
Vankka J. - Digital Synthesizers and Transmitters for Software Radio (2000)(en)
.pdf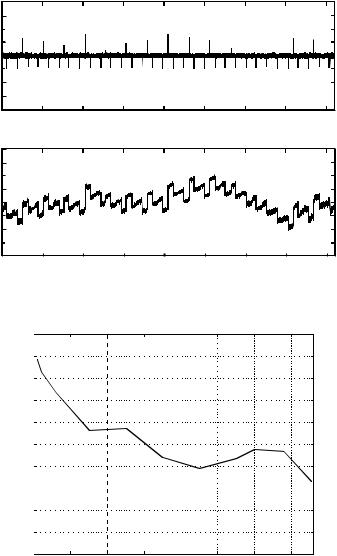

A GSM/EDGE/WCDMA Modulator with On-Chip D/A Converter for |
317 |
Base Stations |
|
The Design Rule Check (DRC) and the Layout Versus Schematic (LVS) were performed for the final layout using Mentor IC-station and Design Architect. After the successful DRC and LVS checks, the final layout was transferred to the fabrication in the GDSII format. The chip was fabricated using a 0.35 m CMOS technology.
Max/R f Lvl |
Marker |
[T1 |
|
RBW |
1 MHz R |
Att |
20 dB |
|
14 dBm |
|
92 |
dB m |
VBW |
1 MHz |
|
|
dBm |
17 dBm |
513 26653 |
|
SWT 800 s |
Unit |
|
|||
7 dB Offset |
LIMIT CHECK : PASSED
1 |
-10
-20
-30 EDG

 _T_U
_T_U
-40
-50
ED
 E_T_L
E_T_L
-60 |
|
-70 |
|
-80 |
TR |
|
|
-8 |
|
Center 19 2 MHz |
80 s/ |
Figure 16-16. Transmitted power level of the EDGE burst versus time. The carrier frequency is 19.2 MHz.
Table 16-3 Spectrum due to Switching Transients (Peak-Hold Measurement, 30 kHz Filter Bandwidth, Reference ≥ 300 kHz with zero offset)
Offset |
Maximum Power Limit |
Measured Maximum |
Measured Maximum |
||||
(kHz) |
(dBc) |
Power (dBc) at Digital |
Power (dBc) at D/A |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Output |
converter Output |
|
|
(GMSK) |
|
(8-PSK) |
(GMSK) |
(8-PSK) |
(GMSK) |
(8-PSK) |
|
|
||||||
400 |
- 60 |
|
-55 |
-77.3 |
-77.7 |
-65.64 |
-65.53 |
600 |
- 70 |
|
-65 |
-95.2 |
-94.2 |
-75.1 |
-75.36 |
1200 |
- 77 |
|
-77 |
-106.3 |
-106.8 |
-80.55 |
-78.57 |
1800 |
- 77 |
|
-77 |
-106.9 |
-107.7 |
-79.92 |
-79.23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|


A GSM/EDGE/WCDMA Modulator with On-Chip D/A Converter for |
319 |
Base Stations |
|
16.9 D/A Converter
As the multicarrier feature requires high dynamic range requirements for the D/A converter, the wordlength was chosen to be 14 bit. The 14-bit on-chip D/A converter is based on a segmented current steering architecture [Bos01]. It consists of a 6b MSB matrix (2b binary and 4b thermometer coded), and an 8b binary coded LSB matrix (Figure 16-12). The static linearity is achieved by sizing the current sources for intrinsic matching [Bos01] and by using layout techniques; this is a prerequisite for obtaining good dynamic linearity. The cascode structure is used to increase the output impedance of the unit current source, which improves the linearity of the D/A-converter.
The dynamic linearity is important in this IF modulator because of the strongly varying signal. Therefore, well-designed and carefully laid out switch drivers and current switches are used. A major function of the switch driver in Figure 16-12 is to adjust the crosspoint of the control voltages, and to limit their amplitude at the gates of the current switches, in such a way that these transistors are never simultaneously in the off state and that the feedthrough is minimized. The crossing point of the control signals is set by delaying the falling edge of the signal [Tak91]. Dummy switch transistors are used to improve the synchronization of the switch transistors control sig-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
M |
arker 1 [T1] |
|
|
|
RBW 30 kHz |
R |
|
Att |
1 dB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
Ref Lvl |
|
|
|
- 44 25 |
dB |
m |
VBW 30 kHz |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
-22 |
dBm |
|
19.98250000 |
MHz |
SWT 200 ms |
Unit |
dBm |
||||||
-2 |
|
1 [T1] |
-44.25 dBm |
||
|
|
||||
-30 |
|
|
19.98250000 |
MHz |
|
|
CH PWR |
-24.09 |
dBm |
||
|
|
||||
-4 |
|
ACP |
Up |
6.56 |
dB |
|
ACP |
Low |
-65.84 |
dB |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
ALT1 |
Up |
-67.67 |
dB |
-5 |
|
ALT1 |
Low -67.88 |
dB |
|
-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
-7 |
|
|
|
|
|
-8 |
|
|
|
|
|
-9 |
|
|
|
cu2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-100 |
|
C0cu1 |
cu1cu2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
-110 |
|
cI1 C0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
cI2 |
|
|
|
|
-122 |
|
3 MHz/ |
|
|
|
Cente |
20 MHz |
|
Span 30 MHz |
||
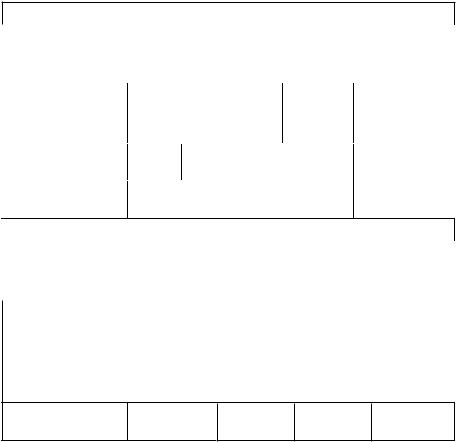
Figure 16-19. Power spectrum of WCDMA signal.
320 |
Chapter 15 |
nals. Disturbances connected to the external bias current are filtered out onchip with a simple one pole low-pass filter. The D/A-converter is implemented with a differential design, which results in reduced even-order distortions and provides a common-mode rejection of disturbances.
16.10 Measurement Results
To evaluate the multi-standard modulator, a test board was built and a computer program was developed to control the measurements. Figure 16-13 illustrates the block diagram of the multi-standard modulator test system. The on-chip D/A converter was used in measurements. Measurements are performed with a 50 Ω doubly terminated cable. The sampling rate of the D/A converter was 76.8 MHz in the measurement. Figure 16-14 shows that typical integral linearity (INL) and differential linearity (DNL) errors are
Table 16-4
Performance Summary
Signal Quality
Measured at |
|
GSM Phase Error |
EDGE EVM (%) |
|
WCDMA EVM |
|||
|
|
(°) |
|
|
|
|
|
(%) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
peak |
rms |
peak |
rms |
rms |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Digital Data at |
|
0.75 |
0.29 |
|
1.263 |
0.27 |
|
1.11 |
D/A Converter Input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Analog Signal at |
D/A |
1.71 |
0.74 |
|
1.55 |
0.37 |
|
1.18 |
Converter Output |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Specifications at |
the |
20 |
5 |
|
22 |
7.0 |
|
17.5 |
base station RF port |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Spectral Properties |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
GSM |
|
|
EDGE |
WCDMA |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
600 kHz offset |
|
600 kHz |
ACLR1 |
ACLR2 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
offset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Digital Data at |
|
-100 |
|
|
-90 |
72.9 |
|
73.3 |
D/A converter input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Analog Signal at |
D/A |
-87.34 |
|
|
-84.58 |
65.84 |
|
67.67 |
Converter Output |
|
|
|
|
|
From Figure |
From Figure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16-19 |
|
16-19 |
Specifications at |
the |
-70 |
|
|
-70 |
45 |
|
50 |
base station RF port



324 |
Chapter 15 |
December 1999.
[Eru93] L. Erup, F. M. Gardner, and R. A. Harris, "Interpolation in Digital Modems Part II: Implementation and Performance," IEEE Trans. on Commun., Vol. COM-41, pp. 998-1008, June 1993.
[Far88] C. W. Farrow, "A Continuously Variable Digital Delay Element," in Proc. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), June
1988, pp. 2641-2645.
[FDD00] 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Networks; UTRA (BS) FDD; Radio transmission and Reception, 3G TS 25.104, V3.3.0, June 2000.
[Fli92] N. J. Fliege, and J. Wintermantel, "Complex Digital Oscillators and FSK Modulators," IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, Vol. SP-40, No. 2, pp. 333-342, Feb. 1992.
[Fli94] N. J. Fliege, Multirate Digital Signal Processing, John Wiley & Sons, 1994.
[Fur99] A. Furuskär, S. Mazur, F. Muller, and H. Olofsson, "EDGE: Enhanced Data Rates for GSM and TDMA/136 Evolution," IEEE Personal Communications, June 1999, pp. 56-66.
[GPP00a] 3GPP Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network, Spreading and Modulation (FDD), TS 25.213 V3.2.0, March 2000. [GPP00b] 3GPP Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network, UTRA (BS) FDD; Radio transmission and Reception, TS 25.104 V3.3.0, June 2000.
[GPP00c] 3GPP Technical Specification Group GERAN, Digital cellular telecommunication system (Phase 2+); Radio transmission and reception, TS 05.05 V8.6.0, September 2000.
[Gra01] "GC4116 Multi-standard Quad DUC Chip," Graychip Data Sheet, April 2001.
[GSM99a] GSM Recommendation 05.04: "Modulation," Dec. 1999. [GSM99b]GSM Recommendation 05.02: "Digital Cellular Telecommunications System (Phase 2+); Multiplexing and Multiple Access on the Radio Path," July 1999.
[GSM99c] GSM Recommendation 05.05: "Radio Transmission and Reception," Dec. 1999.
[Hau93] J. C. Hausman, R. R. Harnden, E. G. Cohen, and H. G. Mills, "Programmable Canonic Signed Digit Filter Chip," U. S. Patent 5,262,974, Nov. 16, 1993.
[Im00] S. Im, W. Lee, C. Kim, Y. Shin, S. H. Lee, and J. Chung, "Implementation of SDR-Based Digital IF Channelizer/De-Channelizer for Multiple CDMA Signals," IEICE Trans. Commun., Vol. E83-B, No. 6, pp.
1282-1289, June 2000.
A GSM/EDGE/WCDMA Modulator with On-Chip D/A Converter for |
325 |
Base Stations |
|
[Int01] "ISL5217 Quad Programmable UpConverter," Intersil Corporation Data Sheet, April 2001.
[Jun94] P. Jung, "Laurent's Representation of Binary Digital Continuous Phase Modulated Signals with Modulation Index 1/2 Revisited," IEEE Transactions on Communications, Vol. 42, No. 2/3/4, February/March/April 1994, pp. 221-224.
[Ket03] J. Ketola, J. Vankka, and K. Halonen, "Synchronization of Fractional Interval Counter in Non-Integer Ratio Sample Rate Converters," in Proc. ISCAS’03, Vol. II, May 2003, pp. 89-92.
[Kos01] M. Kosunen, J. Vankka, M. Waltari, and K. Halonen, "A Multicarrier QAM Modulator for WCDMA Basestation with on-chip D/A Converter," in Proc. Custom Integrated Circuits Conf., May 2001, San Diego, USA, pp. 301-304.
[Kur82] C. F. Kurth, K. J. Bures, P. R. Gagnon, and M. H. Etzel, "A PerChannel, Memory-Oriented Transmultiplexer with Logarithmic Processing," IEEE Trans. on Commun., Vol. COM-30, pp. 1520-1527, July 1982.
[Lau86] P. Laurent, "Exact and Approximate Construction of Digital Phase Modulations by Superposition of Amplitude Modulated Pulses (AMP)," IEEE Transactions on Communications, Vol. COM-34, No. 2, February 1986, pp. 150-160.
[Mur81] K. Murota, "GMSK Modulation for Digital Mobile Radio Telephony," IEEE Transactions on Communications, Vol. 29, pp. 1044-1050, July 1981.
[Par99] K. K. Parhi, VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems: Design and Implementation, John Wiley & Sons, 1999.
[Paš01] R. Paško, L. Rijnders, P. R. Schaumont, S. A. Vernalde, and D. Ćuraþková, "High-Performance Flexible all-digital Quadrature up and down Converter Chip," IEEE J. of Solid State Circuits, Vol. 36, No. 3, pp. 408-
416, Mar. 2001.
[Sam88] H. Samueli, "The Design of Multiplierless FIR Filters for Compensating D/A Converter Frequency Response Distortion," IEEE Trans. Circuits and Syst., Vol. 35, No. 8, pp. 1064-1066, Aug. 1988.
[Sam89] H. Samueli, "An Improved Search Algorithm for the Design of Multiplierless FIR Filters with Powers-of-Two Coefficients," IEEE Trans. Circuits and Syst., Vol. 36, No. 7, pp. 1044-1047, July 1989.
[Sam91] H. Samueli, "On the Design of FIR Digital Data Transmission Filters with Arbitrary Magnitude Specifications," IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, Vol. 38, No. 12, Dec. 1991, pp. 1563-1567.
[Sch81] H. Scheuermann, and H. Göckler, "A Comprehensive Survey of Digital Transmultiplexing Methods," Proc. of IEEE, Vol. 69, No. 11, pp.
1419-1450, Nov. 1981.


 EDGE_SPEC
EDGE_SPEC