pre-flight Checks
- •Weather Operation
- •Colour AWR Controls
- •AWR Summary
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •14 Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR)
- •Introduction
- •Advantages of SSR
- •SSR Display
- •SSR Frequencies and Transmissions
- •Modes
- •Mode C
- •SSR Operating Procedure
- •Special Codes
- •Disadvantages of SSR
- •Mode S
- •Pulses
- •Benefits of Mode S
- •Communication Protocols
- •Levels of Mode S Transponders
- •Downlink Aircraft Parameters (DAPS)
- •Future Expansion of Mode S Surveillance Services
- •SSR Summary
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •15 Distance Measuring Equipment (DME)
- •Introduction
- •Frequencies
- •Uses of DME
- •Principle of Operation
- •Twin Pulses
- •Range Search
- •Beacon Saturation
- •Station Identification
- •VOR/DME Frequency Pairing
- •DME Range Measurement for ILS
- •Range and Coverage
- •Accuracy
- •DME Summary
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •16 Area Navigation Systems (RNAV)
- •Introduction
- •Benefits of RNAV
- •Types and Levels of RNAV
- •A Simple 2D RNAV System
- •Operation of a Simple 2D RNAV System
- •Principle of Operation of a Simple 2D RNAV System
- •Limitations and Accuracy of Simple RNAV Systems
- •Level 4 RNAV Systems
- •Requirements for a 4D RNAV System
- •Control and Display Unit (CDU)
- •Climb
- •Cruise
- •Descent
- •Kalman Filtering
- •Questions
- •Appendix A
- •Answers
- •17 Electronic Flight Information System (EFIS)
- •Introduction
- •EHSI Controller
- •Full Rose VOR Mode
- •Expanded ILS Mode
- •Full Rose ILS Mode
- •Map Mode
- •Plan Mode
- •EHSI Colour Coding
- •EHSI Symbology
- •Questions
- •Appendix A
- •Answers
- •18 Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)
- •Introduction
- •Satellite Orbits
- •Position Reference System
- •The GPS Segments
- •The Space Segment
- •The Control Segment
- •The User Segment
- •Principle Of Operation
- •GPS Errors
- •System Accuracy
- •Integrity Monitoring
- •Differential GPS (DGPS)
- •Combined GPS and GLONASS Systems
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •19 Revision Questions
- •Questions
- •Answers
- •Specimen Examination Paper
- •Appendix A
- •Answers to Specimen Examination Paper
- •Explanation of Selected Questions
- •20 Index

Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) 18
The ellipsoids cannot be a perfect representation, nor can they represent geographical features, e.g. mountains and land depressions. The distance of mean sea level from the centre of the earth depends on gravitational forces which vary both locally and globally. Hence mean sea level will not necessarily coincide with the surface of the ellipsoid. The maximum variation between mean sea level and the surface of the ellipsoid for WGS84 is approximately 50 m. Hence the vertical information provided by any system referenced to this model cannot be used in isolation for vertical positioning, except when in medium/high level cruise with all aircraft using the GNSS reference and in LADGNSS applications - (where the vertical error is removed).
The GPS Segments
GPS comprises three segments:
•The Space Segment
•The Control Segment and
•The User Segment
|
HAWAII |
|
|
|
KWAJALEIN |
|
|
ASCENSION Is. |
|
|
|
DIEGO GARCIA |
THE |
|
|
|
MONITOR |
CONTROL |
|
THE SPACE |
STATIONS |
SEGMENT |
COLORADO |
|
|
SPRINGS |
|
SEGMENT |
|
|
|
THE USER 
SEGMENT
Figure 18.3 The three segments of the GPS operational control
GPS time is measured in weeks and seconds from 00:00:00 on 06 January 1980 UTC. An epoch is 1024 weeks after which the time restarts at zero. GPS time is referenced to UTC but does not run in direct synchronization, so time correlation information is included in the SV broadcast. In July 2000 the difference was about 13 seconds.
Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) 18
307

18 Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS)
The Space Segment
The operational constellation for GPS is specified as comprising 24 SVs. (Currently the USA has 31 SVs providing a navigational service). The orbits have an average height of 10 898 NM (20 180 km) and have an orbital period of 12 hours. The orbital planes have an inclination of 55° and are equally spaced around the equator. The spacing of the SVs in their orbits is such that an observer on or close to the surface of the earth will have between five and eight SVs in view, at least 5° above the horizon. The SVs have 3 or 4 atomic clocks of caesium or rubidium standard with an accuracy of 1 nanosecond.
An SV will be masked (that is not selected for navigation use) if its elevation is less than 5° above the horizon.
(GNSS) Systems Satellite Navigation Global 18
Figure 18.4 The GPS Satellite Constellation
The SVs broadcast pseudo-random noise (PRN) codes of one millisecond duration on two frequencies in the UHF band and a NAV and SYSTEM data message. Each SV has its own unique code.
L1 Frequency: 1575.42 MHz transmits the coarse acquisition (C/A) code repeated every millisecond with a modulation of 1.023 MHz, the precision (P) code, modulation 10.23 MHz repeats every seven days and the navigation and system data message at 50 Hz. The navigation and system data message is used by both the P and C/A codes.
L2 Frequency: 1227.6 MHz transmitting the P code. The second frequency is used to determine ionospheric delays.
L3 Frequency: 1381.05 MHz has been allocated as a second frequency for non-authorized users and its use is the same as the L2 frequency.
308
Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) 18
L1 Carrier 1575.42 Mhz












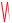











 L1 Signal
L1 Signal
C/A code 1.023 Mhz
Nav/ system Data 50 Hz |
Mixer |
|
 Modulo to Sum
Modulo to Sum
P-Code 10.23 Mhz
L2 Carrier 1227.6 Mhz



 L2 Signal
L2 Signal
Figure 18.5
Only the C/A code is available to civilian users. The reason the use of two frequencies is important will be discussed in GNSS errors. The P code is provided for the US military and approved civilian users and foreign military users at the discretion of the US DOD. The P code is designated as the Y code when anti-spoofing measures are implemented. The Y code is encrypted and therefore only available to users with the necessary decryption algorithms.
The PRN codes provide SV identification and a timing function for the receiver to measure SV range.
The information contained in the nav and system data message is:
• SV position
•SV clock time
•SV clock error
•Information on ionospheric conditions
•Supplementary information, including the almanac (orbital parameters for the SVs), SV health (P-code only), correlation of GPS time with UTC and other command and control functions.
The two services provided are:
•The standard positioning service (SPS) using the C/A code
•The precise positioning service (PPS) using the C/A and P codes
GLONASS also has an operational constellation of 24 SVs positioned in three orbital planes inclined at 65° to the equator. The orbital height is 10 313 NM (19 099 km) giving an orbital period of 11 hours 15 minutes. As in GPS, GLONASS transmits C/A and P codes. The codes are the same for all SVs, but each SV uses different frequencies. The L1 frequency is incremental from 1602 MHz and the L2 frequency from 1246 MHz.
Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) 18
309

18
(GNSS) Systems Satellite Navigation Global 18
Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS)
|
NAVSTAR – USA |
GLONASS – USSR |
Galileo – EU |
|
|
|
|
No. of SVs: |
24 SVs |
24 SVs |
30 SVs |
|
|
|
|
Orbits: |
6 Orbits |
3 Orbits |
3 Orbits |
|
|
|
|
Orbit Height: |
20 180 km |
19 099 km |
23 222 km |
|
|
|
|
|
(10 898 NM) |
(10 313 NM) |
(12 539 NM) |
|
|
|
|
Orbit Inclination: |
55° to equator |
65° to equator |
56° to equator |
|
|
|
|
Orbit Time: |
11 h 56 m |
11 h 15 m |
14 h 8 m |
|
|
|
|
Frequencies: |
L1: 1575 MHz |
L1: 1600 MHz |
E1: 1559 - 1591 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
L2: 1227 MHz |
L2: 1250 MHz |
E5: 1164 - 1215 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
E6: 1260 - 1300 MHz |
|
|
|
|
Codes: |
L1: P & C/A |
L1: P & C/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
L2: P |
L2: P |
|
|
|
|
|
Geoid: |
WGS 84 |
PZ 90 |
ETRS 89 |
|
|
|
|
Figure 18.6 GNSS Systems Comparison
The Control Segment
The GPS control segment comprises:
•A Master Control Station
•A Back-up Control Station
•5 Monitoring Stations
BACK-UP CONTROL STATION |
|
MASTER CONTROL STATION |
|
MONITOR STATION |
|
GROUND ANTENNA |
|
ONIZUKA |
|
COLORADO |
HAWAII |
SPRINGS |
|
|
KWAJALEIN |
ASCENSION |
DIEGO |
|
GARCIA |
Figure 18.7 GPS Operational Control Segment
310
