
- •Why CFD is Important for Modeling
- •How the CFD Module Helps Improve Your Modeling
- •Model Builder Options for Physics Feature Node Settings Windows
- •Where Do I Access the Documentation and Model Library?
- •Typographical Conventions
- •Quick Start Guide
- •Modeling Strategy
- •Geometrical Complexities
- •Material Properties
- •Defining the Physics
- •Meshing
- •The Choice of Solver and Solver Settings
- •Coupling to Other Physics Interfaces
- •Adding a Chemical Species Transport Interface
- •Equation
- •Discretization
- •Transport Feature
- •Migration in Electric Field
- •Reactions
- •Reactions
- •Initial Values
- •Initial Values
- •Boundary Conditions for the Transport of Concentrated Species Interface
- •Mass Fraction
- •Mass Fraction
- •Flux
- •Inflow
- •Inflow
- •No Flux
- •Outflow
- •Flux Discontinuity
- •Flux Discontinuity
- •Symmetry
- •Open Boundary
- •Physical Model
- •Transport Properties
- •Model Inputs
- •Fluid Properties
- •Diffusion
- •Migration in Electric Field
- •Diffusion
- •Model Inputs
- •Density
- •Diffusion
- •Porous Matrix Properties
- •Porous Matrix Properties
- •Initial Values
- •Initial Values
- •Domain Features for the Reacting Flow, Concentrated Species Interface
- •Boundary Conditions for the Reacting Flow, Concentrated Species Interface
- •Reacting Boundary
- •Inward Flux
- •Physical Model
- •Transport Properties
- •Fluid Properties
- •Migration in Electric Field
- •Porous Matrix Properties
- •Initial Values
- •Domain Features for the Reacting Flow, Diluted Species Interface
- •Boundary Conditions for the Reacting Flow, Diluted Species Interface
- •Pair and Point Conditions for the Reacting Flow, Diluted Species Interface
- •Multicomponent Mass Transport
- •Multicomponent Diffusion: Mixture-Average Approximation
- •Multispecies Diffusion: Fick’s Law Approximation
- •Multicomponent Thermal Diffusion
- •References for the Transport of Concentrated Species Interface
- •Domain Equations
- •Combined Boundary Conditions
- •Effective Mass Transport Parameters in Porous Media
- •Selecting the Right Interface
- •The Single-Phase Flow Interface Options
- •Laminar Flow
- •Coupling to Other Physics Interfaces
- •The Laminar Flow Interface
- •Discretization
- •The Creeping Flow Interface
- •Discretization
- •Fluid Properties
- •Fluid Properties
- •Mixing Length Limit
- •Volume Force
- •Volume Force
- •Initial Values
- •Initial Values
- •The Turbulent Flow, Spalart-Allmaras Interface
- •The Rotating Machinery, Laminar Flow Interface
- •Rotating Domain
- •Rotating Domain
- •Initial Values
- •Initial Values
- •Rotating Wall
- •Wall
- •Boundary Condition
- •Interior Wall
- •Boundary Condition
- •Inlet
- •Boundary Condition
- •Velocity
- •Pressure, No Viscous Stress
- •Normal Stress
- •Outlet
- •Boundary Condition
- •Pressure
- •Laminar Outflow
- •No Viscous Stress
- •Vacuum Pump
- •Symmetry
- •Open Boundary
- •Boundary Stress
- •Boundary Condition
- •Periodic Flow Condition
- •Flow Continuity
- •Pressure Point Constraint
- •Non-Newtonian Flow—The Power Law and the Carreau Model
- •Theory for the Pressure, No Viscous Stress Boundary Condition
- •Theory for the Laminar Inflow Condition
- •Theory for the Laminar Outflow Condition
- •Theory for the Slip Velocity Wall Boundary Condition
- •Theory for the Vacuum Pump Outlet Condition
- •Theory for the No Viscous Stress Condition
- •Theory for the Mass Flow Inlet Condition
- •Turbulence Modeling
- •Eddy Viscosity
- •Wall Functions
- •Initial Values
- •Wall Distance
- •Inlet Values for the Turbulence Length Scale and Intensity
- •Initial Values
- •The Spalart-Allmaras Turbulence Model
- •Inlet Values for the Turbulence Length Scale and Intensity
- •Pseudo Time Stepping for Turbulent Flow Models
- •References for the Single-Phase Flow, Turbulent Flow Interfaces
- •Selecting the Right Interface
- •Coupling to Other Physics Interfaces
- •Discretization
- •Fluid-Film Properties
- •Initial Values
- •Initial Values
- •Inlet
- •Outlet
- •Wall
- •Symmetry
- •Discretization
- •Initial Values
- •Initial Values
- •Fluid-Film Properties
- •Border
- •Inlet
- •Outlet
- •Conditions for Film Damping
- •The Reynolds Equation
- •Structural Loads
- •Gas Outflow Conditions
- •Rarefaction and Slip Effects
- •Geometry Orientations
- •References for the Thin-Film Flow Interfaces
- •Selecting the Right Interface
- •The Multiphase Flow Interface Options
- •The Relationship Between the Interfaces
- •Bubbly Flow
- •Coupling to Other Physics Interfaces
- •The Laminar Two-Phase Flow, Level Set Interface
- •Discretization
- •The Laminar Two-Phase Flow, Phase Field Interface
- •Domain Level Settings for the Level Set and Phase Field Interfaces
- •Fluid Properties
- •Mixing Length Limit
- •Initial Values
- •Initial Values
- •Volume Force
- •Volume Force
- •Gravity
- •Boundary Conditions for the Level Set and Phase Field Interfaces
- •Wall
- •Boundary Condition
- •Initial Interface
- •The Turbulent Flow, Two-Phase Flow, Level Set Interface
- •The Turbulent Two-Phase Flow, Phase Field Interface
- •Wall Distance Interface and the Distance Equation
- •Level Set and Phase Field Equations
- •Conservative and Non-Conservative Formulations
- •Phase Initialization
- •Numerical Stabilization
- •References for the Level Set and Phase Field Interfaces
- •Stabilization
- •Discretization
- •Level Set Model
- •Initial Values
- •Initial Values
- •Boundary Conditions for the Level Set Function
- •Inlet
- •Initial Interface
- •No Flow
- •Outlet
- •Symmetry
- •Discretization
- •Initial Values
- •Initial Values
- •Phase Field Model
- •Boundary Conditions for the Phase Field Function
- •Initial Interface
- •Inlet
- •Wetted Wall
- •Wetted Wall
- •Outlet
- •The Level Set Method
- •Conservative and Non-Conservative Form
- •Initializing the Level Set Function
- •Variables For Geometric Properties of the Interface
- •Reference for the Level Set Interface
- •About the Phase Field Method
- •The Equations for the Phase Field Method
- •Conservative and Non-Conservative Forms
- •Additional Sources of Free Energy
- •Variables and Expressions
- •Reference For the Phase Field Interface
- •The Laminar Bubbly Flow Interface
- •Reference Pressure
- •Discretization
- •The Turbulent Bubbly Flow Interface
- •Reference Pressure
- •Discretization
- •Fluid Properties
- •Slip Model
- •Initial Values
- •Initial Values
- •Volume Force
- •Volume Force
- •Gravity
- •Gravity
- •Mass Transfer
- •Mass Transfer
- •Boundary Conditions for the Bubbly Flow Interfaces
- •Wall
- •Liquid Boundary Condition
- •Gas Boundary Condition
- •Inlet
- •Liquid Boundary Condition
- •Gas Boundary Condition
- •Outlet
- •Liquid Boundary Condition
- •Gas Boundary Condition
- •Symmetry
- •Gas Boundary Conditions Equations
- •The Mixture Model, Laminar Flow Interface
- •Stabilization
- •Discretization
- •The Mixture Model, Turbulent Flow Interface
- •Stabilization
- •Mixture Properties
- •Mass Transfer
- •Mass Transfer
- •Initial Values
- •Initial Values
- •Volume Force
- •Volume Force
- •Gravity
- •Gravity
- •Boundary Conditions for the Mixture Model Interfaces
- •Wall
- •Mixture Boundary Condition
- •Dispersed Phase Boundary Condition
- •Inlet
- •Mixture Boundary Condition
- •Dispersed Phase Boundary Condition
- •Outlet
- •Mixture Boundary Condition
- •Symmetry
- •The Bubbly Flow Equations
- •Turbulence Modeling in Bubbly Flow Applications
- •References for the Bubbly Flow Interfaces
- •The Mixture Model Equations
- •Dispersed Phase Boundary Conditions Equations
- •Turbulence Modeling in Mixture Models
- •Slip Velocity Models
- •References for the Mixture Model Interfaces
- •Dispersed Phase
- •Discretization
- •Domain Conditions for the Euler-Euler Model, Laminar Flow Interface
- •Phase Properties
- •Solid Viscosity Model
- •Drag Model
- •Solid Pressure Model
- •Initial Values
- •Boundary, Point, and Pair Conditions for the Euler-Euler Model, Laminar Flow Interface
- •Wall
- •Dispersed Phase Boundary Condition
- •Inlet
- •Two-Phase Inlet Type
- •Continuous Phase
- •Dispersed Phase
- •Outlet
- •Mixture Boundary Condition
- •The Euler-Euler Model Equations
- •References for the Euler-Euler Model, Laminar Flow Interface
- •Selecting the Right Interface
- •The Porous Media Flow Interface Options
- •Coupling to Other Physics Interfaces
- •Discretization
- •Fluid and Matrix Properties
- •Mass Source
- •Mass Source
- •Initial Values
- •Initial Values
- •Boundary Conditions for the Darcy’s Law Interface
- •Pressure
- •Pressure
- •Mass Flux
- •Mass Flux
- •Inflow Boundary
- •Inflow Boundary
- •Symmetry
- •No Flow
- •Discretization
- •Fluid and Matrix Properties
- •Volume Force
- •Volume Force
- •Forchheimer Drag
- •Forchheimer Drag
- •Initial Values
- •Initial Values
- •Mass Source
- •Boundary Conditions for the Brinkman Equations Interface
- •Discretization
- •Fluid Properties
- •Porous Matrix Properties
- •Porous Matrix Properties
- •Forchheimer Drag
- •Forchheimer Drag
- •Volume Force
- •Volume Force
- •Initial Values
- •Initial Values
- •Boundary Conditions for the Free and Porous Media Flow Interface
- •Microfluidic Wall Conditions
- •Boundary Condition
- •Discretization
- •Domain, Boundary, and Pair Conditions for the Two-Phase Darcy’s Law Interface
- •Fluid and Matrix Properties
- •Initial Values
- •Initial Values
- •No Flux
- •Pressure and Saturation
- •Pressure and Saturation
- •Mass Flux
- •Inflow Boundary
- •Inflow Boundary
- •Outflow
- •Pressure
- •Darcy’s Law—Equation Formulation
- •About the Brinkman Equations
- •Brinkman Equations Theory
- •References for the Brinkman Equations Interface
- •Reference for the Free and Porous Media Flow Interface
- •Darcy’s Law—Equation Formulation
- •The High Mach Number Flow, Laminar Flow Interface
- •Surface-to-Surface Radiation
- •Discretization
- •Initial Values
- •Initial Values
- •Shared Interface Features
- •Fluid
- •Dynamic Viscosity
- •Inlet
- •Outlet
- •Consistent Inlet and Outlet Conditions
- •Pseudo Time Stepping for High Mach Number Flow Models
- •References for the High Mach Number Flow Interfaces
- •Selecting the Right Interface
- •The Non-Isothermal Flow Interface Options
- •Coupling to Other Physics Interfaces
- •The Non-Isothermal Flow, Laminar Flow Interface
- •Discretization
- •The Conjugate Heat Transfer, Laminar Flow Interface
- •The Turbulent Flow, Spalart-Allmaras Interface
- •Fluid
- •Dynamic Viscosity
- •Wall
- •Boundary Condition
- •Initial Values
- •Pressure Work
- •Viscous Heating
- •Dynamic Viscosity
- •Turbulent Non-Isothermal Flow Theory
- •References for the Non-Isothermal Flow and Conjugate Heat Transfer Interfaces
- •Selecting the Right Interface
- •The Heat Transfer Interface Options
- •Conjugate Heat Transfer, Laminar Flow
- •Conjugate Heat Transfer, Turbulent Flow
- •Coupling to Other Physics Interfaces
- •Accessing the Heat Transfer Interfaces via the Model Wizard
- •Discretization
- •Heat Transfer in Solids
- •Translational Motion
- •Translational Motion
- •Pressure Work
- •Heat Transfer in Fluids
- •Viscous Heating
- •Dynamic Viscosity
- •Heat Source
- •Heat Source
- •Initial Values
- •Initial Values
- •Boundary Conditions for the Heat Transfer Interfaces
- •Temperature
- •Temperature
- •Thermal Insulation
- •Outflow
- •Symmetry
- •Heat Flux
- •Heat Flux
- •Inflow Heat Flux
- •Inflow Heat Flux
- •Open Boundary
- •Periodic Heat Condition
- •Surface-to-Ambient Radiation
- •Boundary Heat Source
- •Boundary Heat Source
- •Heat Continuity
- •Pair Thin Thermally Resistive Layer
- •Pair Thin Thermally Resistive Layer
- •Thin Thermally Resistive Layer
- •Thin Thermally Resistive Layer
- •Line Heat Source
- •Line Heat Source
- •Point Heat Source
- •Convective Cooling
- •Out-of-Plane Convective Cooling
- •Upside Heat Flux
- •Out-of-Plane Radiation
- •Upside Parameters
- •Out-of-Plane Heat Flux
- •Domain Selection
- •Upside Inward Heat Flux
- •Change Thickness
- •Change Thickness
- •Porous Matrix
- •Heat Transfer in Fluids
- •Thermal Dispersion
- •Dispersivities
- •Heat Source
- •Equation Formulation
- •Activating Out-of-Plane Heat Transfer and Thickness

Edges and Points
•Line Heat Source (edges)
•Pressure Point Constraint
•Point Heat Source
Pairs
•Heat Continuity
•Pair Thin Thermally Resistive Layer
•Temperature
•Boundary Heat Source
•Flow Continuity
•Wall
These features are slightly different than for other interfaces and are described in this section:
•Initial Values
•Fluid
•Inlet
•Outlet
Fluid
The Fluid feature adds the momentum equations and the temperature equation corresponding to an ideal gas but without volume forces and heat sources. Volume forces and heat sources can be added as separate features. Viscous heating and pressure work terms are added by default to the temperature equation.
When the turbulence model type is set to RANS, the Fluid node also adds the equations for k and , or the undamped turbulent kinematic viscosity, depending on which turbulence model that is used.
The thermal conductivity describes the relationship between the heat flux vector q and the temperature gradient T as in q = k T, which is Fourier’s law of heat conduction. Enter this quantity as power per length and temperature.
D O M A I N S E L E C T I O N
By default, All domains are selected.
T H E H I G H M A C H N U M B E R F L O W I N T E R F A C E S | 355

M O D E L I N P U T S
Define the model inputs. If no model inputs are required, this section is empty.
To define the Absolute Pressure, see the settings for the Heat Transfer in
Fluids node as described in the COMSOL Multiphysics User’s Guide.
Tip
Select a Thermal conductivity k (SI unit: W/(m·K)) from the list—From material,
Sutherlands Law (the default), or User defined. If User defined is selected, choose
Isotropic, Diagonal, Symmetric, or Anisotropic based on the characteristics of the thermal conductivity and enter another value or expression in the field or matrix.
Sutherland’s Law
If Sutherlands Law is selected, enter the following model parameters:
•Conductivity at reference temperature kref (SI unit: W/(m·K)))
•Reference temperature Tk,ref (SI unit: K)
•Sutherland constant Sk (SI unit: K)
Sutherland’s law describes the relationship between the thermal conductivity and the total temperature of an ideal fluid according to
T H E R M O D Y N A M I C S
The High Mach Number Flow assumes the fluid to be governed by the ideal gas law. Specify the thermodynamics properties by selecting a gas constant type and selecting between entering the heat capacity at constant pressure or the ratio of specific heats. For an ideal gas the density is defined as
M p p
= ------n-------A-- = ------A---- ,
RT RsT
356 | C H A P T E R 1 1 : H I G H M A C H N U M B E R F L O W B R A N C H
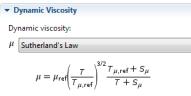
where pA is the absolute pressure, and T the temperature.
•Select a Gas constant type— Specific gas constant Rs (SI unit: J/(kg·K)) or Mean molar mass Mn (SI unit: kg/mol). The default setting is to use the property value
From material. Select User defined to enter another value or expression for either of material property. In both cases, the default uses data From material. Select User
defined to enter other values or expressions. If Mean molar mass is selected, the universal gas constant R 8.314 J/(mol·K), which is a built-in physical constant, is
also used.
•From the Specify Cp or list, select Heat capacity at constant pressure Cp
(SI unit: J/(kg·K)), or Ratio of specific heats (unitless). The default setting is to use the property value From material. Select User defined to enter another value or expression for either of material property.
D Y N A M I C V I S C O S I T Y
The dynamic viscosity describes the relationship between the shear rate and the shear stresses in a fluid.
Select a Dynamic viscosity (SI unit: Pa·s) from the list—From material,
Sutherlands Law (the default), or User defined.
Sutherland’s Law
If Sutherlands Law is selected, enter the following model parameters:
•Dynamic viscosity at reference temperature ref (SI unit: Pa·s)
•Reference temperature T ,ref (SI unit: K)
•Sutherland constant S (SI unit: K)
Sutherland’s law describes the relationship between the dynamic viscosity and the total temperature of an ideal fluid according to
T H E H I G H M A C H N U M B E R F L O W I N T E R F A C E S | 357
