
Инновационные процессы в исследовательской и образовательной деятел
..pdf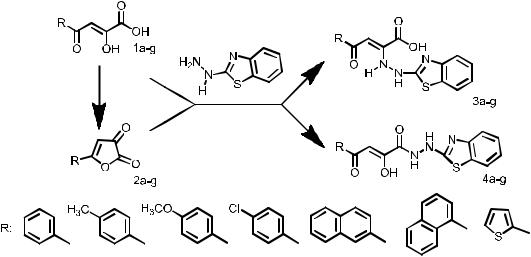
Fig. Scheme of synthesis of 2-hydrazinobenzo[d]thiazole derivatives
The most likely kinds of biological activity of compounds according to PASS Online
Compounds 3a-g |
Compounds 4a-g |
Arylacetonitrilase inhibitor |
Mcl-1 antagonist |
Mucomembranous protector |
Gluconate 2-dehydrogenase |
|
(acceptor) inhibitor |
Gluconate 2-dehydrogenase |
Mucomembranous protector |
(acceptor) inhibitor |
|
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol |
|
phospholipase D inhibitor |
|
The results of computer prediction indicate that benzo[d]thiazole derivatives are potent biologically active compounds with anti-ulcer and anti-cancer action. The pharmacological effect in vivo of obtained compounds is going to be the next investigation step.
References
1.Синтез и биологическая активность новых производных 1,3- бензотиазола / Н.А. Пулина [и др.] // Химико-фармацевтический журнал. – 2014. – Т. 48, № 8. – С. 20–23.
2.Оценка перспективности поиска биологически активных соединений
вряду производных 4-R-2-гидрокси-4-оксо-2-бутеновых кислот / А.С. Кузнецов [и др.] // Глобальный научный потенциал. – 2013. – № 4 (25). – С. 8–11.
3.Предсказание спектров биологической активности органических соединений с помощью веб-ресурса PASS Online / Д.А. Филимонов [и др.] // Химия гетероциклических соединений. – 2014. – № 3. – С. 483–499.
51

M.V. Lantsova
Perm National Polytechnic Research University
ELECTRONIC DOCUMENT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM: SOME PROBLEMS OF IMPLEMENTATION
Document management software is widely used for office paper management and related workflows. However, this paper comments briefly on some special problems connected with software implementation. This study is an attempt to select the main problems and find their solutions in the production company “Iskra”.
Key words: Electronic Document Management System (EDMS), implementation, software, end-user, compatibility, IT-specialist.
EDMS is needed by many organizations to properly manage large volumes of physical documents. Without the use of this system it is almost certain that management of documents will lead to human errors [1].
When this Management System is implemented a lot of problems arise such as technical and end-user’s problems.
The main stages of the software implementation are the following:
1.Examination of the market, development of technical specifications, purchasing the software;
2.System testing, trial maintenance, installation, adjusting and checking software [2].
This Management System (EDMS) was tested and implemented in the production company “Iskra”. Some negative trends were being observed during this process. They are: a big number of end-users (more than 2000), availability of three software platforms (Win 7 x32, x64, WinXP x32) and additional requirements, connected with software compatibility. All these aspects lead to the increase of commitments and amount of work to be done by one technician (Figure).
Fig. The increase of loading to be done per person
52
A survey was conducted between the employers of engineering, technological and design departments of the company “Iskra”. In the result we received subjective opinions of the people who used different software products.
A study of the implementation problems included into this survey has been done. The problems were divided into two groups: technical and end-users’ ones.
We start with technical problems of implementation, they are:
–the lack of full-time for testing PC preloaded with WIN XP, WIN 7 (x32, x64);
–setting up various software; configuring network installation with the use of network installation Group Policy (CAD Compass 13) or manual installation (Microsoft Office 2010);
–tuning software for the end-user.
Labour analysis of IT-specialists shows that there were many negative tendencies in the process of their recent implementation. They are as follows:
–increasing the nomenclature of the supported software without increasing the number of IT specialists;
–increasing the number of operations on software implementation with the support of two operation systems;
–there is no division in the responsibilities between IT specialists: the same people are engaged in technical support, installation, setup and testing.
To solve the technical problems it is necessary to write instructions and rules for users, to explain the reasons and aims of implementations to users, to monitor the use of the software licenses [3].
Now we shall describe the end-users problems (according to the results of inquiry). It is possible to reveal the following problems connected with the ultimate user. They are:
–the complexity of work without learning new software (for example, Office 2010, Compass 13);
–misunderstanding the reasons for the introduction of new software products; negative reaction to the introduction of the increase in labour input;
–lack of middle managers support;
–difficulties, connected with technical support. It takes a lot of time to solve all users’ problems.
There are several solutions to these problems: on one hand, organization of the centralized annunciator for users, on the other hand, distribution of IT specialist’s duties. It is very important to organize the technical support and training courses for employers to practice using software products.
53
Two points of view do not contradict, but complement each other. Apart from this, it is necessary to develop a set of measures aimed at division of labour. It is very important to organize monitoring the license use. Finally, the results of implementation should evaluate its effectiveness in the form of questionnaires, tests, etc.
The aforesaid decisions allow to improve the quality of IT-service in this production company “Iskra”.
References
1.Heckman J. Why document management: a white paper [Электронный ресурс]. − 2015. − URL: http://www.heckmanco.com/docs/DMWhitePaper.pdf.
2.Christon E. Electronic Document Management System. World Applied Sciences Journal. – 2011. – 12 (Special Issue on Computer Applications & Knowledge Management). – P. 55–58.
3.Klischewski R. Towards an ontology for e-document management in public administration – the case of schleswig-holstein // 36th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Hawaii, USA, 6–9 January 2003. – USA. – P. 48–54.
54
V.A. Loskutnikov
Perm National Research Polytechnic University
METHODS FOR IDENTIFYING SYNCHRONOUS
MOTORS TRANSIENT PROCESSES
The paper deals with transient processes of powerful synchronous motors which turn to be long-lasting when voltage recovery and impact excitation experiments are performed. Therefore, they are highly exposed to various random factors. Identification of these processes by means of national standard methods is characterized by an intensive manpower input into oscillogram processing and a high degree of inaccuracy.
Key words: synchronous motors, transient processes, identification methods.
Operating tests are generally required for newly developed hydro and turbogenerators. They include a sudden short-circuit testing to determine reactances and time constants of a motor.
A conventional method of transient parameters identification suggests representing the currents as linear – logarithmic plots that makes it possible to determine time constants and reactances using hand methods. This is undoubtedly time consuming and incurs a lot of inaccuracies.
Identification methods
Identification method referred to in [1] is aimed at minimizing a mean – root square error of the discrete statistical model approximation for a transient component with experimental data on a relatively long section of a discrete transient process. The goal set as a part of research into transient processes and their accurate identification was achieved by means of optimization procedure with a simultaneous change in the armature current steady-state value which occurs during the transient process under the influence of various random factors.
Analog sinusoidal transient process which lasts more than 18 seconds was converted into a discrete one by means of a digital storage oscilloscope. After the peaks with 50 Hz frequency had been defined by means of algorithm the transient process was analytically transformed into discrete elements specified between the envelopes with the frequency of 100 Hz. Separation and identification of transient process components have been implemented with an extensive use of effective point samples on the basis of a valid random factor in the form of time constants. The solution of transient process components separating algorithm and identification of transient process based on the results of laboratory bench testing as a part of voltage recovery experiment are presented in [2].
According to international standards the conventional method of determining a synchronous motor’s transient parameters involves depicting one of the phase currents envelopes as presented in Fig. 1.
55
Fig 1. Stator phase current |
Fig 2. Transient envelope |
Fig 3. Subtransient envelope
Then the envelope is presented in a linear-logarithmic scale as shown in Fig. 2. Finally it is possible to identify different parameters by measuring the slop of lines and intersection of their extrapolation with the ordinates as indicated in Fig. 2 and 3.
The method under discussion is applied separately for two different time intervals:
–subtransient time interval from 0 to 100 ms,
–transient time interval from 200 to 2000 ms.
Identification in different time intervals is required to get equivalent values of all parameters considering that sub-subtransient and subtransient time constants are much smaller than a transient time constant and taking into account the exponential relationship of stator currents.
A conventional approach suggests some practical inconveniences such as the manual envelope processing as well as inadequate accuracy of extrapolation and the slop and intersection determination. Due to manual processing with its limited accuracy the results depend on a person taking measurements and are hard to be accepted from the scientific point of view.
The method suggested in [3] uses dedicated software and allows for a more accurate processing. In addition, new processing can be made right after the
56
currents have been measured without any time delay, thus assuring the commissioning engineer that the measurements were made correctly.
Conclusion
Analysis of the results obtained in [1, 2] proves that despite a considerable time constants scattering in synchronous motors bench testing the developed approach to research and identification of transient processes occurring under the influence of random factors ensures high precision and reliability.
The automated method suggested in [3] gives considerable advantages as compared to the conventional manually performed procedure of parameters identification. These advantages involve time saving, higher accuracy of processing and consequently the results consistency and reproducibility.
New methods can be successfully applied for powerful synchronous motors at lower technical and economic costs.
References
1.Sudakov A.I. Novel approaches to analysis of transition processes identification error by probability-statistical methods during sudden symmetric short-circuit tests of synchronous machines // Acta Technica CSAV (Ceskoslovensk Akademie VED). – 2013. – T. 58, № 4. – С. 381–392.
2.Вероятностно-статистические методы идентификации синусоидально возрастающих переходных процессов синхронных машин / Е.А. Чабанов [и др.] // Фундаментальные исследования. – 2014. – № 12–10. – С. 2135–2141.
3.Schwery A. Fully automated parameter identification for synchronous machines [Электронный ресурс]. – URL: http://lme.epfl.ch/ (дата обращения: 22.01.2015).
57

A.B. Maksimov, E.O. Vagin
Perm National Research Polytechnic University,
OOO “Regional rope center”, Perm
FROM THE EXPERIENCE OF MINE
HOISTING PLANT OPERATION
The experience of mining hoist operation and industrial safety expert reviews are analyzed. The most typical defects and possible causes of their initiation are presented. The schemes of crack allocation in hoisting machine drums are analyzed. The need for creation of more favourable conditions for hoisting plant operation is elicited.
Key words: hoisting machine, hoisting plant, industrial safety expert review, coiling unit, defects.
Hoisting plants whose operation life greatly exceeds the normative values have currently been operating in the majority of mines in Russia.
Any mine is a hazardous production facility. For this reason, hoisting plants operating in mines are subject to industrial safety expert review in accordance with the requirements of the Federal law “About industrial safety…” [1].
The purpose of the expert examination is to determine the possibility of further safe operation on the basis of an expert survey. It includes a thorough analysis of factual parameters and modes of operation, availability and keeping of technical and operational documentation, inspection of hoist equipment conformance to the requirements of industrial safety, assessment of hoist residual life and the effectiveness of maintenance and repair system in a mine.
A hoisting plant is one of the most critical components of the equipment for mines and coalmines. Skip hoisting plants designed to lift the rock mass from the underground workings are the most loaded.
In the course of expert surveys, special attention is paid to hoist rope coiling units. They withstand cyclic static and dynamic loads, as well as significant shortterm overloads in emergency situations or when verification of the braking system parameters with the activation of safety braking is conducted.
The drums are units which are practically not subject to replacing due to high labour costs and potential economic losses caused by such works. This fact draws special attention to the control of their actual operational condition, carrying out adjustment and alignment, repair work, and expert surveys.
The experience of hoisting machine operation and industrial safety expert reviews show that alongside with other defects the most typical are the following ones:
– cracks in the shell ring of the hoisting machine drum, as well as in the weld joints of stiffening rings and ribs to the shell ring;
58

–cracks on the working surface of the drum braking rims;
–cracks in braking beams;
–excessive wear of the hinge coupling sleeves of machine braking units, requiring timely replacement of sleeves;
–defects caused by a poor machine installation, such as inadmissible parameters of the drum shaft and reductor (engine) coincidence, chipping of the rolling contact bearing rings, white metal slide bearings, the tooth ends of toothtype couplings and others.
Crack formation in the drum shell ring and the weld joints of stiffening rings and ribs to the shell ring is an actual problem requiring the solution of safe operation of hoisting machines.
The expert organization, OOO “Regional rope center”, has been monitoring formation and propagation of cracks in hoisting machine drums as part of mine hoisting plant industrial safety examination for more than ten years.
As a result of the drum crack layout analysis of the skip hoisting machines working in different conditions in various mines, the experts determined that cracks were distributed along the inner surface of the shell ring unevenly. The vast majority of the cracks were formed in that part of the drum which was the farthest from the place of the hoisting rope attachment to the drum forehead and they were oriented along the generating shell ring (Figure).
According to the literature review on the subject and the practice of using hoisting machines the main causes of cracking are:
–cyclic static skip hoisting rope loads taken by the drum shell ring and reaching the value of more than 500 kN, as well as, dynamic loads of about 10 % or more from the static load value [2];
–high work intensity of skip hoisting (round the clock operation) [3];
–constructive imperfections of coiling units that are being eliminated in the latest models of hoisting machines [4].
Cracks in hoisting machine drums are the defect requiring timely execution of repair works for their elimination.
In accordance with the place of crack formation in the drum shell ring an appropriate repair technique is selected: welding or drilling the crack ends.
The practice of hoisting machine operation shows that the techniques used at mining enterprises today, whose aim is to eliminate crack formation, are quite effective for their further safe operation. However, the applied repair methods do not rule out the possibility of the reappearance of the above defects.
59
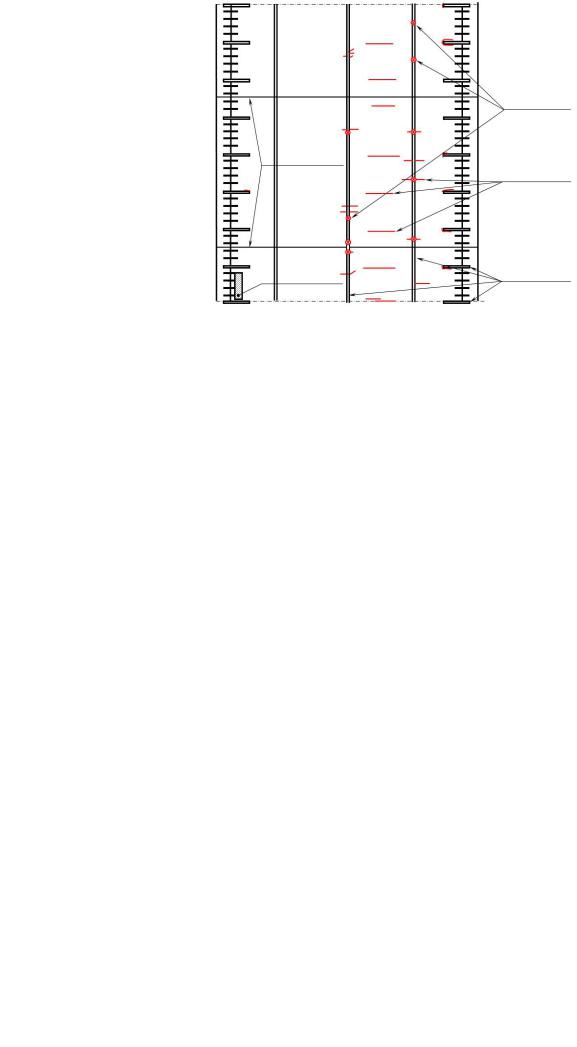
e
a
d
b |
c |
|
|
Fig. Typical locations of cracks in the shell ring of the hoisting machine drum |
|
(scan, view from inside): a – erection joints; b – rope socket; |
|
c – stiffening rings and ribs; d – cracks in the shell ring; e – cracks on ribs |
|
According to the authors, a more detailed study of causes of the crack formation in coiling units including the use of complex mathematical models of the loads taken by the drum shell ring, as well as practical testing, is actual. It can allow developing the most effective repair method and a more advanced design of hoisting machine drums.
In addition, it is recommended to perform work aimed at reducing the dynamic hoisting rope load taken by the coiling unit, which can help reduce crack formation intensity and create the most favorable conditions for hoisting plant operation, on the whole.
References
1.О промышленной безопасности опасных производственных объектов: Федеральный закон от 21 июля 1997 г. № 116-ФЗ (ред. 31.12.2014 г.).
2.Ильин С.Р., Трифанов Г.Д., Воробель С.В. Комплексные экспериментальные исследования динамики скипов рудоподъемного ствола // Горное оборудование и электромеханика. – 2009. – № 8. – С. 29–34.
3.Трифанов Г.Д. Расшифровка и анализ записей регистраторов параметров шахтных подъемных установок. – Пермь: Изд-во Перм. гос. техн. ун-та, 2009. – 154 с.
4.Шахтный подъем: научно-производственное издание / В.Р. Бежок, В.И. Дворников, И.Г. Манец, В.А. Пристром; под общ. ред. Б.А. Грядущего, В.А. Корсуна. – Донецк: Юго-Восток, Лтд, 2007. – 624 с.
60
