
- •Микроэкономика
- •Неценовые факторы, влияющие на спрос.
- •Частичное равновесие на совершенно конкурентном рынке в краткосрочном периоде.
- •Производственная функция.
- •Издержки производства.
- •Проблемы рынка: несправедливость (неравенство доходов) и провалы рынка (внешние эффекты, общественные блага, монополизация, асимметрия информации).
- •Высокая степень дифференциации доходов и проблема бедности.
- •Кривая Лоренца и коэффициент Джини.
- •Перераспределение доходов государством.
- •Положительные и отрицательные внешние эффекты в производстве и в потреблении.
- •Роль государства в интернализации внешних эффектов: корректирующие налоги и субсидии.
- •Общественные блага.
- •Чистое общественное благо.
- •Проблема «безбилетника». Роль государства в предоставлении общественных благ.
- •Несовершенная конкуренция и эффективность рыночной модели.
- •Антимонопольная политика государства.
- •Асимметрия информации на рынках товаров.
- •Макроэкономика
- •Основные макроэкономические проблемы.
- •Макроэкономические агенты и рынки, их характеристики и основные связи между ними.
- •Доходы и расходы основных экономических агентов.
- •Кругооборот доходов и расходов: двухсекторная, трехсекторная и четырехсекторная модели кругооборота.
- •Изъятия и инъекции.
- •Система национальных счетов.
- •Основные методологические принципы СНС.
- •Основные показатели макроэкономических измерений.
- •Методы исчисления ВВП: производственный, конечного использования, распределительный.
- •Чистый национальный продукт и национальный доход.
- •Номинальные и реальные макроэкономические показатели.
- •Базовые и текущие цены.
- •Номинальный и реальный ВВП
- •Индексы цен и дефлятор ВВП.
- •Инфлирование и дефлирование ВВП.
- •Совокупный спрос.
- •Сущность совокупного спроса и его отличие от индивидуального спроса.
- •Кривая совокупного спроса.
- •Ценовые (эффект процентной ставки, эффект богатства,эффект импортных закупок) и неценовые факторы спроса; их влияние на кривую совокупного спроса.
- •Совокупное предложение и его кривая.
- •Ценовые и неценовые факторы совокупного предложения.
- •Совокупное предложение в коротком и долгом периоде.
- •Кейнсианская и неоклассическая трактовка поведения совокупного предложения.
- •Кейнсианский, промежуточный и классический отрезки кривой совокупного предложения.
- •Модель AD-AS.
- •Кривые в модели
- •Совокупный спрос
- •Совокупное предложение
- •Равновесие в модели AD-AS
- •Реальное равновесие
- •Потенциальное равновесие
- •Краткосрочное и долгосрочное макроэкономическое равновесие.
- •Понятие инфляции.
- •Измерение инфляции.
- •Открытая и подавленная инфляция.
- •Виды инфляции в зависимости от ее темпов: умеренная и галопирующая, гиперинфляция.
- •Ожидаемая и неожиданная инфляция.
- •Стагфляция
- •Инфляция спроса и издержек
- •Основные социально-экономические последствия инфляции.
- •Реальные издержки предвиденной и непредвиденной инфляции.
- •Инфляция и перераспределение богатства
- •Инфляционный налог
- •Кривая Филлипса
- •Политика занятости государства
- •Понятие денег.
- •Природа и функции денег.
- •История происхождение денег.
- •Виды денежных средств.
- •Основные типы денежных систем.
- •Денежный рынок — как часть финансового рынка.
- •Совокупный спрос на деньги.
- •Трансакционный спрос на деньги.
- •Спекулятивный спрос на деньги.
- •Функция спроса на деньги и уравнение количественной теории денег.
- •Современные теории к анализу спроса на деньги.
- •Предложение денег.
- •Денежные агрегаты.
- •Равновесие на денежном рынке.
- •Процесс расширения депозитов в банковской системе.
- •Банковский мультипликатор.
- •Денежная база и денежная масса.
- •Денежный мультипликатор.
- •Цели государственного регулирования экономики и границы государственного воздействия.
- •Основные экономические функции государства.
- •Сущность и функции налогов.
- •Налоговая система государства и ее элементы.
- •Виды налогов и их воздействие на экономику.
- •Кривая Лаффера.
- •Государственный бюджет.
- •Сбалансированность государственного бюджета.
- •Государственный долг.
- •Фискальная политика государства: понятие и виды.
- •Мультипликаторы фискальной политики.
- •Современные тенденции государственного регулирования экономики.
- •Денежно-кредитная политика
- •Основные цели кредитно-денежной политики государства:
- •Политика дешевых денег
- •Политика дорогих денег
- •Определения
- •Совокупный спрос
- •Эффект процентной ставки
- •Эффект материальных ценностей (эффект богатства)
- •Эффект импортных закупок
- •Кривая совокупного предложения
- •Инвестиции
- •Общие определения
- •Мультипликационный эффект
- •Валовой национальный продукт (ВНП)
- •Налог
- •Безработица
- •Закон Оукена
- •Дефлятор ВВП
- •Индекс потребительских цен
- •Количество денег в обращении
- •Формула Фишера
- •Количество денег в обращении
- •Норма обязательных резервов
- •Решение задач
- •Национальный доход
- •Уровень инфляции
- •Закон Оукена
- •Располагаемы доход
- •Дополнительное предлоджение денег
- •Шоки спроса и предложения
- •Расчёт кредитных возможностей банка и банковской системы
- •Формулы
- •Микро
- •Макро
- •Основные графики
- •Supply and Demand Shifts
- •Producer/Consumer Surplus
- •Price Floor
- •Price Ceiling
- •A Firm’s Cost Curves
- •Lorenz Curve
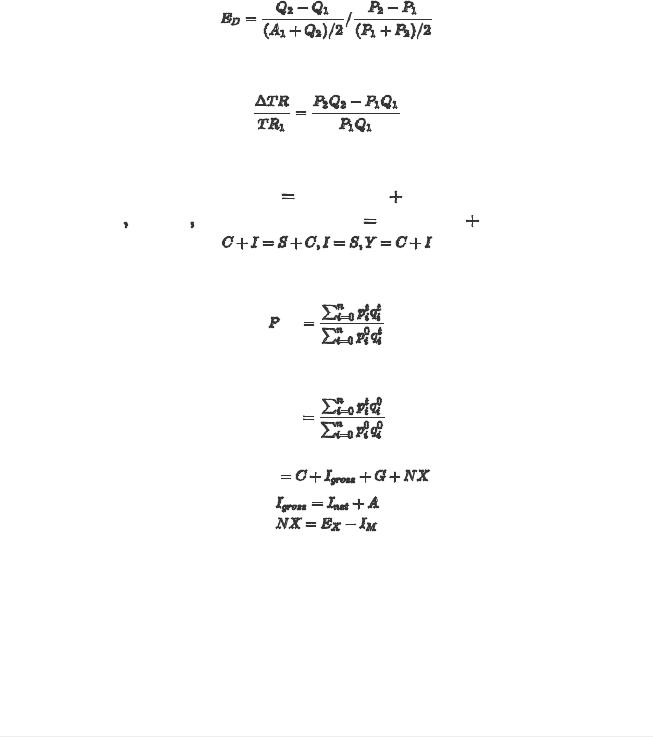
Изменение выручки фирмы в процентном выражении
Равенство доходов и расходов
Дефлятор ВВП
Индекс потребительских цен
ВНП = ВНП + ЧДФ ЧВП = ВВП - А ЧНП = ВНП - А НД = ЧНД - косвенные налоги ЛД = НД - Взносы на соц страхование - Налог на прибыль корпорации - Нераспределенная прибыль корпораций + Трансферты + Проценты, выплаченные государством по ценным бумагам - Проценты, выплаченные домохозяйствами = НД - Взносы на соц страхование - прибыль корпораций + Дивиденды + Трансферты + Проценты, выплаченные государством по ценным бумагам - Проценты, выплаченные домохозяйством
Основные графики
Production Possibilities Curve (ppc) |
Кривая производственных возмножностей |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
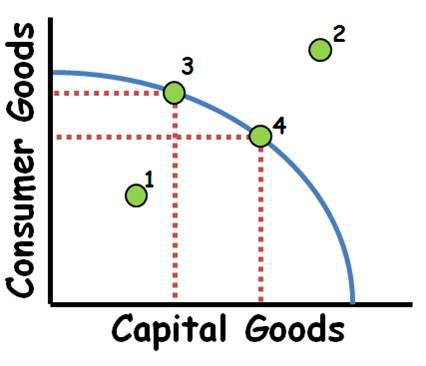
Production Possibilities Fr ontier/Curve
1. Ine cient use of resources, but it is possible to produce at this point.
2.Scarcity prevents this level of production without new resources. (trade may also make this point possible). 3 to 4 Increasing opportunity costs if PPC is concave. This is due to resources not being equally adaptable both products. For constant costs the PPC will be a straight line. •Increases in the quality or quantity of resources as well as technological improvements will shift the PPC outward. •Decreases in the quality or quantity of resources will shift the PPC inward.
Supply and Demand Shifts
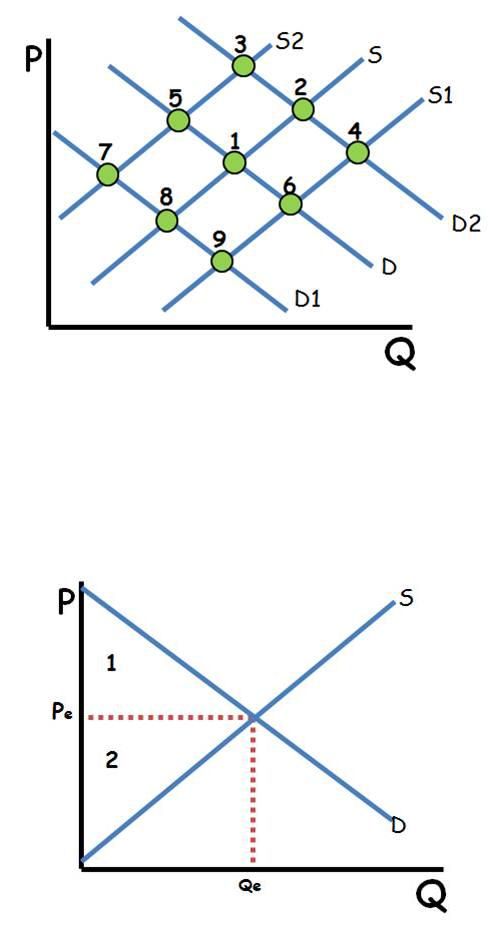
Single Shifts •Demand ↑=P ↑ Q ↑: Point 1 to 2 •Demand ↓=P ↓ Q ↓: Point 1 to 8 •Supply ↑= P↓ Q↑: Point 1 to 6 •Supply ↓= P ↑ Q↓:Point 1 to 5 Double Shifts •When 1 axis shows an increase then decrease with each shift, that axis is indeterminate. •Demand ↓ Supply ↓ P Indeterminate Q ↓:Point 1 to 8 to 7. •Demand ↑ Supply ↑ P Indeterminate Q ↑: Point 1 to 2 to 4. •Demand ↑ Supply ↓ P ↑ Q Indeterminate: Point 1 to 2 to 3. •Demand ↓ Supply ↑ P ↓ Q Indeterminate: Point 1 to 8 to 9
Producer/Consumer Surplus
•Consumer surplus is the di erence between what consumers are willing to pay (the demand curve) and the price they actually pay. It is found by taking the price consumers pay from the y axis straight across to the demand curve or the quantity exchanged (which ever is less), then going up until you hit the demand curve. •Producer surplus is the di erence between the marginal cost of production and the price. It is found by taking the price producers receive from the y axis straight across to the supply curve or the quantity exchanged (which ever is less), then going down until you hit the supply curve. 1.Consumer Surplus
2.Producer Surplus 1+2= Economic Surplus
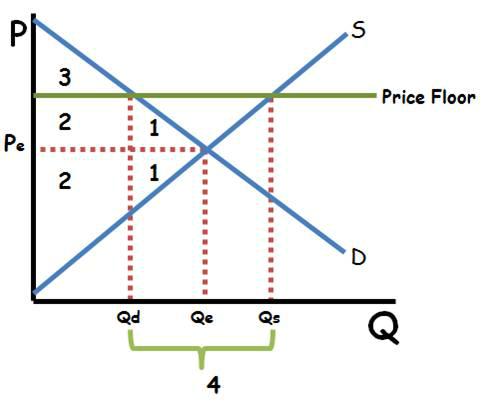
Price Floor
1.Triangle is dead weight loss 2.Producer surplus 3.Consumer Surplus 4.There is a surplus of products in the market (Qs>Qd) •The quantity that actually exchanges hands is Qd (there can be more sold than consumers are willing to buy at the current price.
Price Ceiling
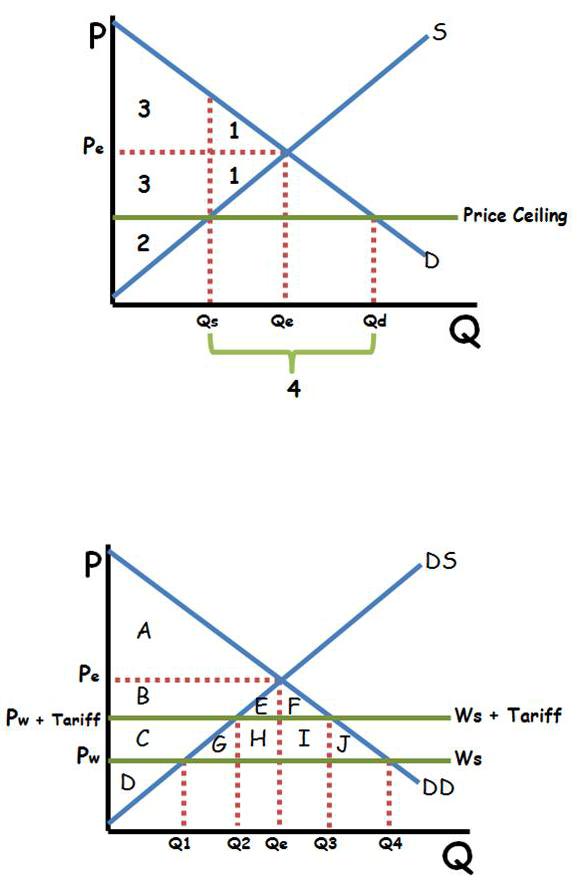
1.Triangle 1 is dead weight loss 2.Producer surplus 3.Consumer Surplus 4.There is a Shortage of products in the market (Qs<Qd) •The quantity that actually exchanges hands is Qs (there can be more sold than producers are willing to sell at the current price.
Per-Unit Tax with
no
Externalities
