
Build The Ultimate Custom PC (2005)
.pdf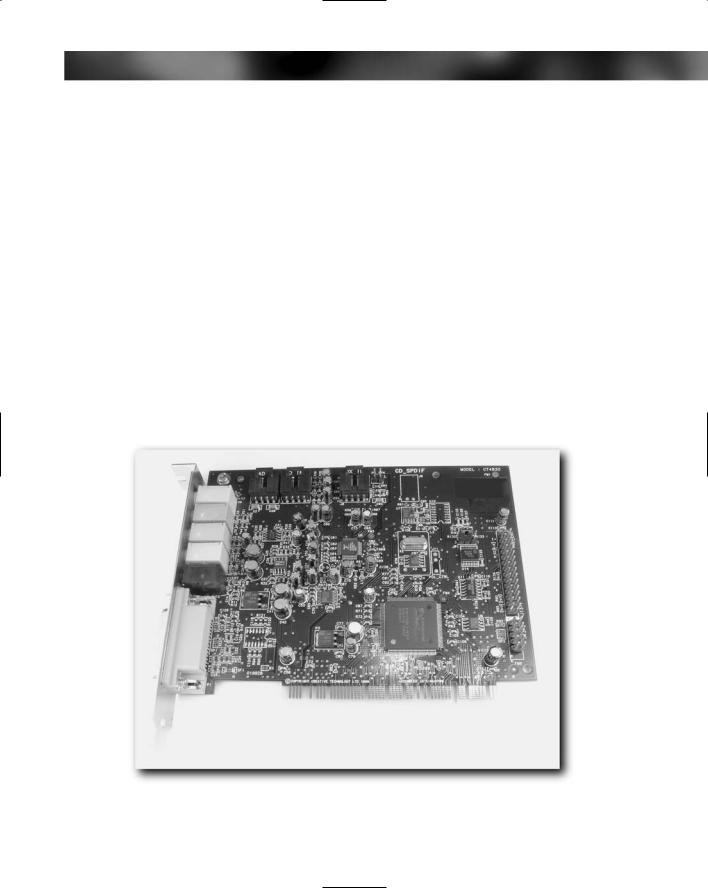
Chapter 9 — Choosing Sound Capability 129
You may recall that when we looked at on-board video adaptors in the previous chapter we said that overall we weren’t that thrilled by them and that on the whole you could get much better performance from a separate video adaptor card costing not much more than $30 or so. However, it seems that on-board sound capability is generally of better quality than its video counterpart. This is due in part to the fact that sound card technology is simpler than video technology. (Put simply it’s easier to create a sound processor and output system than it is a video adaptor.) However, another important reason is that, overall, there is less stress and demand placed on the sound system, and thus lower-performance and lower-quality devices are still capable of performing acceptably.
Because of this, many people, including those who use their PC for gaming and playing videos or DVDs, might find the sound system provided by the motherboard to be adequate for their needs.
However, sound generated by on-board systems will never be as good as what you will get with a separate, dedicated, sound card.
Sound Cards
The most popular choice in PC sound systems is the PCI-based sound card that will slip into an expansion slot. By far the most popular range of sound cards you will see for sale are manufactured by Creative Labs and distributed under the SoundBlaster™ label. In the SoundBlaster product range you will find a variety of cards.
FIGURE 9-5: A generic sound card.

130 Part I — Choosing Components for Your PC
The PCI-based sound card is very much like any other expansion card. The sound card has connectors along one edge that fit into the expansion slot, and the metal back plate of the card has the connectors and jack ports for speakers, microphones, and other devices.
FIGURE 9-6: Close-up of card connectors.
A broad range of sound cards are available, ranging from budget cards that have an acceptable sound quality output to expansive cards that are capable or high-quality audio output for the discerning gamer or music listener (although to get good output you will need good speakers).
The best guide as to quality is price. As with video adaptors, sound card technology moves quickly and what is innovative today will be midrange in a few months and budget in a year or so. The basic rule is that the more you want out of a card, the more you are going to have to pay. At the budget end, you will find cards that cater for those requiring basic stereo audio output, while at the higher end you’ll find sound cards packing technology such as surround sound and front panel controls that fit into a free 5-1/4-inch drive bay and give you controls such as volume, balance, and even graphic equalizers.

Chapter 9 — Choosing Sound Capability 131
The main advantage of opting for a PCI-based sound card over an on-board system is that you can choose exactly what you want. If your needs are basic you can stick with the on-board sound system or buy a budget PCI card. If you want more, you’ll have to spend more to get extra features. However, there’s no doubt that a separate sound card will give you greater overall performance.
USB Speakers
One new innovation is the USB speaker. These are USB speakers that don’t require a separate sound card. They plug into a free USB port and work directly from that.
Although innovative, we don’t recommend these for a new system. Although they are handy for upgrading the sound system on a laptop or for giving a new lease on life to an old system where you might not have the space for a separate sound card (when you are upgrading from on-board sound), the cost can be quite high and the results from them unpredictable. Sound card technology is also far more robust and less prone to compatibility problems that can affect some systems using USB speakers.
“Out-the-Front” Sound
Some sound cards give you the ability to have jacks at the front of the PC for things like microphones and speakers, while others even allow you to control the card through a panel that consists of knobs and dials such as volume, balance, and so on. Cards that incorporate these features are more expensive than regular cards, but they are worth considering if you are someone who feels you will be using your PC a lot for music or home entertainment. Having an easy-to-reach and non-software way of controlling basic audio functions can be very useful indeed (and climbing round the back of the PC to reach the connectors can be a major headache at the best of times!).
Some cases come with front panel connectors for microphones and speakers too, but these either plug into the connectors at the rear of the sound card or require specific motherboard or sound card support.
Speakers
No matter what the quality of your sound card, it’s the speakers that actually do the job of turning the electrical signals from the card into air movements that we then detect as sound. A good pair of speakers isn’t going to improve on a bad sound card, but poor speakers can give you a poor audio experience from even the best sound system.

132 Part I — Choosing Components for Your PC
FIGURE 9-7: A set of generic speakers.
A number of different types of speaker are available. The most popular and most common is the standard stereo speaker; however, because the PC is slowly becoming part of the home entertainment system, there is now also a good range of surround sound speakers available for the PC. These require specific sound card support, but they can be used to create that all-round audio effect otherwise only found in real life and in the best cinema theatre. Such system are normally called “5.1 surround sound” systems and come with six speakers:
One front speaker, called a “center” channel
Two speakers at the front, one on either side
Two speakers at the rear, one on either side
One low-frequency speaker called a subwoofer to add low bass to the overall sound (handy for deep rumbles from games or DVDs)
These systems not only come with speakers (and note that the subwoofer is usually quite large), but they also come with a control box that connects to the PC. Out of the control box comes all the speaker wiring. Surround sound systems involve trailing a lot of wiring about, and care needs to be taken to route the wires in such a way that they don’t get damaged or trip up people.

Chapter 9 — Choosing Sound Capability 133
How to Choose Speakers
There are three aspects of a set of speakers that are important to consider when buying speakers:
Build quality
Power
Cabling and connectors
Build Quality
You can spot cheap speakers just by looking at them. They will be small and made of plastic, and when you tap them they will sound tinny or hollow. (The best sound that a speaker can give out when tapped is a dull, dead thud but this is rare from PC speakers.)
By now you probably know what we are going to say before we even say it — as with most things, you get what you pay for. You can’t expect to get rich tones and natural highs and lows from a $10 pair of speakers. However, don’t despair because even poor speakers can actually output quite decent audio, but the problem with small, light speakers is that they have a tough time keeping up with the low frequencies. It all depends on what you expect your PC speakers to do.
For general office use and a PC that is going to see a lot of Internet use, then a budget pair of speakers will suffice. However, if you want good sound output (say, for a gaming PC or a home entertainment PC that is going to play a lot of DVDs and video), then you are going to need better-quality speakers and expect to pay $50–$100 for a reasonable set and more than $250 for a good-quality set. A high-quality 5.1 surround sound system can cost much more. It all depends on what you want from the system.
A Cheaper Option: Don’t want to bother getting high-quality speakers but want good sound output from your system sometimes? A simple answer is to get a good-quality pair of headphones and use them. Good-quality headphones will set you back a lot less than good-quality speakers and won’t bother your spouse, parents, or neighbors as much!
One thing that is absolutely vital on a set of speakers is that they have decent feet on them. Without these the speakers will rattle or vibrate when working, and this will add unwanted sound effects into the audio. Speakers must sit firmly on the surface on which they are going to be resting on. Rubber feet on speakers are generally a good idea. They improve the sound quality and stop the speakers from sliding about the place.
Power
How are your speakers powered? There are several options:
Unpowered speakers
Battery-powered speakers
Mains-powered speakers

134 Part I — Choosing Components for Your PC
Unpowered speakers are handy, but the output from them is more than likely to be poor and they won’t be up to gaming and video. Generally these are no good for anything other than office PCs.
You can completely dismiss the idea of battery-powered speakers. These will cost you a fortune to run, and the batteries will die at exactly the wrong time.
That leaves mains-powered speakers as the best choice for most PC owners. These give the best audio output and won’t be silenced by dead batteries. Also, to reduce on cabling some come with an adaptor that slots between the power supply unit and main code and draws its power needs from there, eliminating the need for a separate power outlet.
FIGURE 9-8: Power adaptor.
Cabling and Connectors
Good-quality speakers will have good cabling and high-quality connectors. Budget speakers will have cabling and connectors of variable quality. In order to get decent audio output, you will need speakers that have good cable fitted with decent molded connectors on the end.
Chapter 9 — Choosing Sound Capability 135
A good test of cable quality is to hold the cable near the connector and see how far away from the connector you can hold it without the wire flopping over. Good-quality cable should be able to hold the weight of the connector and at least 6 inches (15 cm) of cable without flopping over.
Check the cable and connector for cuts in the sheathing, bad kinks in the cable, and damage. All these will have an adverse effect on audio output.
Summary
In this chapter, we’ve looked at the PC sound output system and looked at different ways that you can get your PC to output sound.
As well as looking at on-board sound, sound cards, and USB speakers, we’ve also looked at different kinds of speakers that are available and looked at simple ways to tell the difference between good speakers and poor-quality speakers.
In the next chapter, you will be looking at the variety of cabling and fittings that are present inside a PC.
Take Action
Before you move on to the next chapter, be sure that you’re prepared:
■Spend some time now considering your audio needs. Is the PC going to be a general office PC that will need little in the way of audio? Or will you use it for gaming, playing music, and so on?
■Factor the pros and cons of a separate sound card as opposed to on-board sound. Remember, if in doubt, you can always add a separate sound card at a later stage.

A Tour of Cables
and Fittings
To someone unfamiliar with the inside of a working PC looks like, it has countless cables and fittings that snake from one component to another in a random, haphazard maze (people expected a lot of “tech”
crammed into a small space, but they don’t expect all the cabling that goes with it!). Thankfully, it isn’t as haphazard as it may seem at first and there is logic to it all! Once you know what you are looking at and understand what connects to what and why you’ll begin to notice that everything is laid out quite logically!
In this chapter, we’ll look at the cables and fittings that connect everything inside a PC and look at how you can identify each cable and know what they are for and where each one goes.
Power Cables
A PC has three different types of power cable supplying power to three different devices:
Motherboard power block. This is the largest power connector block — a long, broad connector with 20 or more pins (see Figure 10-1). Some motherboards have a 20-pin connector, while others have a 24-pin connector. Some have 20-pin connectors and a separate 4-pin block — ultimately, it depends on the motherboard. This fits onto the motherboard and supplies all the power needs of the motherboard and the attached expansion cards.
Most new motherboards that support high-power processors actually have 24-pin power connectors, and it’s critical to know the difference and get a power supply that matches your motherboard. You can convert down from 24-pin to 20-pin, but you can’t convert up.
Hard drive/CD/DVD drive power cables. These cables provide power for the drives. Also, these cables can be used for case fans and to provide additional power for other devices (see Figure 10-2).
Floppy drive power cable. This provides power for the floppy drive (see Figure 10-3).
chapter
in this chapter
˛Power cables
˛Front panel connections
˛Hard drive data cables
˛Floppy drive data cables
˛Fans and coolers
˛Case speaker
˛USB connector header
˛Drive fittings
˛Motherboard fittings

138 Part I — Choosing Components for Your PC
FIGURE 10-1: Motherboard power block.
FIGURE 10-2: Drive power connectors.
