
2015ARKH-P5-Field Development Evaluation(80s)
.pdf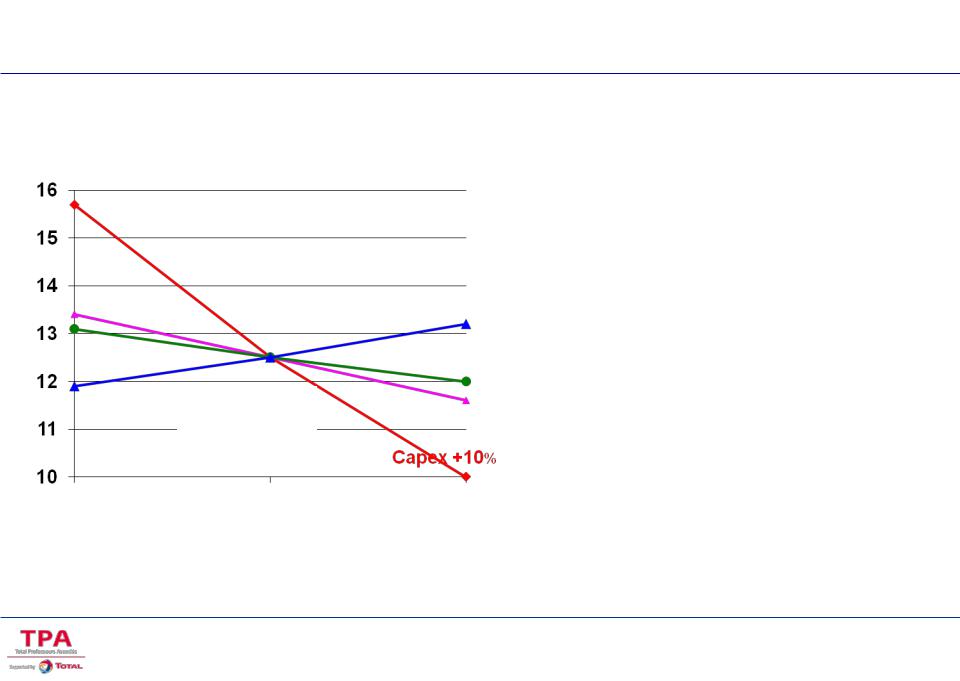
Petroleum Field Evaluation Process
Introduction to Economic Analysis
Economic model /Sensitivity
IRR %
Capex - 10 %
Opex - 10 %
BASE CASE
Loan ter +2 Y Interest Rate
© Sensibility will be analysed for various factors (very often project specific) capex, opex, interest rate, reduced
revenues,terms
Loan ter- 2 Y
©The base case scenario is a key step to be selected by the Owner
Opex + 10 %
51

Petroleum Field Evaluation Process Introduction to Economic Analysisacts
Sensitivity and scenarios analysis
The sensitivity factors considered are often project specifics. In the oil business the most commonly used are – Capex, Reserves, Opex, Oil price, Taxes.
The Opex impact on economics is often relatively limited
The impact of the installations removal (decommissioning) at the end of the field life is also limited
The impact of the schedule delays is very often underestimated.
Tuesday, 15 September 2015
52

Some Key Aspects during Development studies
53

PROJECT MANAGEMENT
DEVELOPMENT STUDY PHASES
Environmental Baseline Survey –E.B.S.
uIn order to know precisely what is the situation before implementation of the Project, it is required spending time and money to collect all environmental data.
u Existing pollution can be identified so that the Project will not be charged with it.
uExisting fauna, flora will be listed and solution to minimize the Project Impact can be initiated.
u When habitation and/or social life are already in place, it is the time to do the full inventory. u EBS can be organised and awarded as soon as the Site area is identified.
uEBS can be organised over a few months, start during the conceptual study and be completed during the preproject
54
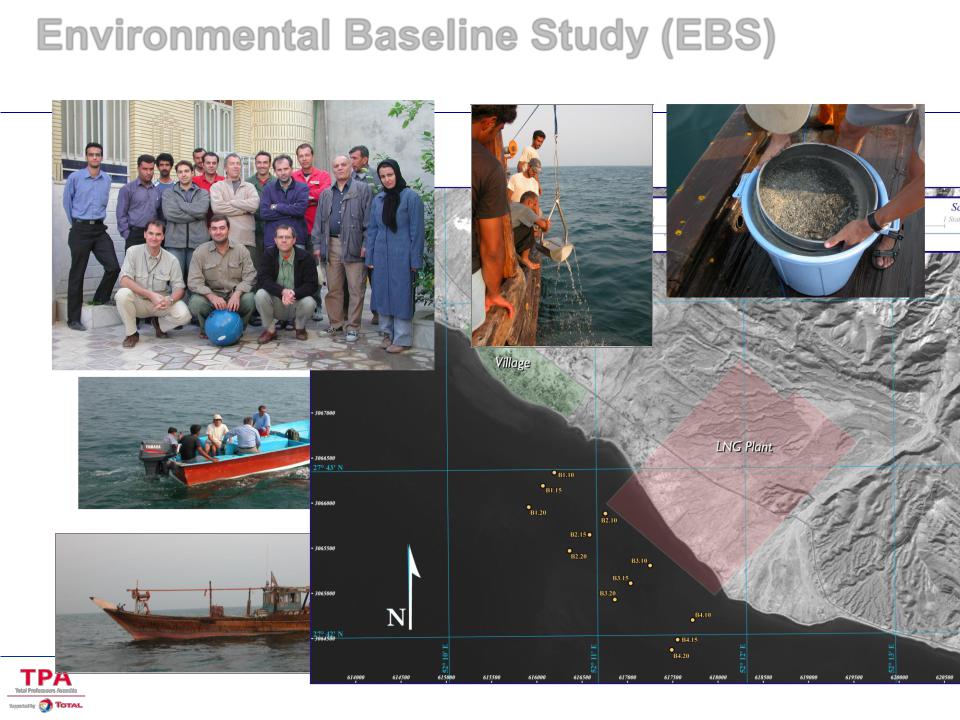
Environmental Baseline Study (EBS)
Sediment and benthic macrofauna sampling

Biodiversity
CREOCEAN-SERT, 2006
56

PROJECT MANAGEMENT
DEVELOPMENT STUDY PHASES
Operating Philosophy
Purpose of the Operating Philosophy
 The Operating Philosophy is a document prepared during the Conceptual and Pre project phases which, for a given project,
The Operating Philosophy is a document prepared during the Conceptual and Pre project phases which, for a given project,
uestablishes the COMPANY Surface Operations principles to ensure a safe, efficient and cost effective operation,
u explains the way in which the Surface Operations will be organised and carried out
uidentifies issues impacting on the installation design and requiring particular studies or definition during the engineering phases,
uis a reference document at any phase of the field development in all matters dealing with operations.
u Is part of the hand over dossier to the Operator.
uis a self-supporting document involving only necessary information. No specific details in other disciplines, such as Safety and Process
57

PRE-PROJECT: OPERATING PHILOSOPHY
Main operating principles (production, utilities, export system, control system, alarms, etc..)
HSE aspects
Metering
Laboratory and QC (Quality Control)
Staffing (Main organization chart),
Logistics means and Logistics base
Transportation issues (personnel, goods, etc…)
Opex (Operating costs) estimation
Commissioning and Start-up philosophies
58

PROJECT SANCTION or DECISION TO DEVELOP
The timing for the Decision depends of the development characteristics (oil, gas,
LNG unit ….) and the terms of the Petroleum Contract
It occurs generally after completion of the preproject study but very often the final decision to invest is postponed at the end of the Basic Engineering or FEED
(Front End Engineering Design ) for large projects
In addition a detailed risk evaluation (political, reservoir, technology
,economics,…..) is performed to back up the Decision to develop..
It can be a long and complex process as it requires operator and partners companies management and authorities approval.
Even for small projects this decision is always formalized
59

PROJECT SANCTION :
KEY CHALLENGES : HSE – HEALTH SAFETY & ENVIRONMENT
Technological risks :
Generated by toxic, flammable, explosive substances
Risks concerning individuals, environment, integrity of installations and production
Occupational risks :
Injuries or fatalities caused by the hazards in the workplace and the nature of the work
EBS & EIA
Environmental Baseline Study (EBS)
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)
60
