
- •Foreword
- •Cerebrum: Medial Views
- •Cerebrum: Inferior View
- •Basal Nuclei (Ganglia)
- •Thalamus
- •Cerebellum
- •Brainstem
- •Fourth Ventricle and Cerebellum
- •Accessory Nerve (XI): Schema
- •Arteries to Brain and Meninges
- •Arteries to Brain: Schema
- •Arteries of Brain: Inferior Views
- •Cerebral Arterial Circle (Willis)
- •Arteries of Brain: Frontal View and Section
- •Arteries of Brain: Lateral and Medial Views
- •Arteries of Posterior Cranial Fossa
- •Veins of Posterior Cranial Fossa
- •Deep Veins of Brain
- •Subependymal Veins of Brain
- •Hypothalamus and Hypophysis
- •Arteries and Veins of Hypothalamus and Hypophysis
- •Relation of Spinal Nerve Roots to Vertebrae
- •Autonomic Nervous System: General Topography
- •Spinal Nerve Origin: Cross Sections
- •Olfactory Nerve (I): Schema
- •Optic Nerve (II) (Visual Pathway): Schema
- •Oculomotor (III), Trochlear (IV) and Abducent (VI) Nerves: Schema
- •Trigeminal Nerve (V): Schema
- •Facial Nerve (VII): Schema
- •Vestibulocochlear Nerve (VIII): Schema
- •Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX): Schema
- •Vagus Nerve (X): Schema
- •Accessory Nerve (XI): Schema
- •Hypoglossal Nerve (XII): Schema
- •Nerves of Heart
- •Autonomic Nerves and Ganglia of Abdomen
- •Nerves of Stomach and Duodenum
- •Nerves of Stomach and Duodenum (continued)
- •Nerves of Small Intestine
- •Nerves of Large Intestine
- •Nerves of Kidneys, Ureters and Urinary Bladder
- •Nerves of Pelvic Viscera: Male
- •Nerves of Pelvic Viscera: Female
- •Median Nerve
- •Ulnar Nerve
- •Radial Nerve in Arm and Nerves of Posterior Shoulder
- •Radial Nerve in Forearm
- •Sciatic Nerve and Posterior Cutaneous Nerve of Thigh
- •Tibial Nerve
- •Common Fibular (Peroneal) Nerve
- •Organization of the Brain: Cerebrum
- •Organization of the Brain: Cell Types
- •Blood-Brain Barrier
- •Synaptic Transmission: Morphology of Synapses
- •Synaptic Transmission: Neuromuscular Junction
- •Synaptic Transmission: Visceral Efferent Endings
- •Synaptic Transmission: Inhibitory Mechanisms
- •Synaptic Transmission: Chemical Synaptic Transmission
- •Synaptic Transmission: Temporal and Spatial Summation
- •Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): Brain Ventricles and CSF Composition
- •Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): Circulation of CSF
- •Spinal Cord: Ventral Rami
- •Spinal Cord: Membranes and Nerve Roots
- •Peripheral Nervous System
- •Autonomic Nervous System: Schema
- •Autonomic Nervous System: Cholinergic and Adrenergic Synapses
- •Hypothalamus
- •Limbic System
- •The Cerebral Cortex
- •Descending Motor Pathways
- •Cerebellum: Afferent Pathways
- •Cerebellum: Efferent Pathways
- •Cutaneous Sensory Receptors
- •Cutaneous Receptors: Pacinian Corpuscle
- •Sensory Pathways: I
- •Sensory Pathways: II
- •Sensory Pathways: III
- •Visual System: Receptors
- •Visual System: Visual Pathway
- •Auditory System: Cochlea
- •Auditory System: Pathways
- •Vestibular System: Receptors
- •Vestibular System: Vestibulospinal Tracts
- •Gustatory (Taste) System: Receptors
- •Gustatory (Taste) System: Pathways
- •Olfactory System: Receptors
- •Olfactory System: Pathway
- •Installing Adobe Acrobat Reader 5.0
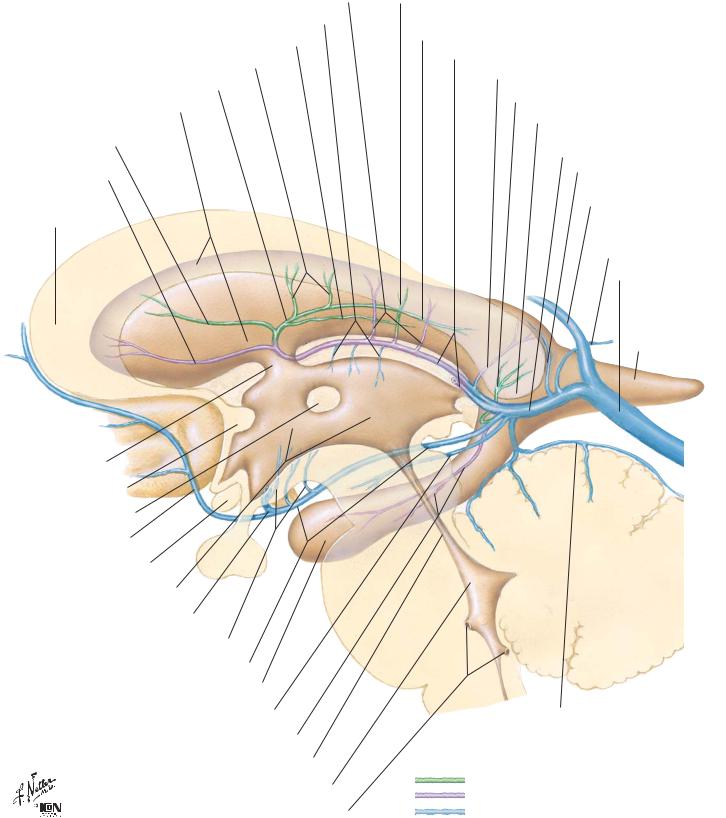
Subependymal Veins of Brain |
NEUROANATOMY |
Posterior veins of septum pellucidum
Superior thalamic veins
Superior choroid vein
Transverse veins of caudate nucleus
Superior thalamostriate vein
Lateral ventricle
Anterior vein of caudate nucleus
Anterior vein of septum pellucidum
Genu of corpus callosum
Interventricular foramen (Monro)
Anterior commissure
Interthalamic adhesion
Anterior cerebral vein
Optic chiasm
3rd ventricle Deep middle cerebral vein
Inferior thalamostriate veins
Basal vein (Rosenthal)
Temporal (inferior) horn of lateral ventricle
Posterior mesencephalic vein
Hippocampal and inferior ventricular veins
Cerebral aqueduct
4th ventricle
Lateral and median apertures of 4th ventricle
Lateral direct vein
Posterior terminal vein of caudate nucleus (posterior part of thalamostriate vein)
Internal cerebral veins (right and left)
Medial (atrial) vein of lateral ventricle
Lateral (atrial) vein of lateral ventricle
Splenium of corpus callosum
Great cerebral vein (Galen)
Dorsal vein of corpus callosum
Inferior sagittal sinus
Internal occipital vein
Straight sinus
Occipital (posterior) horn of lateral ventricle
Cerebellum
Superior vermian vein
Veins on lateral wall of ventricle
Veins on medial wall and floor of ventricle
All other veins
19
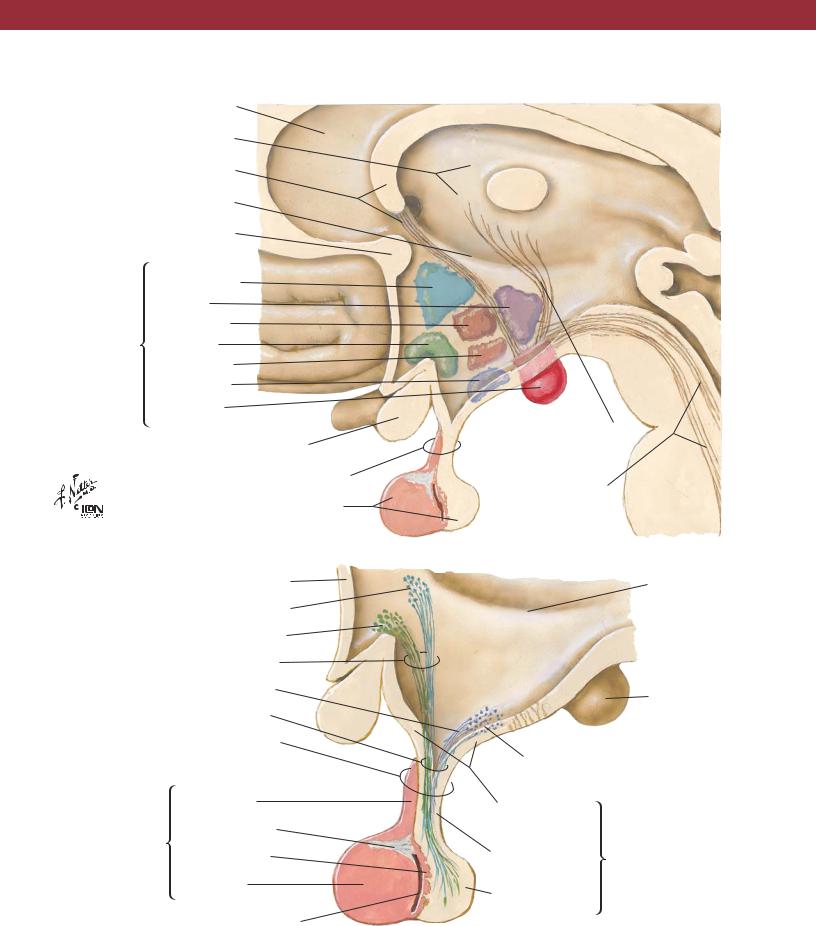
NEUROANATOMY
Septum pellucidum
Thalamus
Fornix
Hypothalamic sulcus
Anterior commissure
|
Paraventricular |
|
Posterior |
Principal |
Dorsomedial |
|
|
nuclei of |
Supraoptic |
hypothalamus |
Ventromedial |
|
|
|
Arcuate |
|
(infundibular) |
|
Mammillary |
Optic chiasm
Infundibulum (pituitary stalk)
Hypophysis (pituitary gland)
Lamina terminalis
Paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus
Supraoptic hypothalamic nucleus
Supraopticohypophyseal tract
Tuberohypophyseal tract
Hypothalamohypophyseal tract
Infundibulum (pituitary stalk)
|
Pars tuberalis |
Adenohypophysis |
Fibrous trabecula |
(anterior lobe of |
|
pituitary gland) |
Pars intermedia |
|
Pars distalis |
|
Cleft |
Hypothalamus and Hypophysis
Mammillothalamic tract
Dorsal longitudinal fasciculus and other descending pathways
Hypothalamic sulcus
Mammillary body
Arcuate (infundibular) nucleus
Median eminence of tuber cinereum
Infundibular |
Neurohypophysis |
|
(posterior lobe |
||
stem |
||
of pituitary gland) |
||
|
||
Infundibular |
|
|
process |
|
20
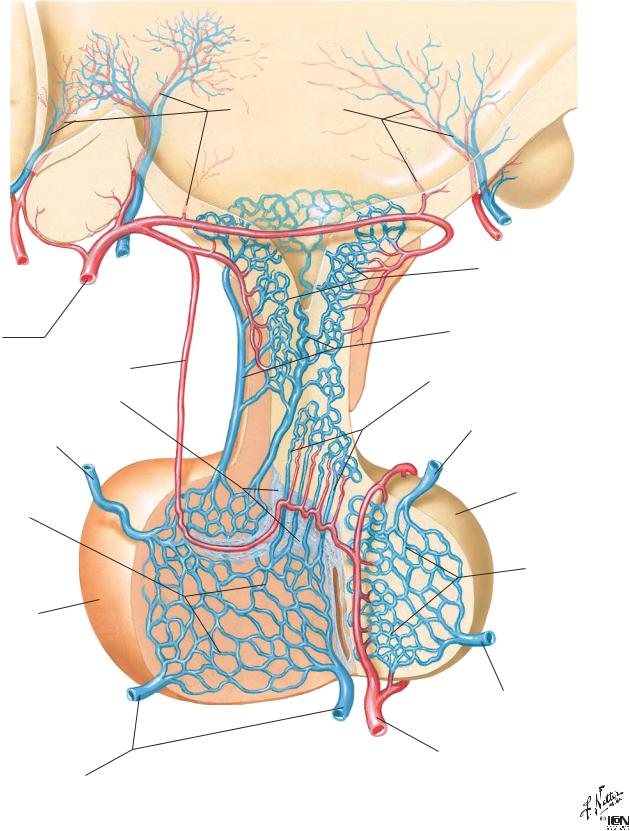
Arteries and Veins of Hypothalamus and Hypophysis |
NEUROANATOMY |
Superior hypophyseal artery
Artery of trabecula
Trabecula (fibrous tissue)
Efferent hypophyseal vein to cavernous sinus
Secondary plexus of hypophyseal portal system
Adenohypophysis (anterior lobe of pituitary gland)
Efferent hypophyseal veins to cavernous sinus
Hypothalamic vessels
Primary plexus of hypophyseal portal system
Long hypophyseal portal veins
Short hypophyseal portal veins
Efferent hypophyseal vein to cavernous sinus
Neurohypophysis (posterior lobe of pituitary gland)
Capillary plexus of infundibular process
Efferent hypophyseal vein to cavernous sinus
Inferior hypophyseal artery
21
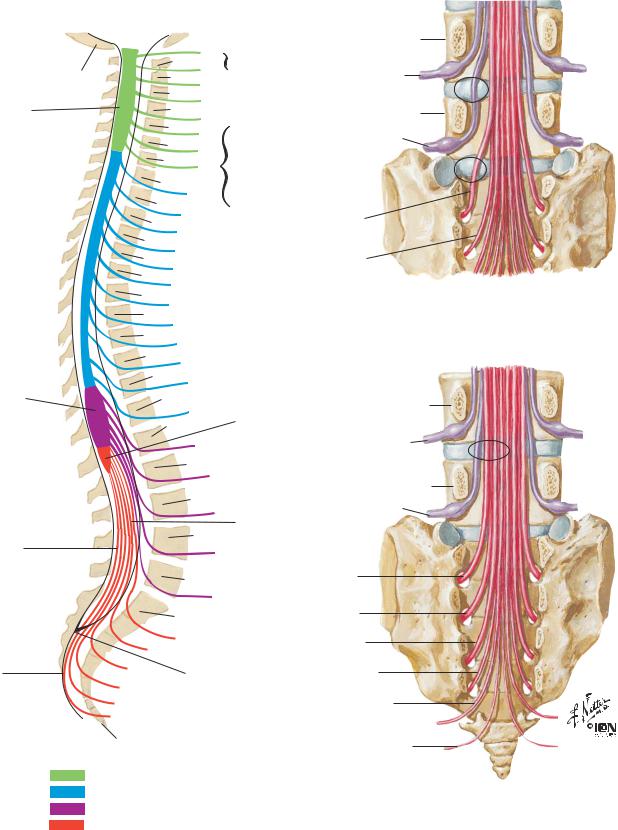
NEUROANATOMY |
Relation of Spinal Nerve Roots to Vertebrae |
Cervical enlargement
Lumbar enlargement
Internal terminal filum (pial part)
External terminal filum (dural part)
Base of skull
C1 
C1
C2
C2
C3
C3
C4
C4
C5
C5 C6
C6 C7
C7 C8
T1
T1
T2
T2
T3
T3
T4
T4
T5
T5
T6
T6
T7
T7
T8
T8
T9
T9
T10
T10
T11 T11
T12
T12
L1
L1
L2
L2
L3
L3
L4
L4
L5
L5
C1 spinal nerve exits above C1 vertebra
C8 spinal nerve exits below
C7 vertebra
(there are 8 cervical nerves but only
7 cervical vertebrae)
Conus medullaris (termination of spinal cord)
Cauda equina
L4
L4
L5
L5
S1
S2
Lumbar disc protrusion does not usually affect nerve exiting above disc. Lateral protrusion at disc level L4–5 affects L5 spinal nerve, not L4 spinal nerve. Protrusion at disc level L5–S1 affects S1 spinal nerve, not L5 spinal nerve
L4
L4
L5
L5
S1
|
Sacrum |
|
S1 |
|
S2 |
S3 |
Termination of |
|
|
S4 |
dural sac |
S5
Coccygeal nerve
Coccyx
Cervical nerves Thoracic nerves Lumbar nerves
Sacral and coccygeal nerves
S2
S3
S4
S5
Coccygeal nerve
Medial protrusion at disc level L4–5 rarely affects L4 spinal nerve but may affect L5 spinal nerve and sometimes S1–4 spinal nerves
22
