
2015ARKH-P5-Field Development Evaluation(80s)
.pdf
ARKHANGELSK STATE TECHNICAL
UNIVERSITY
OFFSHORE FIELD DEVELOPMENT PROCESS, CONCEPTS
AND FACILITIES
OCT 2015
---------------
PART 5 : FIELD DEVELOPMENT EVALUATION
-----------------
Daniel Saincry

TABLE OF CONTENTSPART 7 FDDP
FIELD DEVELOPMENT DECISION PROCESS
RESERVES UNCERTAINTIES
APPRAISAL PHASE & PRELIMINARY STUDIES
CONCEPTUAL STUDIES
PRE-PROJECT STUDIES
PROJECT PREPARATION & DECISION TO DEVELOP
EXAMPLE OF AN OFFSHORE FIELD DEVELOPMENT PROJECT
2

MAIN PHASES OF E&P ACTIVITIES
|
Field |
|
Exploration |
Development |
Any additional development following |
|
Appraisal |
the initial development |
|
Development Studies |
>20 y |
3 y |
||
|
|
||||
|
Preliminary |
|
|
||
|
Conceptual |
|
|
|
|
|
Pre-project |
Project |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Production profile |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
INVESTMENT |
|
|
||
|
DECISION |
|
Field |
||
1-3 y |
2-4 y |
3-4 y |
Field operations |
abandonmentTime |
|
Discovery |
“First Oil” |
End of |
Restored |
|
production Site |
||||
|
|
|||
New business
3
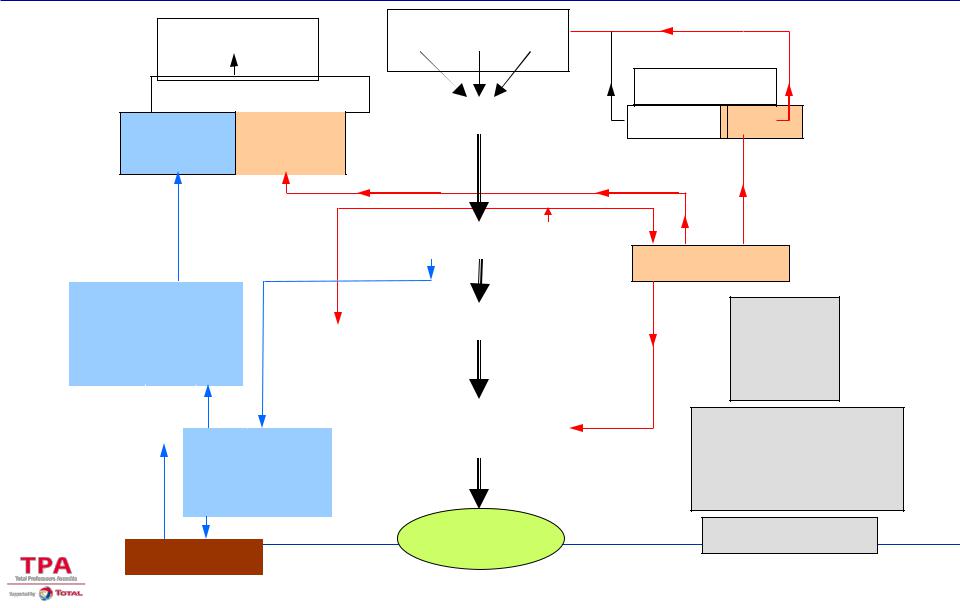
PRODUCING FIELD FUNCTIONAL DIAGRAM
Injection |
Production |
|
|
||
wells |
|
|
|||
wells |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
Enhanced recovery |
|
Artificial lift |
|||
Flowlines |
|
|
|||
Water |
Gas |
Pumping |
Gaslift |
||
|
|||||
|
|
|
|||
Injection injection
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oil & gas process |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Water injection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
Storage |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
Filtration |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Deaeration |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
HP pumping |
|
|
Flare / Vent |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Metering |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Produced |
|
|
|
|
& Export |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
water |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
treatment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tankers |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Sea / River |
|
|
Pipelines |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Compression
Utilities
Electricity
Water
Air
ESD / Safety
Gas/Fire detection Fire Fighting Emergency generator
Living quarters
4

RESERVES UNCERTAINTIES

RESERVES (1) acts
Reserves are the technically & commercially recoverable quantities of hydrocarbons trapped in the reservoir.
Each reservoir is UNIQUE.
The recovery factor of an oil reservoir is in the range of 35 % of the Original Oil In Place (OOIP), and 70 % of the Initial Gas In Place (IGIP) for a gas reservoir.
The reservoir recovery factor always depends of the reservoir exploitation/depletion method: natural flow, artificial lift, water injection, gas injection, water / gas alternate injection ………
Reserves estimations are always subject to important UNCERTAINTIES. They are estimated by using probabilistic methods & simulations.
6

RESERVES (2) acts
The PROVEN reserves = 1P or P 90 , i.e. there is a 90 % probability that the actual reserves are above P 90.
The PROBABLE (or MOST LIKELY) reserves = 2P or P 50 , i.e. there is a 50 % probability that the actual reserves are above P 50.
The POSSIBLE reserves = 3P or P 10, i.e. there is a 10 % probability that the actual reserves are above P 10.
The higher are the reservoir uncertainties, the bigger is the gap between P 90 and P 10
7

RESERVES (3) acts
Companies formal reserves as indicated to the SEC – Security & Exchange Commission – are 1 P reserves.
2P reserves are used, in most of Oil & Gas Companies, for the base case of economic simulations (providing that economics are still robust with 1P reserves), and for sizing the production facilities.
8

FIELD EVALUATION PROCESS
When an oil or gas discovery has been made, there are many key questions to answer (among many others):
What to do with this discovery ? develop/produce it, or not ?
How much oil/gas can be produced ?
Which development scheme to select ?
How much will it cost ? Is it an economical development ?
How long before production start-up ?
What are the risks ?
etc…
Development studies are performed to try to answer these questions and to hopefully be able to take a “go ahead” decision
More generally, the objective of the Field Evaluation Process is to define a development scheme allowing the optimization of the hydrocarbon recovery at the lowest cost, taking into account the reservoir uncertainties
9

FIELD DEVELOPMENT STUDIES: OBJECTIVES AND KEY ACTIVITIES
OBJECTIVES
Evaluate economic |
Preliminary Studies |
potential |
|
|
Conceptual Studies
Select development concept
Define concept |
Pre-project Studies |
Prepare for sanction |
|
|
Project
ACTIVITIES
•Appraisal requirements
•Preliminary dev. scheme
•Technical feasibility
•Preliminary planning & costs estimate
•Screening of alternatives
•Confirmation of feasibility
•Key parameters definition
•Concept selection
•Statement Of Requirements
•Facilities and wells description
•Project execution principles
•Basic & detailed
•Project economics engineering
•Procurement, Fabrication, Construction & installation, Drilling
10
