
- •T. J. Djankova, a. A. Burinskaja, s. A. Zakharenkov technology of finishing textile materials
- •1. Principal views of textile fibers
- •2. Preparation of cellulose materials for dyeing and printing
- •2.1. Bleaching of cotton textiles
- •2.2. Mercerization
- •3. Application of optical bleaches
- •3.1. Optical bleaching substances
- •3.2. Test on presence of an optical bleach
- •4. Dyeing
- •4.1. Technical classification of dyes
- •4.3. Mordant dyes
- •4.4. Acid metalline dyes
- •The abovementioned recipe and procedure of dyeing are standart and can be changed and specified according to type of the equipment and also kind of coloring material.
- •4.5. Direct dyes Direct dyes may be used for dyeing cotton and other cellulose fibers. Direct dyes simple in application, are suitable for dyeing on any equipment, well combined with each other.
- •4.6. Reactive dyes
- •4.6.1. Cellulose dyeing. Batch methods of dyeing
- •Table 4.1. Dyes Bath Composition and Dyeing Conditions
- •4.6.2. Continuous dyeing
- •4.7. Cationic dyes
- •Dyeing by fast-fixing dyes
- •Dyeing of newly-formed braid
- •4.8. Disperse dyes
- •4.9. Vat dyes
- •Indigo-molecular structure Vat Yellow-molecular structure
- •Dye. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3 % from weight of a fiber
- •4.10. Sulfur dyes
- •4.11. Azo dyes synthesized in the fiber
- •5. Printing
- •5.1. Reactive dyes printing
- •5.2. Pigments printing
- •5.3. Thermoprinting of fibrous materials
- •6. Final finishing
- •6.1. Giving to fabrics of properties of water pushing away
- •6. 2. Giving to textile cloths of oil- hidrofobization
- •6.3. Giving to fabrics of fireproof properties
- •6.4. Giving to fabrics of anti-shrinkage chemical properties, form-stable finishing
- •Application Rules
- •7. Dyeing from Emulsions
- •7.1 Auxiliaries solvents
- •7.2 Emulsifiers
- •7.3 Dyeing with water-soluble dyestuffs.
- •7.4. Basic dyeable synthetic fibers
- •7.5. Physic-chemical fundamentals of emulsion technique
- •Influence of the temperature on the stability of an emulsion
- •Influence of additives on the stability of an emulsion
- •The optical properties of a water/perchloroethylene emulsion
- •Vapour pressure of a water/perchloroethylene emulsion
- •7.6 Equipment for dyeing from organic solvents
- •8. Equipment for dyeing and finishing factories.
- •8.1. Machine for washing, bleaching and dyeing “colorado”
- •8.2. Мachine «petra» f. Biancalani For obtaining effects of “worked surface”
- •8.3. High temperature machine mcs comby jigger
- •8.4. Hydraulic drying cylinder machines “jigger jht” by exclusivas tepp s.A. (Spain)
- •8.5. Vertical high-temperature high-pressure yarn dyeing plant
- •8.6. Flow line for combined bleaching and dyeing of fabrics лкб-140
- •Specification
- •8.7. Rapidstretch
- •8.8. Technodye rapid system Main features.
- •8.9. Superflux ne
- •Finally
- •8.7. Rapidstretch 84
6. Final finishing
Final finishing can be general and special purpose. A main purpose of final furnish of general – improvement of properties to textile materials (softness or rigidity, fullness, form-stable finishing) and special purpose one – giving properties depending on service conditions (oil- hidrofobization, fireproof or antibacterial properties).
The kind of applied finishing depends on the chemical nature of a fibre and material appointment. Finishing of textiles from silk, flax, wool is simple and is usually a little connected with chemical influences on a processed material. The structure of cotton fibre allow to apply widely the preparations entering chemical reaction with a fibre without deterioration of properties of a fibre.
Processes of final finishing are subdivided on mechanical (drying, teasing, cutting and cleaning) and chemical processes are spent with use of finishing preparations. Compositions for final finishing usually divide into three groups: washed off, a little washed off and indelible. Washed off compositions leave completely after the first washing. The indelible – compositions, which leave after 5 washings no more, than on 15 – 20 %.
Procedure of finishing consists of impregnation, drying at 100-110 °C, fixation at 130-150 °C 5 – 3 min. Usually thermal processing carry out in devices of convective type. The temperature and duration of processing are defined by a finishing preparation, a kind of final finishing and initial humidity of a material before heat treatment.
6.1. Giving to fabrics of properties of water pushing away
Cellulose fibers and fabrics from them by the nature are capable to co-operate with water molecules. It is caused by presence in a macromolecule of cellulose of the big number functional groups ОН. Contacting to them, water molecules form hydrogen communications and thereof are strongly kept by a fiber.
In comparison with waterproof, products from hydrophilic fibers become soiled faster as together with water in them dust and soot particles easily get. Hence, at the message to textile materials of ability to push away water and simultaneously oil.
To eliminate the tendency of cellulose to absorption of water and to give to fibers and fabrics water-repellent properties, it is necessary for those or different way to block OH -groups of cellulose and to prevent their contact to water molecules. To solve a task in view it is possible two ways:
- drawing on a surface of a fabric of a continuous film of waterproof substances, rubbers, PVC etc. This film closes a time of a fabric and does its water-proof and simultaneously air-tight. This way is successfully realized at manufacturing of raincoats, capes, technical fabrics;
blocking of a surface of separate fibers and threads, not closing a fabric porosity. It probably to carry out condensation in a submicroscopic porosity of a fiber of a film of modified polysiloxane (PDMS), shielding OH- groups of cellulose from contact to water molecules, or by means of chemical updating OH-groups with their transformation into corresponding groupings of waterproof character.

As reagents for the message to fabrics of properties of water pushing away now most often use following connections:
- emulsion of wax, containing salts of aluminium or zirconium;
- siliconorganic substances (polysiloxane);
- organic complexes of chrome or aluminium;
- F-derivatives, for example the following:
 ,
,
Under the influence of alkali it is connection on a fibre passes in active form which reacts with cellulose According to the scheme:
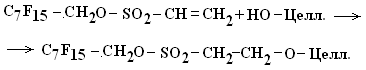
- derivative of pyridine, for example hloridestearylamino-methylpiridin - the structures containing fluorine;
- methylol derivatives of various compounds containing long alkyl chains, for example, products of condensation methylol melamine derivatives and N-oximethilstearylamide (a preparation Fobotex FTC).
Any chemical compound intended for giving to fibrous materials of waterproof properties, should possess a chain carbon and fluorine atoms and polar or other active groups by means of which hydrophobizing agent joins a fiber. On all its extensive internal surface of a molecule hydrophobizing substances settle down so, that the waterproof ends form a continuous barrier, i.e. A new waterproof surface.
At use hydrophobizing agents with a long hydrocarbonic chain the maximum effect of water pushing away is reached at presence in a chain of 16-18 carbon atoms. Longer chains tend to curling, and in the presence of shorter chains the affinity of the polar groups keeping molecules of hydrophobizing agent on a fiber negatively affects. Quality of water-repellent furnishes and water repellency degrees are estimated on following indicators:
- Water absorption which is defined by quantity of the water absorbed by a trimmed fabric at its keeping in distilled water during 1 and 60 mines;
- Quantity of the water absorbed by a fabric at overhead irrigation;
- The water penetration defined by Shoppers method on height of a water column at which fabrics on a surface are formed first three drops of water.
Silcophobe h-1022 - waterborne cationic emulsion of modified polysiloxane (PDMS) for the use as hydrophobic agent.
Solid Contents: 29.0–31.0 %
PH 4.0-5.0
For straight hydrophobizing dilution 1:3 up to 1:35 Silcophobe H-1022: water.
Alamin S based on melamine modified with fatty acids, used to communicate specific properties to the fabrics, like water-proof properties, soft filled feel, stability against multiple washings, against light and weather, higher stability against rubbing. Mass fraction of the basic substance: 45 ±2 %; toxicity moderately dangerous substance.
Application Rules
The emulsion based on the preparation is prepared by melting in hot (70 – 80 °C) water at active stirring. It is recommended to add the following chemicals into the working solution:
- alamin S 60-80;
- 40 % acetic acid 15-20;
- catalyst (magnesium chloride, ammonium chloride) 3-4.
- temperature of the solution 20 – 70 °C.
