
- •Nuclear safety (ядерная безопасность)
- •Nuclear facility, nuclear power plant (ядерная установка)
- •Nuclear installation (ядерная установка)
- •Nuclear fuel(ядерное топливо)
- •Nuclear material(ядерный материал)
- •Storage(хранение)
- •Dry storage (сухое хранение)
- •Wet storage (мокрое хранение)
- •Nuclear fuel cycle (ядерный топливный цикл)
- •Background (фон)
- •Fluence (флюенс)
- •Physical protection (физическая защита)
- •Safety (безопасность)
- •Nuclearsecurity(физическая/ядерная безопасность)
- •Depleted uranium (обедненный уран)
- •Enriched uranium (обогащенный уран)
- •Natural uranium(природный уран)
- •Uranium enriched in the isotope uranium-235 or uranium-233 (уран, обогащенный изотопом уран-235 или уран-233)
- •Fuel assembly (тепловыделяющая сборка)
- •Fuelelement(тепловыделяющий элемент, твэл, топливный элемент)
- •Sabotage(диверсия)
- •Regulatory body(регулирующий орган)
- •Radioactive (радиоактивный)
- •Spent fuel(отработавшее топливо)
- •Decontamination (дезактивация)
- •Fissile material(делящийся материал)
- •References
Background (фон)
The dose or dose rate attributable to all sources other than the one(s) specified. L Strictly, this applies to measurements of dose rate or count rate from a sample, where the background dose rate or count rate must be subtracted from all measurements.
---Background is used more generally, in any situation in which a particular source (or group of sources) is under consideration, to refer to the effects of other sources. It is also applied to quantities other than doses or dose rates, such as activity concentrations in environmental media [22].
---Natural background means the doses, dose rates or activity concentrations associated with natural sources or any other sources in the environment that are not amenable to control [22].
--- The highest level of background radiation is in the state of Kerala and city of Chennai in southern India, where people receive average doses above 30 millisieverts per year, or 3.42 microsieverts an hour, according to the World Nuclear Association. India has vast amounts of thorium in its soil [44].
Fluence (флюенс)
A measure of the strength of a radiation field.
---Particle
fluence, Ф. A measure of the density of
particles in a radiation field, defined as:
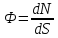 , where dN is the number of particles on a sphere of cross-section
area dS [5].
, where dN is the number of particles on a sphere of cross-section
area dS [5].
---Energy fluence, Ψ. A measure of the energy density of a radiation field,
defined
as:
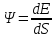 , where dE is the radiation energy incident on a sphere of
cross-sectional area dS [5].
, where dE is the radiation energy incident on a sphere of
cross-sectional area dS [5].
---In general physics, the fluence is defined as the time-integrated flux of some radiation or particle stream [25].
Physical protection (физическая защита)
Measures for the protection of nuclear material or authorized facilities, designed to prevent unauthorized access or removal of fissile material or sabotage with regard to safeguards, as, for example, in the Convention on the Physical Protection of Nuclear Material [1].
---Physical protection (also called physical security) consists of a variety of measures to protect nuclear facilities and material against sabotage, theft, diversion, and other malicious acts [17].
---Nuclear facilities that require physical protection include nuclear reactors, fuel cycle facilities, and spent fuel storage and disposal facilities [17].
---Since a terrorist can seldom be identified before the act, the first line of defense against terrorists is usually proactive physical protection of the target (a barrier between the terrorist and the target) [26].
Safety (безопасность)
The protection of people against exposure to ionizing radiation or radioactive materials and the safety of radiation sources, including the means for achieving this, and the means for preventing accidents and for mitigating the consequences of accidents should they occur [6].
---Important features of a good searching system are high sensitivity, high resolution, high scanning rates, low false alarms, and safety [26].
---Modern x-ray inspection systems, such as those found at airports, are designed to insure radiation safety [26].
---Aside from the personal safety of the individuals, it is clear that the response force must survive intact and so must be trained in tactics for the safety of its personnel [26].
