
- •In general…
- •2. Составьте словосочетания:
- •In particular… dentistry
- •In particular … pediatrics
- •1. Study the words in the box. Match nouns in 1 with nouns in 2 to make compounds nouns.
- •2. Study the phrases in the box. Complete each phrase with one word.
- •3. Read extracts a-f.
- •4. Look at the pictures, showing a journey through a&e (Accident and Emergency). What happens at each stage?
- •1. Which of the instruments above is needed for each of the following procedures?
- •2. A surgeon is talking to a medical student about assisting at operations. Complete his advice using words from a, b and c above.
- •In particular…
- •In particular… pediatrics Acute Respiratory Infections in Children
- •1. Сопоставьте следующие английские слова с однокоренными русскими. Обратите внимание на совпадение или расхождение объема значений:
- •3. Назовите русские термины общего корня:
- •4. Переведите без словаря:
- •6. Укажите форму множественного числа следующих английских терминов, которые сохранили свои латинские или греческие окончания:
- •7. Назовите английские слова одного корня со следующими русскими словами:
- •8. Выпишите из текста все слова, значение которых вы определили по сходству со словами латинского или русского языков и проверьте по словарю совпадение или расхождение их значений:
- •1. Match the words to make fix phrases.
- •2. Study the words and phrases in the box. Match the beginning and the ending to make set pharases.
- •5. Read the extract from the Hadford University handout about public health in the us.
- •6. Match the words in italics from ex.5 with the following definitions. Use the dictionary to check words you don’t know.
- •7. Complete the table with any derivatives of the following:
- •3.2. Лексические значения суффиксов и префиксов.
- •1. Выделите суффиксы. Определите, к какой части речи относятся слова с этими суффиксами:
- •3. Определите значения следующих слов по словообразующих элементам и сходству их корней с русскими и латинскими корнями:
- •Information Leaflet.
- •Verbs The words listed in the table below are nouns. What are the verb forms of these nouns?
- •1. Проанализируйте перевод следующих терминов и терминологических словосочетаний, обозначающих качественные и количественные характеристики (при необходимости используйте словарь):
- •2. Переведите следующие термины и терминологические словосочетания, используйте приведенные ниже тэ, обозначающие месторасположение, направление и время.
- •Implications of mapping the human genome.
1. Which of the instruments above is needed for each of the following procedures?
- making an incision - keeping the sides of the wound open - cutting sutures - holding the cut ends of blood vessels before they are tied
2. A surgeon is talking to a medical student about assisting at operations. Complete his advice using words from a, b and c above.
An ____must be able to carry out the following tasks to help the surgeon. Firstly, he or she must help in ___the patient and putting the ____in place to provide _______conditions. Expert handling of a ___is essential to allow the surgeon to see what he is doing. The assistant must also keep the operation site free of blood, by careful use of the tying and cutting _____, and with the insertion of a _____, if necessary. Finally, the assistant may be asked to close the wound with ____or other devices.
3. Find words in C and D opposite with the following meanings: - cut into pieces -correct (something that was damaged) - freed from surrounding tissues - removed by cutting out - spread of liquid into an area - making sure something is not damaged - small metal devices to hold the edge of a wound together - unnecessary - sewing up of the wound - flat, thin pieces of tissue that lie on top of one another
In particular…
DENTISTRY Management of acute dental pain
General medical practitioners are often called upon to manage acute dental pain in emergency situations, for example, out of hours or in rural areas, where it may not be possible for a dentist to provide immediate treatment. Common acute oral problems are usually easy to diagnose. Simple management can alleviate pain and further discomfort until a dentist can be called upon.
Most problems can be identified by the history and examination. Several dental conditions have typical symptoms with different types of pain.
When investigating acute dental pain, the history should focus on the pain's: location, type, frequency and duration, onset, exacerbation and remission (for example the response to heat or cold), severity, area of radiation. Associated pathology and referred pain should also be considered. Common types of oro-facial pain likely to cause a patient to seek emergency care are categorised in the box below. The character of the pain can point to a diagnosis.
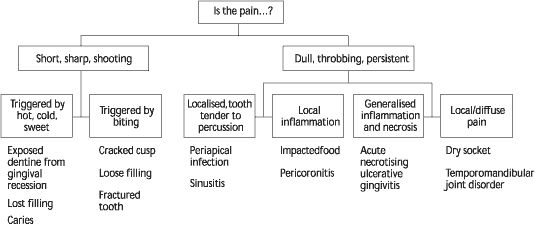 There
are several simple tests that may assist in diagnosis of dental
pain.
Some of the most commonly used tests are the following
-Pulp
sensitivity test
Dry ice, or an ordinary ice stick (made in a
plastic or glass tube), is placed on the cervical third (neck region)
of the tooth crown. A response to the stimulus indicates that the
pulpal tissue is capable of transmitting nerve impulses. No response
may indicate pulp necrosis.
There
are several simple tests that may assist in diagnosis of dental
pain.
Some of the most commonly used tests are the following
-Pulp
sensitivity test
Dry ice, or an ordinary ice stick (made in a
plastic or glass tube), is placed on the cervical third (neck region)
of the tooth crown. A response to the stimulus indicates that the
pulpal tissue is capable of transmitting nerve impulses. No response
may indicate pulp necrosis.
-Percussion test Using an instrument handle, the tooth is tapped in the longitudinal axis. A painful response suggests possible periapical inflammation.
If it is possible to obtain a screening radiograph, such as an orthopantomograph (OPG), this may assist in the diagnosis and localization of the cause of the pain. The radiograph should show clearly the apical and periapical structures of teeth and associated tissues. The relationship of the maxillary molars and premolars to the floor of the maxillary sinus can be examined, and radiographs may reveal recurrent caries or periapical radiolucencies associated with an established infection.
While antibiotics are appropriate in the management of certain dental infections, they are not indicated if the pain results from inflammatory (non-infective) or neuropathic mechanisms. The degree of pain is not a reliable indicator of acute infection.
⃰ Acute Dental Trauma
Acute dental trauma is a serious injury to one or more parts of your mouth. Your injury may include damage to any of your teeth, the tooth socket, the tooth root, or your jaw. You can also have injuries to the soft tissues of your mouth. These include your tongue, cheeks, gums, and lips. Severe injuries can expose the soft pulp inside the tooth.
Dental trauma usually occurs from a direct hit to your mouth or jaw. Accidents, such as falling off a bicycle or a car accident can cause dental trauma. A direct hit can also happen during sports activities.
The signs and symptoms of acute dental trauma are the following: tooth damage, bleeding or bruising, facial fracture, tooth or bite change.
Treatment will depend on the type of dental trauma. A tooth that moves slightly may heal on its own. A soft tissue wound may be closed using stitches.
Tooth repair procedures can be beneficial as well as any of the following: pain medicine, antibiotics, Td vaccine (diphtheria and tetanus) and mouthwash.
Without treatment, you an infection may develop. A tooth may also become discolored or stay out of place. A chipped tooth with a sharp edge may cut the tongue or other soft tissues around it or the patient may lose one or more teeth.
