
- •Adhesion molecules
- •Naming names
- •Immunoglobulin superfamily
- •ICAM
- •SIGLEC
- •Junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs)
- •Claudins
- •Occludin
- •Integrins
- •Inactive to primed
- •Primed to active
- •Cadherins
- •Selectins
- •Cartilage link proteins
- •Integrins, cell survival, and cell proliferation
- •Inside-out signalling and the formation of integrin adhesion complexes
- •Outside-in signalling from integrin adhesion complexes
- •Integrins and cell survival
- •Integrins and cell proliferation
- •References

Signal Transduction to and from Adhesion Molecules
severely reduced and they become quiescent. This may reach such a point they fail to maintain their size and this inevitably results in a loss of viability.95 The apoptotic process that ensues is due to the enhanced permeability of the mitochondrial outer membrane to cytochrome c. In cells starved of glucose, this is signalled by detachment of hexokinase from the mitochondrial outer membrane. Beyond its widely recognized role in phosphorylating glucose, hexokinase may also be involved in the linkage between the mitochondrial outer membrane pores and the adenine nucleotide transporter of the inner membrane, ensuring pore integrity and transport selectivity. By maintaining the cell surface expression of the glucose transporter GLUT4 (see page 558), sustained activation of PKB prevents apoptosis of cells even in the absence of growth factors. As a consequence, the activity and the mitochondrial association of hexokinase is maintained and leakage of cytochrome c is prevented.96
Finally, the action of PKB is certainly not limited to these survival processes. It also protects cyclin D1 against degradation and stimulates protein synthesis through activation of the kinase mTOR (see page 559).
Integrins and cell proliferation
FAK signalling reinforces the Ras–ERK pathway
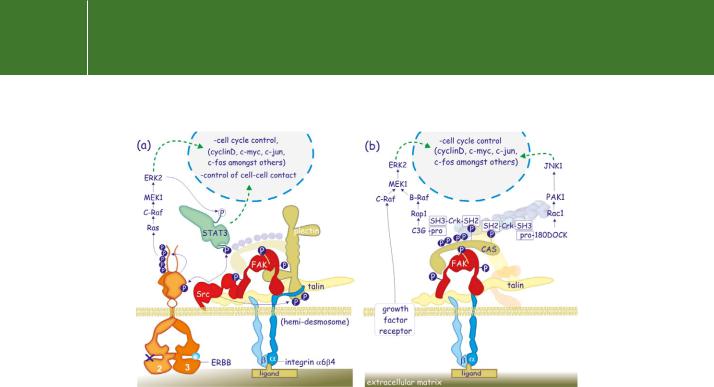
As we have seen, clustered integrins bind FAK which undergoes autophosphorylation and then recruits Src to cause further phosphorylation and the formation of an activated tyrosine protein kinase complex. With most integrins, the phosphorylated FAK binds the adaptor complex Grb2/ Sos and then activates the Ras–ERK pathway (Figure 13.17).97 With other integrins ( 1 1, 5 1, and V 3), activation of the ERK pathway requires the palmitoylated kinase Fyn that links to the -subunit and, through SH3 linkage to Shc. Shc is then phosphorylated and this leads to recruitment of the Grb2/ Sos complex.98 This additional Ras–ERK signal is important for a sustained activation of ERK. If EGF or PDGF is provided to suspended fibroblasts, the activation of the ERK pathway is merely transient; there is no increase in the expression of cyclin D1 and expression of the cell cycle inhibitors p21CIP/WAF and p27KIP is fully maintained. The cells fail to proliferate and, sooner or later, they undergo apoptotic death.99
An alternative route for the stimulation of ERK is through phosphorylation of CAS by Src/FAK. Tyrosine phosphorylated CAS preferentially binds the SH2/ SH3 adaptor protein Crk, which is either linked to the Rap1 guanine exchange factor C3G or to the Rac1 exchange factor 180DOCK100,101 (Figure 13.18b). This results in activation of both Rap1 and Rac1, leading to activation of B-Raf, with prolonged activation of ERK, and leads to activation of JNK-1.102,103 The sustained signal ensures progression from G0 to G1 and entry into the cell cycle.104
403
Signal Transduction
FIG 13.18 FAK-mediated signalling. (a) In epithelial cells, integrin 6 4 attached to the extracellular matrix forms a hemidesmosome, a specialized adhesion complex. These are linked to intermediate filaments via plectin (resembles plakoglobin). ErbB2/3 receptors are recruited, leading to phosphorylation of ErbB2 by Src bound to FAK. This promotes the activity of the ErbB2 kinase and enhances the growth factor receptor signalling output. (Note that ErbB3 is kinase dead and cannot phosphorylate ErbB2, see page 318). Src also phosphorylates STAT3, this signal being enforced by a second (serine) phosphorylation by ERK2. ERK2 and STAT3 cooperate in the regulation of cell–cell contacts and the cell cycle (cyclin D, c-Myc, c-Jun, c-Fos,
and more). In breast tumour cells, this pathway promotes cellular invasion. Finally, the 4-integrin subunit is also a target of Src and this may affect its interaction with plectin. The ghosts decorating CAS indicate tyrosine phosphorylation sites. (b) Two examples of FAK signalling via the intermediate of CAS. The phosphotyrosines of CAS bind the SH2 domain of Crk. The proline-rich regions (PR) of C3G and 180DOCK (guanine nucleotide exchange factors) bind the SH3 domain of Crk. Their recruitment to the focal adhesion complex causes the activation of Rap1 and Rac1. Rap1 signals to B-Raf, which then
phosphorylates MEK1, thus enforcing the growth factor receptor-stimulated Ras–ERK pathway, whereas Rac1 stimulates PAK1, which signals to JNK1. Both ERK and JNK stimulate expression of genes that initiate progression into the G1 phase of the cell cycle (cyclinD, c-myc, etc.).
FAK-mediated regulation of cell cycle inhibitors
Focal adhesion sites also regulate the expression of the cell cycle inhibitor p27KIP, which plays a dual role in cell cycle regulation. At low levels it promotes progression through G1 because it stabilizes the complexes of cyclin D with CDK4 or CDK6, and it enhances nuclear retention, resulting in a more effective phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein. At high concentrations
it blocks proliferation by inhibiting the activity of the cyclin complexes. Replacement of FAK with a kinase-dead mutant blocks DNA synthesis due to growth factors and this coincides with sustained elevated levels of p27KIP.
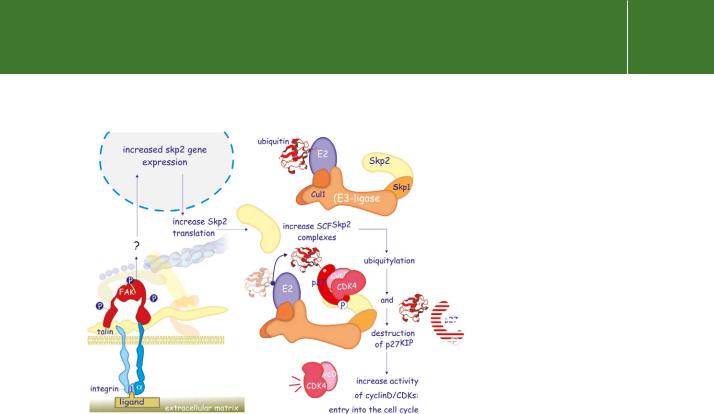
FAK effectively controls the expression level of p27KIP by stimulating its destruction. More directly, it acts to induce Skp2, the receptor component of one of the different SCF E3-ubiquitylation complexes. The elevated levels of
404
Signal Transduction to and from Adhesion Molecules
FIG 13.19 Regulation of destruction of p27KIP by the integrin signalling complex. Increased expression of Skp2, due to activated FAK, enhances the formation of the ubiquitin ligase complex SCFSkp2. Skp2 is the receptor component of this complex and it selectively binds (phosphorylated) p27KIP, leading to its polyubiquitylation and destruction. The cells thus lose a cell cycle inhibitor, so favouring entry into G1 phase.
Skp2 augment the assembly of SCFSkp2 complexes and this targets p27KIP for ubiquitylation and destruction by the proteasome105 (see Figure 13.19).
FAK-mediated activation of growth factor receptors
Growth factor receptors certainly play a role in the activation of integrins, but the reverse is also true.34,106 A good example is the interaction between the integrin V 3 and the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR).
Adherence to extracellular matrix causes phosphorylation of four tyrosine residues on the EGFR in a manner dependent on the adaptor protein CAS and the kinase Src. The number of receptors activated and the number of tyrosines phosphorylated is less than that induced by EGF, and there is a failure to achieve a full proliferative response. Addition of EGF then phosphorylates a further tyrosine and so it seems that the full response to low-level stimulation by EGF requires the additional integrin-mediated phosphorylation of the receptor.107 The importance of this interplay between integrins and growth factor receptors is accentuated by the finding that integrin 6 4 amplifies the transformation of breast cancer cells that over-express the ErbB2 receptor. This amplification occurs through Src-mediated phosphorylation of ErbB2108
405

Signal Transduction
(see Figure 13.18a) though the tyrosine residue in question is not normally phosphorylated by the EGFR itself (see Figure 12.5 page 322, and page 323). Src also phosphorylates the transcription factor STAT3, a process that relates to enhanced invasiveness of epithelial cells.
list of abbreviations
Abbreviation |
Full name/description |
SwissProt entry |
Other names/OMIM |
|
|
|
|
115RhoGEF |
Rho guanine nucleotide exchange |
Q92888 |
|
|
factor 115 kDa |
|
|
|
|
|
|
actinin- |
|
P12814 |
F-actin cross-linking protein |
|
|
|
|
Bad |
Bcl2-associated death promotor |
Q92934 |
Bcl2 antagonist of cell death |
|
|
|
|
C3G |
Crk SH3-binding guanine nucleotide |
Q13905 |
RapGEF1 |
|
release protein |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cadherin-1 |
Ca2 -dependent adherence |
P12830 |
E-cadherin, Uvomorulin |
CAS |
Crk-associated substrate |
P56945 |
p130CAS |
|
|
|
|
caspase-9 |
cystein-containing aspartate cleaving |
P55211 |
ICE-like apoptotic protease 6 |
|
protease |
|
|
|
|
|
|
catenin- |
|
P35221 |
cadherin-associated protein |
|
|
|
|
catenin- |
|
P35222 |
|
|
|
|
|
catenin- |
|
O60716 |
p120ctn |
|
|
|
|
CD |
cluster of differentiation |
|
CD56, NCAM140 |
|
|
|
|
CD44 |
cluster of differentiation-44 |
P16070 |
Hermes antigen, Epican |
|
|
|
|
CELSR1 |
Cadherin EGF LAG Seven-pass |
Q9NYQ6 |
flamingo homologue 1 |
|
Receptor-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
claudin-4 |
|
O14493 |
CPE-receptor |
|
|
|
|
Crk |
C10 regulator of kinase |
P46108 |
p38 |
|
|
|
|
cyclinD1 |
|
P24385 |
PRAD1 and BCL-1 oncogene |
|
|
|
|
desmocollin |
|
Q08554 |
desmosomal glycoprotein-2/3 |
|
|
|
|
desmoglein |
desmosomal glycoprotein-1 |
Q02413 |
|
|
|
|
|
desmoplakin |
desmosomal plaque protein |
P15924 |
|
Continued
406
Signal Transduction to and from Adhesion Molecules
Abbreviation |
Full name/description |
SwissProt entry |
Other names/OMIM |
|
|
|
|
ELAM-1 |
endothelium leukocyte adhesion |
P16581 |
CD62E, E-selectin |
|
molecule-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ERBB2 |
erythroblastoma-B2 |
P04626 |
Neu proto-oncogene, human |
|
|
|
EGF receptor-2 (Her2), |
|
|
|
MIM:164870 |
|
|
|
|
ERBB3 |
erythroblastoma-B3 |
P21860 |
human EGF receptor-3 (Her3), |
|
|
|
MIM:190151 |
|
|
|
|
FAK-1 |
focal adhesion kinase-1 |
Q05397 |
pp125FAK |
|
|
|
|
FAT |
focal adhesion targeting domain (in |
|
|
|
FAK) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
FERM |
domain found in four point 1, ezrin, |
|
|
|
radixin and moesin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Flamingo |
see www.sdbonline.org/fly/ |
Q9V5N8 |
starry night, stan |
|
dbzhnsky/starynt1.htm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
FoxO1 |
forkhead box protein 01 |
Q12778 |
FKHR |
|
|
|
|
glut4 |
glucose transporter-4 (insulin |
P14672 |
|
|
responsive) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Grb2 |
growth factor receptor bound |
P62993 |
|
|
protein-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ICAM-1 |
inter cellular adhesion molecule-1 |
P05362 |
CD54 |
|
|
|
|
IGS4B |
immunoglobulin superfamily-4 |
Q8N126 |
|
|
|
|
|
integrin L |
|
P20701 |
CD11a, LFA-1 achain |
|
|
|
|
integrin V |
|
P06756 |
CD51, vitronectin receptor |
|
|
|
|
integrin 2 |
|
P05107 |
CD18, LFA-1, p150/95, C3 |
|
|
|
|
integrin 3 |
|
P05106 |
GPIIIa |
|
|
|
|
JAM1 |
junctional adhesion molecule-1 |
Q9Y624 |
|
|
|
|
|
LARG |
leukemia-associated RhoGEF |
Q9NZN5 |
|
|
|
|
|
LFA-1 |
lymphocyte function antigen |
P20701 |
CD11a, aLb2 |
|
|
|
|
LYVE |
lymphatic vessel endothelial |
Q9Y5Y7 |
|
|
hyaluronic acid receptor-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mac-1 |
macrophage-1 |
P11578 |
M( 2), CD11b(CD18) |
Continued
407

Signal Transduction
Abbreviation |
Full name/description |
SwissProt entry |
Other names/OMIM |
|
|
|
|
Mdm2 |
mouse double minute-2 protein |
Q00987 |
E3-ubiquitin protein ligase |
|
|
|
|
NCAM-1 |
neural cell adhesion molecule-1 |
P13591 |
|
|
|
|
|
p27KIP |
(cyclin-dependent) kinase inhibitory |
P46527 |
|
|
protein of 27 kDa |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PAK1 |
p21-activated kinase-1 |
Q13153 |
|
|
|
|
|
PECAM |
platelet endothelial cell adhesion |
P16284 |
|
|
molecule, CD31 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PI 3-kinase p110 |
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase protein |
P42336 |
|
|
110 kDa |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PI 3-kinase p85 |
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
Q92569 |
|
|
regulatory subunit protein 85 kDa |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PKB |
protein kinase B alpha |
P31749 |
Akt1, C-Akt |
|
|
|
|
plectin-1 |
|
Q15149 |
hemidesmosomal protein-1 |
|
|
|
|
Rap1A |
ras-related protein-1A |
P62834 |
Krev-1 |
|
|
|
|
RapL |
regulator for cell adhesion and |
QWWW0 |
ras association domain- |
|
polarization in lymphoid tissues |
|
containing protein 5 |
|
|
|
|
Rbx1 |
Ring Box protein-1 |
P62877 |
Roc1 |
|
|
|
|
RhoA |
ras homologue-A |
Q9QUI0 |
|
|
|
|
|
Riam |
rap1-GTP interacting adaptor |
Q7Z5R6 |
amyloid beta (A4) precursor |
|
molecule |
|
protein-binding |
|
|
|
|
Selectin-E |
|
P16581 |
CD62E, ELAM |
|
|
|
|
Selectin-L |
|
P14151 |
CD62L, LECAM, LAM-1 |
|
|
|
|
Selectin-P |
|
P16109 |
|
|
|
|
|
SIGLEC-12 |
sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin |
Q96PQ1 |
|
|
proteins |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Skp2 |
S-phase kinase-associated protein-2 |
Q13309 |
F-box protein/LRR-repeat |
|
|
|
protein1 |
|
|
|
|
Sos1 |
son of sevenless-1 |
Q07889 |
RasGEF |
|
|
|
|
Src |
Sarcoma |
P12931 |
p60Src, c-Src |
|
|
|
|
STAT3 |
signal transducer and activator of |
P40763 |
|
|
transcription-3 |
|
|
Continued
408
