
- •I. Reading skills
- •2. Read and translate the following text into Ukrainian. Engineering is one of the oldest occupations in the history of mankind
- •3. Find the answers to the questions.
- •History of Mechanical Engineering
- •I. Reading skills
- •2. Read and translate into Ukrainian the following text. Engineering materials
- •3. Find the answers to the questions in the text.
- •Mechanical Properties of Materials
- •2. Listen to the text “The Materials Cycle and the Role of Materials science and Engineering” and try to understand it.
- •3. True or false statements.
- •4. Listen to the text once again and answer the following questions.
- •V. Communicative skills
- •1. The elements which are the building blocks for all materials.
- •3. Physical and some other properties of Materials.
- •Physical and Some Other Properties of Materials
- •4. Properties of Materials.
- •Analyze the table “Properties” below.
- •Resume, what do Properties of Materials imply? Tell about Mechanical, Physical, Chemical, Dimensional properties of Materials particularly.
- •I. Reading skills
- •2. Read and translate the following text into Ukrainian.
- •For structural and wear applications
- •3. Find the answers to the questions in the text.
- •4. Complete the sentences.
- •5. Match the following English words and word-combinations with their Ukrainian equivalents:
- •6. True or false statements.
- •II. Retell the text “Non-metallic Materials. Advantages and Limitations of Non-metallic Materials for Structural and Wear Application”.
- •III. Rendering
- •I. Reading skills
- •2. Read the text and translate it into Ukrainian. Metals. Iron and Steel
- •3. Find the answers to the questions in the text.
- •4. Complete the sentences.
- •5. Match the following English words and word-combinations with their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •6. True or false statements.
- •II. Retell the text “Metals. Iron and Steel”
- •III. Rendering
- •1. Read the text and translate it into Ukrainian using a dictionary. Classification of iron and steel. Methods of manufacture
- •I. Reading skills
- •2. Read and translate the following text into Ukrainian. Heat Treatment of Steels. Heat Treatment Operations
- •3. Find the answers to the questions.
- •4. Complete the sentences.
- •5. Match the following English words and word-combinations with their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •6. True or false statements.
- •II. Retell the text “Heat Treatment of Steels”
- •III. Rendering
- •1. Read the text and translate it into Ukrainian using a dictionary. Heat-Treatment Operations
- •I. Reading skills
- •2. Read and translate the following text into Ukrainian.
- •3. Find the answers to the questions.
- •4. Complete the sentences.
- •5. Match the following English words and word-combinations with their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •6. True or false statements.
- •II. Retell the text “Non-ferrous metals and their alloys. Aluminum”.
- •III. Rendering
- •1. Read the text and translate it into Ukrainian using a dictionary. Other engineering metals and their alloys
- •2. Read and translate the following text into Ukrainian. Lathes
- •3. Find the answers to the questions.
- •4. Complete the sentences.
- •5. Match the following English words and word-combinations with their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •6. True or false statements.
- •II. Retell the text “Lathes”
- •III. Rendering
- •1. Read the text about machining of metals, analyze the table and translate all the information into Ukrainian using a dictionary. Machining of metals
- •2. Read and translate into Ukrainian the following text. Cutting Tools
- •3. Answer the following questions.
- •4. Complete the sentences.
- •5. Match the following English words with their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •6. True or false statements.
- •II. Retell the text “Cutting Tools”.
- •III. Rendering
- •1. Read the text and analyze the pictures.
3. Physical and some other properties of Materials.
a) Read and remember new words:
attract [əʹtrækt] v притягувати, приваблювати
cause [kƆ:z] v спричиняти
compound [ʹkƆmpaund] n суміш
corrode [kəʹrəud] v роз’їдати, іржавіти
corrosion [kəʹrəuʒ(ə)n] n корозія
density [ʹdensiti] n щільність, концентрація
distinguish [disʹtiŋgwi∫] v відрізняти
liquid [ʹlikwid] n рідина
melt [melt] v плавити
observer [əbʹzə:və] n спостерігач
opaque [ouʹpeik] adj непрозорий, світлонепроникний
optical [ʹƆtik(ə)l] adj оптичний
patch [pæt∫] (of light) n пляма, уривок
ratio [ʹrei∫iəu] n коефіцієнт, співвідношення
resistance [riʹzist(ə)ns] n опір
solid [ʹsƆlid] n тверде тіло
specific gravity [ʹgræviti] n питома вага
thermal [ʹθə:m(ə)l] adj термальний, тепловий
b) Read and analyze the text.
Physical and Some Other Properties of Materials
Materials may be useful because of their physical and other properties. Some of these include:
Density is the weight of a material per unit volume.
Specific gravity is the ratio of the mass or weight of a solid or liquid to the mass or weight of an equal volume of water.
Melting point is the point at which a material liquefies on heating or solidifies on cooling. Some materials have a melting range rather than a single melting point.
Color is the property of light by which an observer may distinguish between two structure-free patches of light of the same size and shape.
Other properties.
Chemical properties. These have to do with how a material reacts to chemical compounds. Corrosion resistance is a chemical property. This tells how well a material resists the chemical reactions caused by air and water. Iron will corrode, but aluminum will not.
Optical properties. A material’s optical properties have to do with how it reacts to light. Opaque materials do not allow light to pass through. Some opaque materials, such as aluminum foil, reflect light.
Electrical properties. Materials that allow electricity to pass through easily are called conductors. Copper and gold are good conductors.
Thermal properties. How does a material react to heat? Those are its thermal properties. Most metals conduct heat well. They are used in radiators.
Magnetic properties. Some materials are attracted to magnets. Iron is an example. Other materials, such as aluminum, do not react to magnets at all.
c) Answer the following questions.
What Chemical properties of Materials do you know?
What are Electrical properties?
How do Materials react to heat?
What Materials are attracted to magnets?
What are Physical properties of Materials?
d) Discuss the problem of physical and other properties of materials.
4. Properties of Materials.
Analyze the table “Properties” below.
Properties
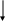
Mechanical
Hardness
Fatigue
Tensile
Impact
Creep
Wear
Stiffness
Compression
Shear
Physical
Density
Electrical
Magnetic
Conduction
Expansion
Flammability
Melting point
Chemical
Environmental resistance
Composition
Bonding
Structure
Dimensional
Flatness
Surface finish
Stability
Critical size
