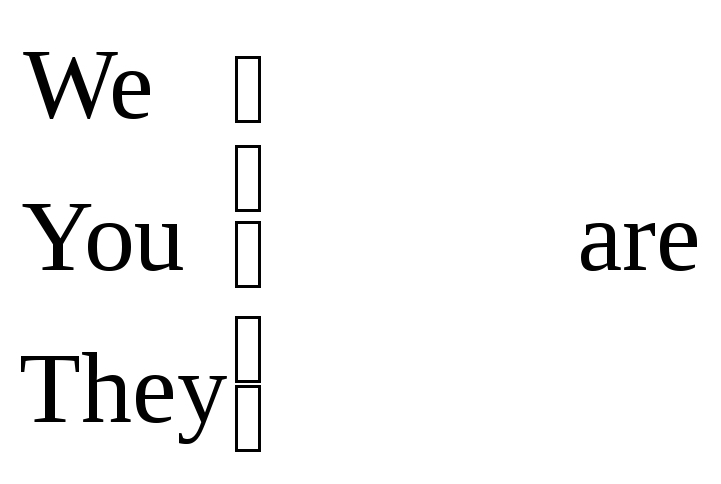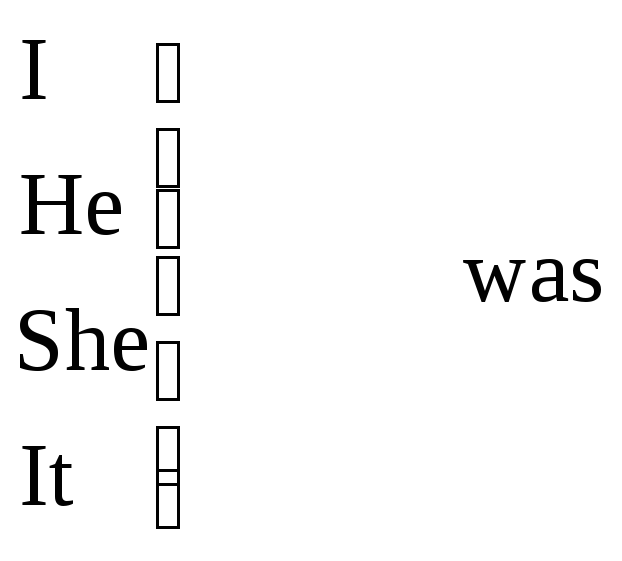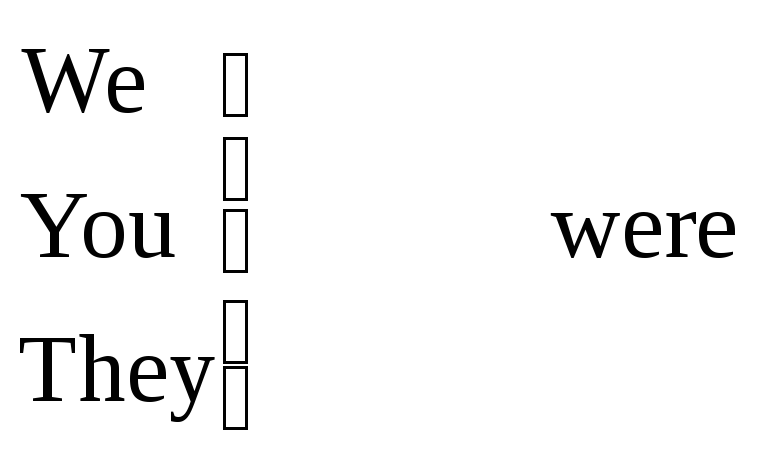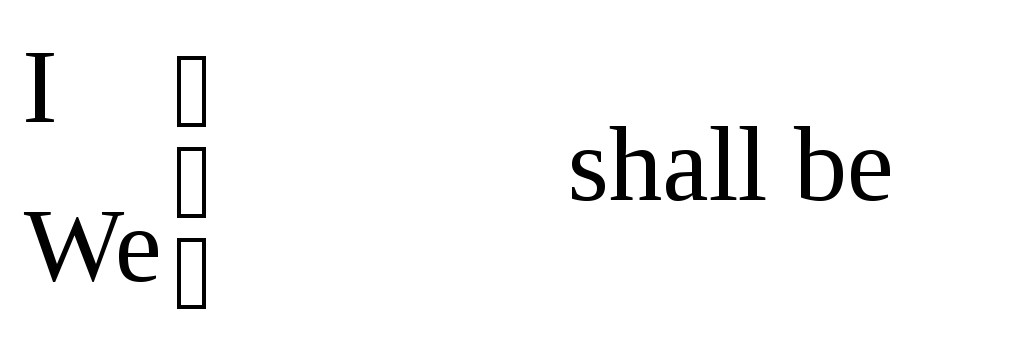- •Хакасский государственный университет
- •Part II Texts for Supplementary Reading
- •Предисловие
- •The main parts of the computer
- •Using a mouse
- •Lesson 2
- •Word-building (словообразование) (1)
- •Keyboard
- •Windows program keyboard shortcuts
- •Lesson 3
- •Buses and interfaces
- •Word-building (2)
- •Lesson 4
- •Structure (phrases)
- •A) “hardware”
- •B) “data”
- •Lesson 5
- •What is a microprocessor?
- •Pentium, pentium pro, pentium II and pentium III
- •Lesson 6
- •Word-building (3)
- •Lesson 7
- •General dram concepts
- •Structure ( 2)
- •Lesson 8
- •Storage media
- •Word-building (4)
- •Incompatible, unrecoverable, unavailable, unusable, unsuitable, non-removable, non-contiguous, non-volatile.
- •Structure (3)
- •Lesson 9
- •«Ware» terms
- •Section II. Software lesson 10
- •Structure (4) Ex.2 a) Read the sentences and analyze their structure:
- •Programming language generations
- •Lesson 11
- •Word-building (5)
- •What is object-oriented software?
- •Inheritance
- •Object-oriented languages
- •Lesson 12
- •General operating system concepts
- •Wysiwyg – structure (5)
- •Imperative sentences (commands and instructions) :
- •Starting and quitting windows nt
- •2.Using the desktop
- •Ex.5 Translate into English:
- •Ex.6 Say a few words about:
- •Revision (sructure)
- •Lesson 14
- •Ex.3 Translate into English:
- •Config.Sys commands
- •Ex.6 Agree or disagree:
- •Lesson 15
- •Ex.1 Translate the following technologies into Russian:
- •Ex.2 a) Read and translate into Russian:
- •Ex.5 Read and translate into Russian: operating system overview
- •Operating systems and file systems
- •Lesson 16
- •General database concepts
- •Ex.4 Choose the right synonym to the word ‘query’: a) requirement; b) retrieval; c) request.
- •Section III. Networking lesson 17
- •What is a network?
- •How are networks categorized?
- •How does p2p work?
- •Information transmission media
- •Lesson 18
- •Computing network components
- •Ex.10 Read and translate into Russian:
- •Ex.11 Translate into English:
- •Lesson 19
- •The internet
- •Internet protocols
- •Surfing The Net. By Shirley.
- •Lesson 20
- •Basic security and licensing terms
- •How bytes and bits work
- •System case
- •How pci works
- •Motherboard and system devices
- •Graphics adapter
- •How it works
- •System cache
- •Ethernet
- •Traditional ethernet
- •Fast ethernet
- •Gigabit ethernet
- •How a computer virus works
- •General virus types
- •All maliicous codes aren’t viruses
- •Intel software license agreement (Final, Single User) (abstract)
- •Glossary
- •Defragment
- •Device Driver
- •Formatting
- •Operating system
- •Plug-n-Play
- •Program
- •Vesa Local Bus
- •Virtual Memory
- •It Crossword Puzzle
- •Answer keys
- •It Crossword Puzzle
- •List of acronyms and abbreviations
- •1. Terms used in computer field
- •2. Basic abbreviations used in scientific field
- •3.Irregular verbs
- •Bibliography Основная литература
- •Справочная литература
Lesson 7
Text A. General DRAM Concepts.
Text B. Partitions and Volumes.
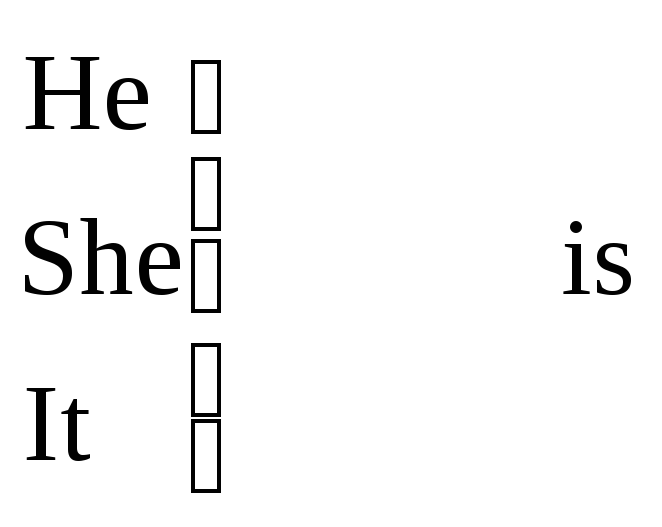
Structure. The verb -to be.
Ex.1 Read and memorize the following words:
certain [sƏ:tn] – определенный
cell [sel] – ячейка
spreadsheet [´spredʃi:t] - электронная таблица
order [´ɔ:dƏ] - порядок
sequential [sı´kwenʃıƏl] - последовательный
(to) arrange [Ə´reındʒ] – располагать, организовывать
row [rƏu] – ряд, строка
column [´kɔlƏn] – столбец
(to) specify [´spesıfaı] – специфицировать, устанавливать
(to) determine [dı´tƏ:mın] – определять
Ex.2Read and translate into Russian:
General dram concepts
"DRAM" is short for "Dynamic Random Access Memory." "Dynamic" indicates that for the memory chip to remember data, the memory chip requires every bit to be refreshed within a certain time period. When power is removed from a DRAM, the data is lost. "Random Access" indicates that each cell in the memory chip can be read or written in any order. This contrasts to a sequential memory device where data must be read or written in a certain order.
The bits of a DRAM are arranged in cells where each cell contains a specific number of bits. For example, a 4 MB x 4 Bit DRAM has four bits per cell. The cells of a DRAM are arranged like a spreadsheet and accessed by a row address and a column address. A typical DRAM access starts by specifying a row address, then specifying a column address. Next, a signal is pulled active or non-active to determine if the access is a read or a write. Then the DRAM places the data from the cell on the data output if the access is a read; or, the DRAM writes the data from the data inputs into the cell if the access is a write.
Ex.3 Translate into English:
высокоскоростная буферная память
рабочее пространство
терять содержимое
выключать
энергонезависимый
программно-аппаратные средства
постоянное питание
сигналы/импульсы обновления
передавать пакеты данных
время установки
регенерировать/переписывать
определенный период времени
каждая ячейка
в любом порядке/в определенном порядке
электронная таблица
доступ/обращение
определять
последовательное устройство памяти
данные на выходе
ввод данных
Ex.4 Make up sentences:
Size, how, will, fast, memory, programs, determines, operate.
The, is used, the contents, to read, transistor, of the capacitor.
SIMMs, in, come, pin, two, configurations: 30 pin and 72 pin, (single in-line memory modules).
Ex.5 Revise the prepositions:
For, from, with, without, within, in, to, into, on, by, per.
Structure ( 2)
Ex.6 a) Read the sentences and analyze their structure:
The queue ([kju:] - очередь) priority is invalid.
The password is shorter than required.
The computer isn't active on this domain.
The directories are unavailable.
The workstations are out of the specified resource.
The tables are full.
to be + adjective ( preposition or phrase)
|
Disk |
is |
empty |
|
Диск |
(есть) |
пустой |
|
подлежащее |
глагол-связка |
именная часть сказуемого |
|
Что? Кто? |
что делает |
каким является |
Note: in computer messages the auxiliary verb to be can be omitted (as well as the definite and indefinite articles).
e.g. The directory is empty. = Directory empty.
|
The Present Tense |
The Past Tense |
The Future Tense | ||
|
sg. |
pl. |
sg |
pl |
sg/ pl |
|
I am
|
|
|
|
|
Note : you can also use will with the first person singular and plural (I/we will)
b) Choose the sentences that suit the above given pattern:
Full disk.
Disk is full.
Incompatible diskette.
Disk unusable.
Too many files open.
Sector size too long.
File allocation table bad.
Bad diskette.
c) Use the sentences (ex.4a) in the Past and Future Tenses:
Ex.7 Read and translate into Russian:
 The
root ([ru:t] - корневой) directory is the directory that
includes all other directories.
The
root ([ru:t] - корневой) directory is the directory that
includes all other directories. The chip is very small, but it has millions of circuits.
Typical clock speeds for AT-compatibles are 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, and 20 MHz.
The first Intel "CPU on a chip" was the 4004 processor. It was more like a pocket calculator than a real computer.
A pipeline is the sequence of processing stations that decode instructions, fetch ([feʧ] - выбирать) data, perform the operation, and save the results.
Imaging is the capture ([´kæpʧƏ] - захват, сбор), storage, manipulation, and display of image.
S
 treaming
video is a sequence of "moving images" that are sent in
compressed form.
treaming
video is a sequence of "moving images" that are sent in
compressed form.Speech or voice recognition is the ability of a machine or program to recognize ([´rekƏɡnaız] - опознавать, распознавать) and carry out (выполнять) voice commands.
A
 udio
is sound within the acoustic range ([reındʒ]
- диапазон,
пределы)
available to humans.
udio
is sound within the acoustic range ([reındʒ]
- диапазон,
пределы)
available to humans. PCMCIA is an organization consisting of some 500 companies that has developed a standard for small, credit-card-sized devices, called PC Cards.
Ex.8 Read and memorize the following abbreviation and words:
DOS (Disk Operating System) - дисковая операционная система
FAT (File Allocation Table) – таблица размещения файлов
MBR (Master Boot Record [´rekƏd]) - главная загрузочная запись
active partition - активный раздел
primary [´praımƏrı] partition - первичный, основной раздел
extended partition - расширенный раздел
volume [´vɔljum]- том
(to) assign [Ə´saın]– назначать, приписывать
separate [´sep(Ə)rıt] - отдельный, раздельный, другой
location [lƏ(u)´keıʃ(Ə)n] - (рас)положение
(to) install [ın´stɔ:l] – инсталлировать, устанавливать
utility [ju(:)´tılıtı] – программа, утилита
Ex.9 Read and translate into Russian:
PARTITIONS AND VOLUMES
T he
first primary partition that contains a DOS file structure (a FAT
file system) is called thePrimary
DOS Partition
for that disk. If it is on the first hard disk, it becomes the C:
drive. Microsoft requires that DOS, Windows 95, and Windows NT store
their bootable system files on this drive. The three Microsoft
operating systems always start by loading files off the C drive.
he
first primary partition that contains a DOS file structure (a FAT
file system) is called thePrimary
DOS Partition
for that disk. If it is on the first hard disk, it becomes the C:
drive. Microsoft requires that DOS, Windows 95, and Windows NT store
their bootable system files on this drive. The three Microsoft
operating systems always start by loading files off the C drive.
One of the four partitions on the disk can be the Extended Partition. It can be subdivided into logical volumes. Each logical volume is assigned a disk letter and can be formatted with a file system.
The MBR identifies the location and size of the Extended Partition, but the MBR has no information about the logical volumes. An OS can be installed on a logical volume, but it cannot be booted directly from the MBR. You install a boot sector and some sort of Loader utility on one of the three Primary Partitions. Next, the MBR boots the Loader utility. The Loader utility can have information about the logical volumes and find an operating system stored in them.
Ex.10 Translate into Russian:
Загрузочная запись содержит ключевую информацию о диске.
Корневой каталог – это последняя часть системной области.
Таблица размещения файлов (FAT) – это набор записей, соответсвующих (tocorrespond) каждому кластеру не диске.