- •А.Д. Музафарова а.Г. Ковалева
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
- •This week: software
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Internet: Voice recognition takes off
- •Programming languages.
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Int — international organization
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
- •The 15 enemies of the Internet
- •Internet crime
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
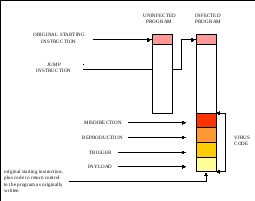
- •How a virus infects a program
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Video Games
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice setion 3
- •Vocabulary practice setion 4
- •Twitter's transmitters
- •Vocabulary practice section 1
- •Good Web Design? What Is It?
- •Vocabulary practice section 2
- •Vocabulary practice section 3
- •Top Five Ways to Make Your Site More Popular
- •1. Strong Hosting
- •2. Optimize Your Website
- •3. Take Advantage of Social Media Optimization
- •4. Get Your Visitors Involved
- •5. Emphasize Usability in Your Design
- •You’ve been in graphics too long if…
- •Internet
- •Web design
How a virus infects a program
2. Make a report about one or several cyber crimes that are not described in the Key information sections.
3. Make a report on one of the following topics.
The history of hacking. Famous hackers.
Notable computer viruses.
Notable computer criminals.
FUN AND GAMES SECTION
1. Find the answer to each clue. The first letter has been given in each case.
A computer system is penetrated by outsiders, and regular users are unable to gain access
Software scans inbound and outbound email to detect and block any damaging content
Organizations that work to prevent and investigate crimes, such as the police and the FBI
This ensures that all people can enjoy access to justice and the freedom of speech
An informal word meaning to look at something secretly, to discover information
|
1 |
d |
|
|
|
|
|
|
о |
|
|
s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
2 |
a |
|
|
|
- |
v |
|
|
|
|
|
p |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
l |
|
|
|
e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
|
4 |
h |
|
|
|
|
|
r |
|
|
|
|
|
|
l |
|
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Solve the anagrams by reading the clues and putting the letters in order to form words. Enter the solutions in the table to find the mystery words. Define the found expression.
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Software that collects information from computers secretly…………………….…..…YEARSPW
2. Illegal copying and distribution of copyrighted content ………………….………………IYARCP
3. A self-contained and self-copying virus……………………………………………………MRWO
4. What a computer gets when it has caught a virus……….……………………………OIIECFNNT
5. A program that helps computers prevent undesirable access........................................ AIELLWRF
6. Internet crime of obtaining money or possessions……….………………………………….AMCS
7. What dishonest people do with information or money……………………………………..AELTS
8. The law that Internet pirates break…...……………………………………………..YOIPRCTHG
9. A disguised or embedded virus…………………...………………………………………AONJRT
10. What a person doing illegal things on the net is……...………………………………IIALMNRC
11. What viruses do to a computer…………………………………………………………EAAMGD
12. Actions that are against the laws …………………………………………………..…..EAILLLG
13. Software which aims to do harm to computers………………………………………EAARWLM
14. The crime of getting bank information………………………………………………..IIGNHHSP
15. Harmful programs that spread over the net………………………………………………..UIRSV
16. The crime of deceiving people to gain something….……………………….……………UADRF
17. The crime of stealing……………..……………………………………………………….ETTFH
18. A group of letters or numbers that gives access to a system…………...…………...OADRPSSW
HUMOR SECTION
What does each of the cartoons imply? Why is it funny, in your opinion? Explain its humour.
|
|
|
|
|
MULTIMEDIA & NETWORKS |
KEY INFORMATION SECTION 1
|
|
|
|
Multimedia is simply multiple forms of media integrated together. Media can be text, graphics, audio, animation, video, data, etc. An example of multimedia is a web page on the topic of Mozart that has text regarding the composer along with an audio file of some of his music and can even include a video of his music being played in a hall.
The term Multimedia is said to date back to 1965 and was used to describe a show by the Exploding Plastic Inevitable. The show included a performance that integrated music, cinema, special lighting and human performance. Today, the word multimedia is used quite frequently, from DVD's to CD ROMs to even a magazine that includes text and pictures.
Multimedia is usually recorded and played, displayed or accessed by information content processing devices, such as computerized and electronic devices, but can also be part of a live performance.
Besides multiple types of media being integrated with one another, multimedia can also stand for interactive types of media such as video games, CD ROMs that teach a foreign language, or an information Kiosk at a subway terminal. Other terms that are sometimes used for multimedia include hypermedia and rich media.
Multimedia (as an adjective) also describes electronic media devices used to store and experience multimedia content. Multimedia is similar to traditional mixed media in fine art, but with a broader scope. The term "rich media" is synonymous for interactive multimedia.
The term reach media was coined to describe a broad range of digital interactive media. Rich media can be downloadable or may be embedded in a webpage. If downloadable, it can be viewed or used offline with media players such as Real Networks' RealPlayer, Microsoft Media Player, or Apple's QuickTime, among others.
|
|
The defining characteristic of rich media is that it exhibits dynamic motion. This motion may occur over time or in direct response to user interaction. Two examples of dynamic motion that occur over time are a streaming video newscast and a stock "ticker" that continually updates itself. |
An example of dynamic motion in response to user interaction is a prerecorded webcast coupled with a synchronized slide show that allows user control. Another is an animated, interactive presentation file embedded in a web page.
Elements of rich media are increasingly used in education, in areas ranging from distance learning to web-based teaching and instructional tools.
Not surprisingly, rich media presents numerous accessibility challenges. However, rich media can be made accessible if all the elements are developed with accessibility in mind and the end product is used or viewed on accessible media players. Accessible rich media typically includes captioning, audio description, and navigation using a keyboard.
|
Hypermedia can be considered one particular multimedia application. The World Wide Web is a classic example of hypermedia, whereas a non-interactive cinema presentation is an example of standard multimedia due to the absence of hyperlinks. The first hypermedia work was, arguably, the Aspen Movie Map. |
|
Atkinson's HyperCard popularized hypermedia writing, while a variety of literary hypertext and hypertext works, fiction and nonfiction, demonstrated the promise of links. Most modern hypermedia is delivered via electronic pages from a variety of systems including Media players, web browsers, and stand-alone applications. Audio hypermedia is emerging with voice command devices and voice browsing.
Multimedia software is usually interactive, so you can choose what you want to watch, listen to or write.
|
|
Hypertext means that you can click on a word and jump to another screen with more information; hypermedia is similar, but works with sounds and images (e.g. the Web). To run multimedia software you need a fast CPU, expandable RAM and a large hard disk. But what marks a computer out as a multimedia PC is its audio and video capabilities: a sound card, a microphone, a decent pair of speakers, a high-quality monitor and a |
DVD writer, and its performance depends on all these components working in harmony.
Multimedia may be broadly divided into linear and non-linear categories. Linear active content progresses without any navigational control for the viewer such as a cinema presentation. Non-linear content offers user interactivity to control progress as used with a computer game or used in self-paced computer based training. Hypermedia is an example of non-linear content.
Multimedia presentations can be live or recorded. A recorded presentation may allow interactivity via a navigation system. A live multimedia presentation may allow interactivity via an interaction with the presenter or performer.