
новая папка / 80
.pdf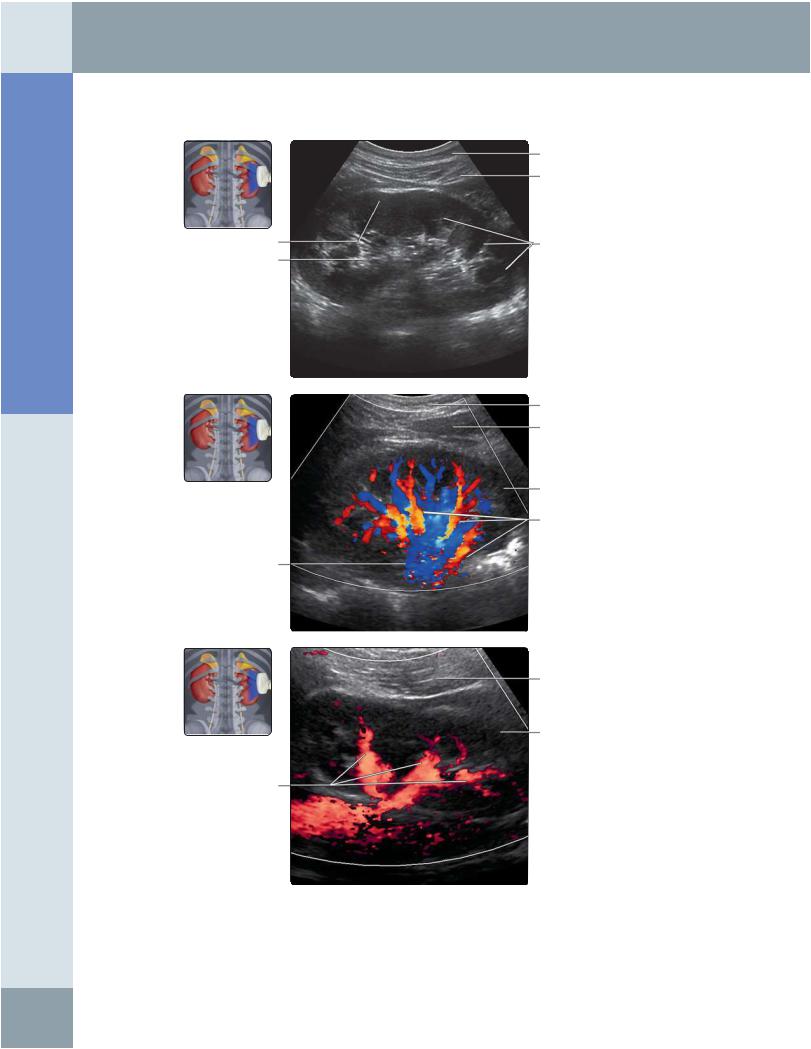
Kidneys
AbdomenAnatomy: |
RIGHT KIDNEY, POSTERIOR ABDOMEN SCAN |
|
|
|
Renal cortex |
|
Renal sinus echoes |
Renal vein
Renal vessels
Subcutaneous fat
Right latissimus dorsi muscle
Renal medullary pyramids
Subcutaneous fat
Right latissimus dorsi muscle
Right renal cortex
Renal arteries
Right latissimus dorsi muscle
Right renal cortex
(Top) Longitudinal grayscale ultrasound of the right kidney scanning from the posterior approach shows normal medullary pyramids. It is a good way for standardizing renal length measurements in children. (Middle) Posterior longitudinal color Doppler ultrasound of the right kidney is shown. This evaluation of the position of major vessels is useful to avoid major vessels during renal interventional procedures, such as renal biopsy or nephrostomy. (Bottom) Posterior longitudinal power Doppler ultrasound of the right kidney is shown. Note that power Doppler ultrasound does not provide information about the direction of flow within vessels.
54
Kidneys
Right erector spinae muscle
Right psoas muscle
Vertebral body
Right erector spinae muscle
Right quadratus lumborum Right psoas muscle
Vertebral body
Right erector spinae muscle
Right quadratus lumborum
Right psoas muscle
Vertebral body
RIGHT KIDNEY, POSTERIOR ABDOMEN SCAN
Rib shadowing
Right kidney
Right kidney
Renal hilum
Subcutaneous fat
Lower pole of right kidney
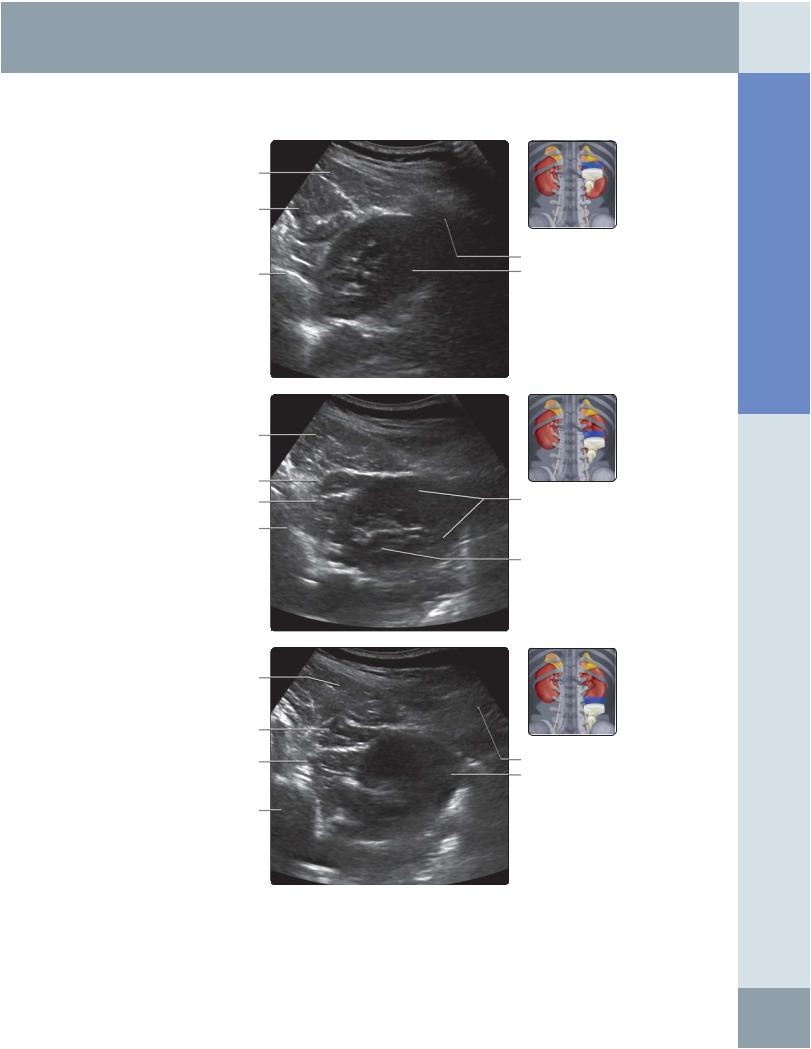
(Top) Transverse grayscale ultrasound of the right kidney scanning from the posterior approach is shown. Scanning through the posterior approach is useful while performing interventional procedures, such as nephrostomy or renal biopsy. However, visualization/image quality may be impaired by thick paraspinal muscles and rib shadowing. This image shows the upper pole of the right kidney. (Middle) Transverse grayscale ultrasound from the posterior approach shows the mid pole of the right kidney. (Bottom) Transverse grayscale ultrasound from the posterior approach shows the lower pole of the right kidney.
Abdomen Anatomy:
55
Anatomy: Abdomen
Kidneys
RIGHT MAIN RENAL ARTERY AND VEIN
Right lobe of liver
Right renal mid pole
Right renal artery
Continuous forward systolic flow
Pulsatile renal venous waveform
Right rectus abdominis muscle
Right renal vein
Inferior vena cava
Right renal artery
Right renal artery
Continuous forward diastolic flow
Right renal vein
Right renal artery
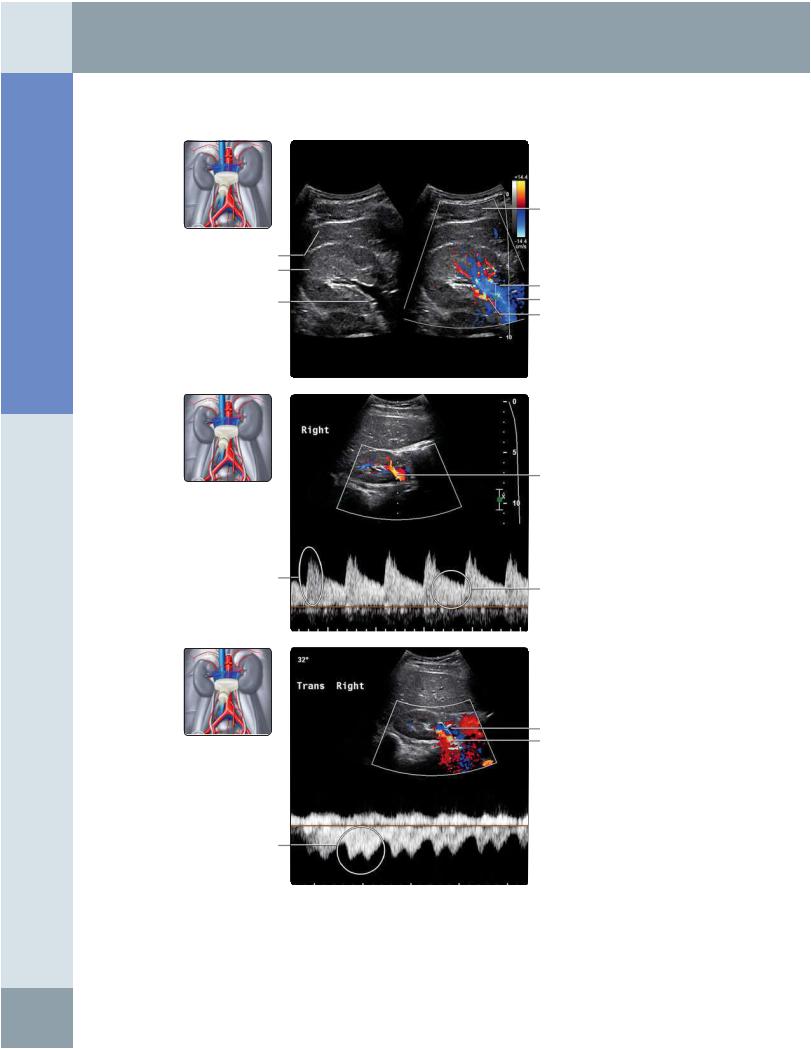
(Top) Transverse split screen showing simultaneous grayscale and color Doppler ultrasound of the right renal hilum is shown. Note that the right renal artery lies posterior to the renal vein and inferior vena cava. The renal artery normally measures 5-8 mm in caliber. (Middle) In this spectral Doppler waveform of the right renal artery, note the low-resistance renal waveform with continuous forward systolic and diastolic flow. Normal PSV ranges from 60-140 cm/s; not more than 180 cm/s. Normal resistivity index is < 0.7 and normal pulsatility index is < 1.8. (Bottom) Spectral Doppler waveform of the right renal vein is shown, which mirrors the pulsatility in the inferior vena cava. The renal vein normally measures 4-9 mm in caliber. Normal PSV ranges from 18-33 cm/s.
56
Kidneys
RIGHT INTRARENAL ARTERY AND VEIN
Intrarenal veins
Segmental renal arteries
Renal cortex
Main renal vein
Right renal cortex
Segmental renal vein
Intrarenal renal artery
Continuous antegrade arterial flow
Renal venous waveform with mild phasic variation
Segmental renal vein
Arterial pulse included by Doppler gate
Segmental renal vein spectral Doppler waveform with phasic variation
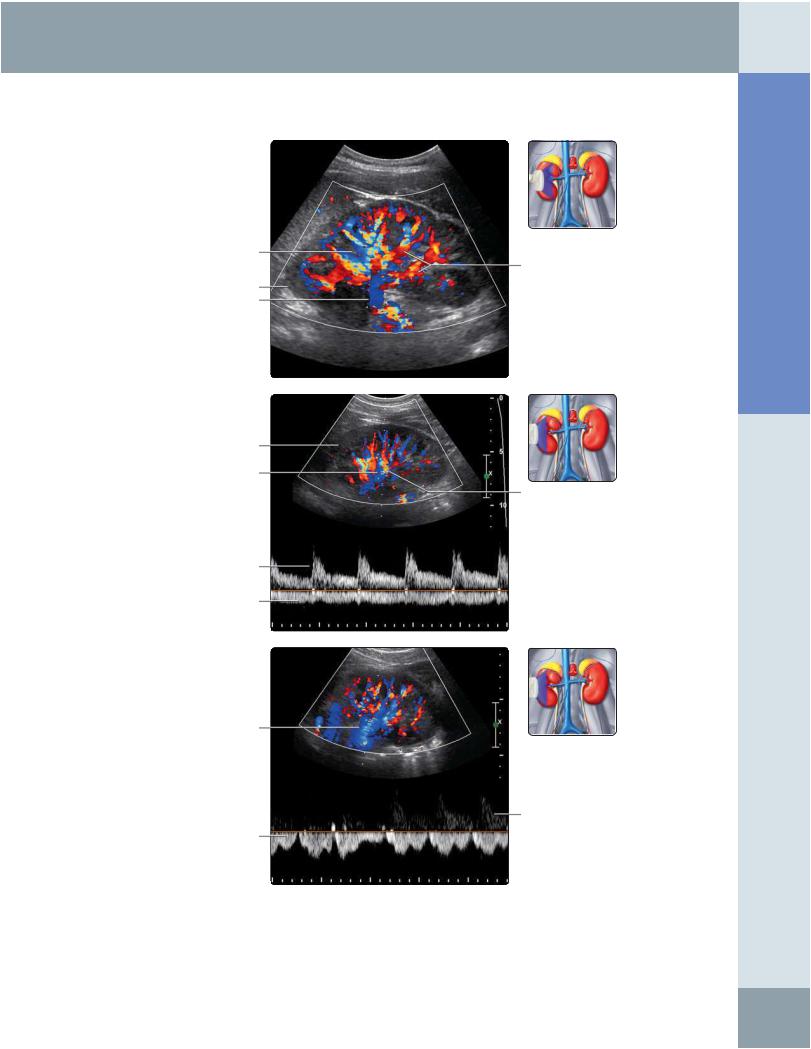
(Top) Longitudinal color Doppler ultrasound of the right kidney shows renal artery branches as red and renal vein branches as blue. (Middle) In this spectral Doppler waveform of a right segmental renal artery branch, note the low-resistance arterial Doppler waveform with continuous diastolic flow, similar to that seen in the more proximal renal artery. The venous waveform shows minimal phasicity. (Bottom) In this spectral Doppler waveform of a right segmental renal vein branch, note the phasic variation in the renal vein, which can vary depending on systemic venous pressure and cardiac and fluid status.
Abdomen Anatomy:
57
Anatomy: Abdomen
Kidneys
LEFT KIDNEY, POSTEROLATERAL SCAN
Subcutaneous fat
Left latissimus dorsi muscle
Perinephric fat
Renal cortex
Renal sinus echoes
Renal vessels
Rib shadow
Renal cortex
Renal sinus echoes
Bowel gas
Latissimus dorsi
Rib shadow
Renal vascular pedicle
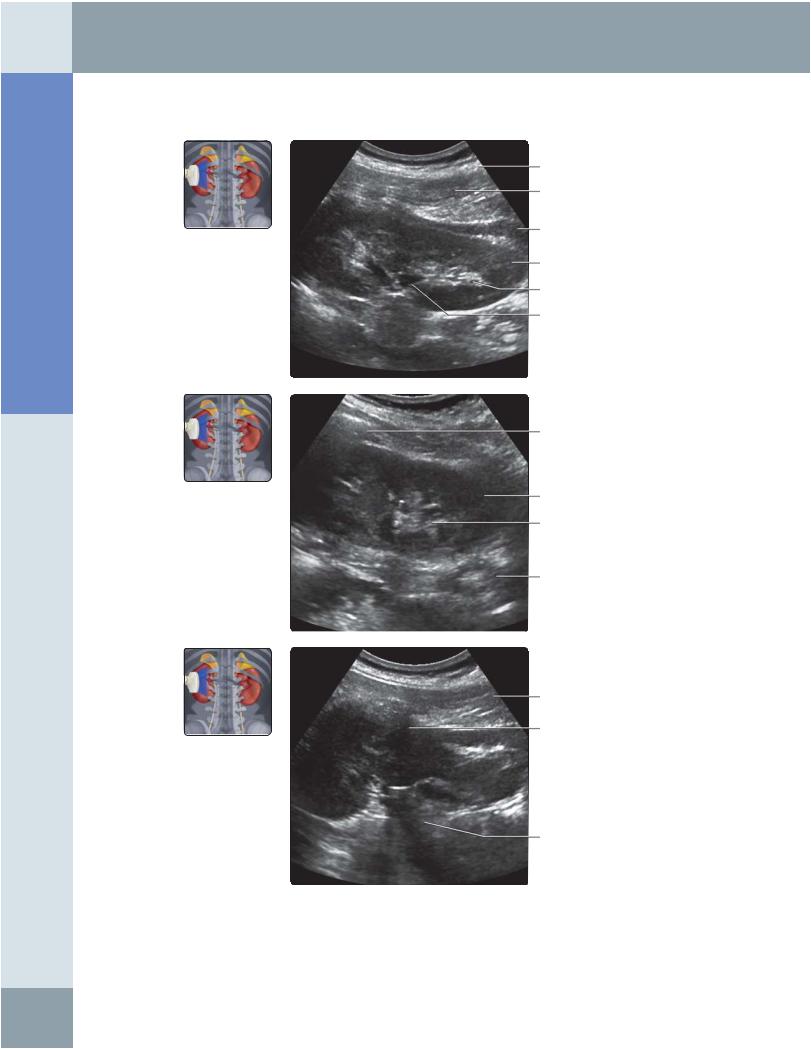
(Top) Longitudinal grayscale ultrasound of the left kidney scanning from the posterolateral approach is shown. This approach avoids interference from bowel gas shadowing. (Middle) Longitudinal grayscale ultrasound of the left kidney scanning from the posterolateral approach with the transducer angling more posteriorly when compared with the previous image. Note shadowing from rib degrading imaging of the upper pole. (Bottom) Longitudinal grayscale ultrasound of the left kidney scanning from the posterolateral approach with the transducer angling more anteriorly when compared with the previous 2 images.
58
Kidneys
LEFT KIDNEY, CT CORRELATION
Spleen
Renal hilum
Left kidney
Left psoas muscle
Left hemidiaphragm
Left kidney
Vertebral bodies
Left psoas muscle
Abdomen Anatomy:
|
Spleen |
Superior mesenteric vein |
Left kidney |
|
|
Superior mesenteric artery |
|
Bowel loops |
Gas in descending colon |
|
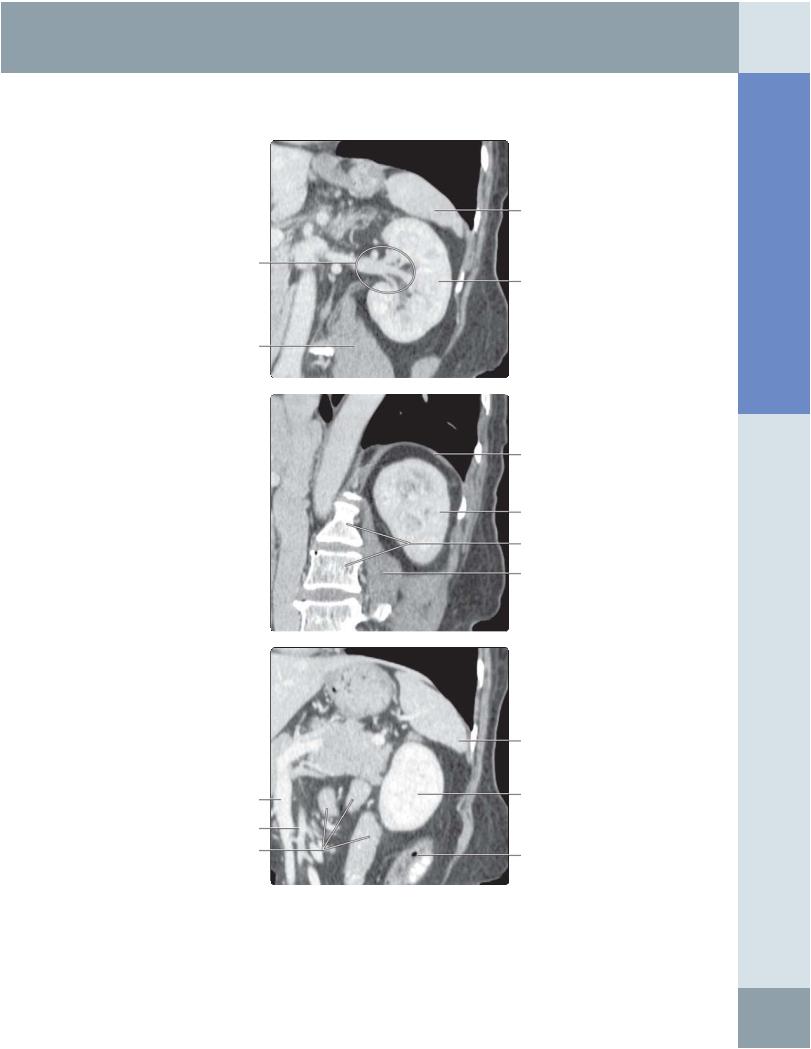
(Top) The 1st in a series of 3 correlative longitudinal oblique multiplanar reconstruction CT images of the left kidney, through planes commonly used when examining the patient with ultrasound, shows clear visualization of the kidney, renal pedicle, and surrounding structures. This makes multidetector row CT the imaging modality of choice (over ultrasound) in patients suspected to have renal injury. (Middle) Correlative longitudinal oblique multiplanar reconstruction CT of the left kidney in a plane more posterior to the previous image. (Bottom) Correlative longitudinal oblique multiplanar reconstruction CT of the left kidney in a plane more anterior than the previous 2 images.
59
Anatomy: Abdomen
Kidneys
LEFT KIDNEY, ANTERO LATERAL TRANSVERSE SCAN
Spleen
Bowel
Bowel
Renal hilum
Bowel
Medullary pyramid
Rib shadow
Left kidney
Sinus echoes
Oblique abdominal muscles
Left kidney
Renal sinus echoes
Oblique abdominal muscles
Left kidney
Perinephric fat
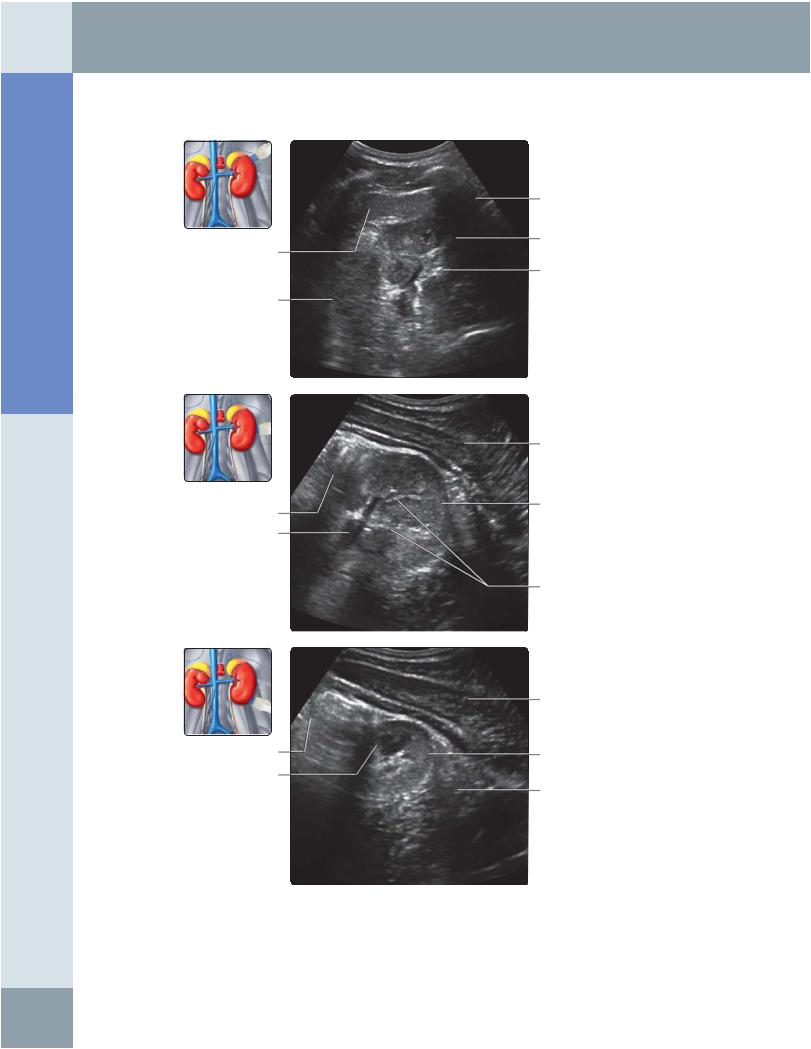
(Top) Transverse grayscale ultrasound of the upper pole of the left kidney using the anterolateral approach. Note that the image quality is limited by interference from gas in the stomach and bowel. The presence of bowel loops anteriorly also limits the use of this approach for interventional procedures on the left kidney. (Middle) Transverse grayscale ultrasound of the mid pole of the left kidney using the anterolateral approach. (Bottom) Transverse grayscale ultrasound of the lower pole of the left kidney using the anterolateral approach.
60
Kidneys
Perinephric fat
Left renal vein
LEFT KIDNEY, CT CORRELATION
Stomach
Spleen
Bowel
Left kidney
Descending colon
Left kidney
Descending colon
Left kidney
Left psoas muscle
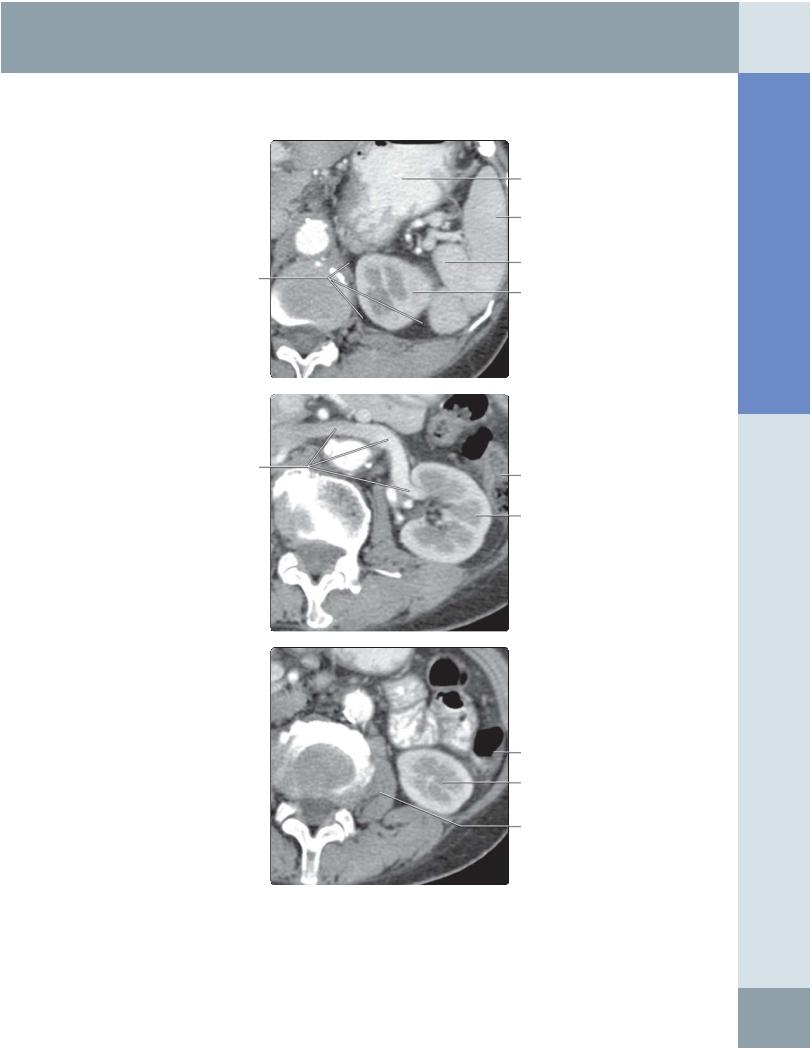
(Top) The 1st in a series of 3 correlative transverse CT images of the left kidney, through planes commonly used when examining the kidney, is shown using the anterior approach. Note the relationship of the spleen to the upper pole of the left kidney, allowing it to be used as an acoustic window, particularly in patients with splenomegaly. This transverse CT image shows the upper pole of the left kidney. (Middle) Correlative transverse CT image of the mid pole of the left kidney at the level of the left renal vein. (Bottom) Correlative transverse CT image of the lower pole of the left kidney.
Abdomen Anatomy:
61
Anatomy: Abdomen
Kidneys
LEFT KIDNEY, ANTERIOR TO ANTEROLATERAL TRANSVERSE SCAN
Shadowing from rib |
Spleen |
|
Renal cortex
Renal medullary pyramid
Medullary pyramid
Renal vein
Vertebral body
|
Abdominal wall muscles |
Bowel |
Renal cortex |
|
Left psoas muscle |
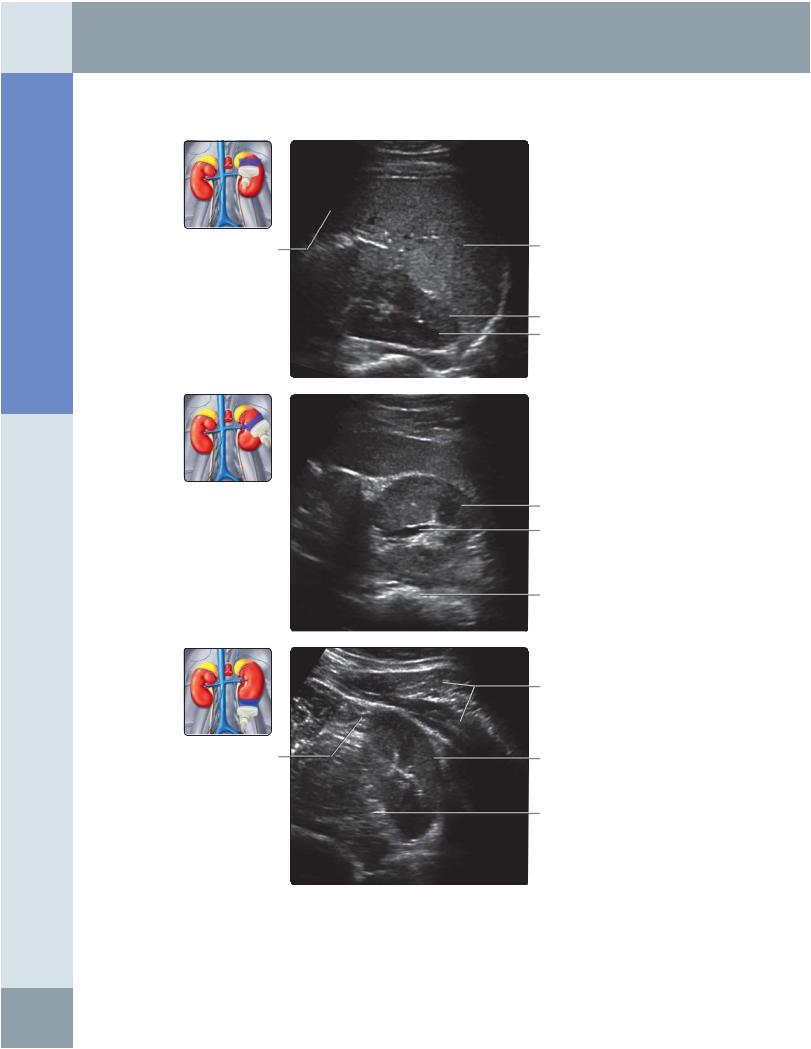
(Top) Transverse grayscale ultrasound of the upper pole of the left kidney using the anterolateral approach. Note the proximity of the kidney to the skin surface and the absence of intervening bowel loops. Adjacent spleen provides an imaging window; however, ribs cast a shadow. (Middle) Transverse grayscale ultrasound of the mid pole of the left kidney using the posterolateral approach. (Bottom)
Transverse grayscale ultrasound of the lower pole of the left kidney using the posterolateral approach.
62
Kidneys
LEFT KIDNEY, POSTERIOR ABDOMEN SCAN
Subcutaneous fat
Left latissimus dorsi muscle
Left renal cortex
Perirenal fat
Subcutaneous fat
Left latissimus dorsi
Left renal cortex
Left renal artery branches
Main renal vein
Subcutaneous fat
Left latissimus dorsi muscle
Left renal cortex
Renal vessels
Artifacts
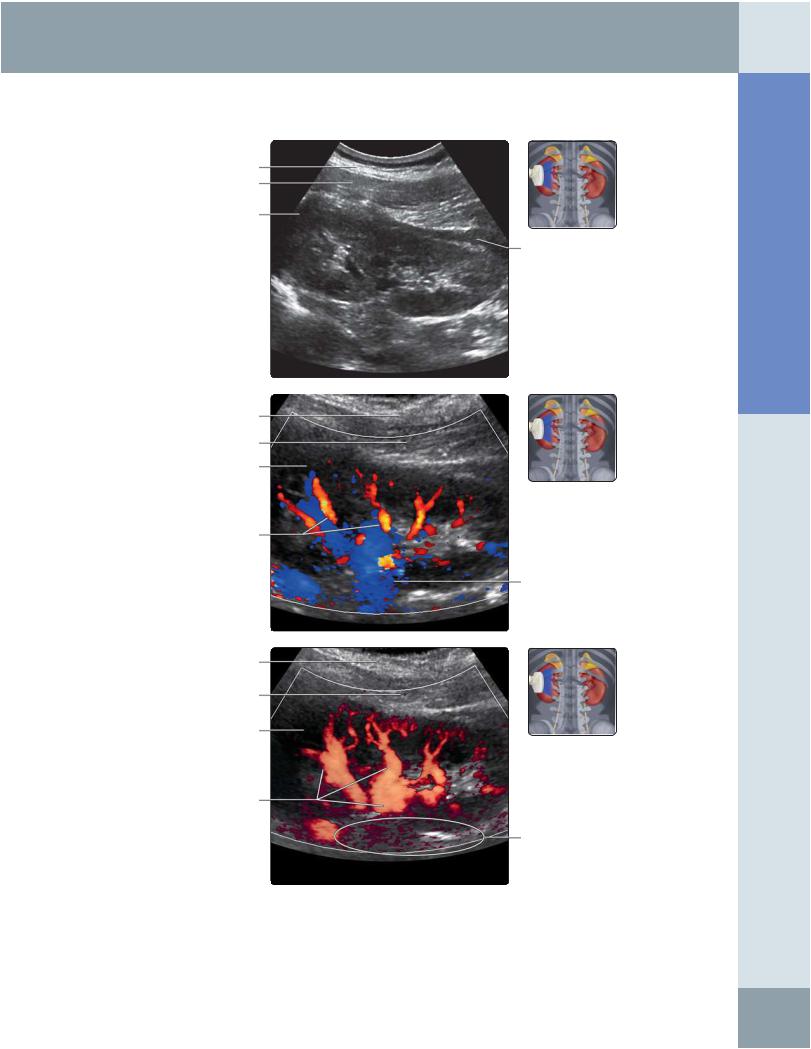
(Top) Longitudinal grayscale ultrasound of the left kidney scanning from the posterior approach shows renal veins that may mimic hydronephrosis. Color Doppler ultrasound should be used to differentiate fluid from vessels. This view is useful for performing renal interventional procedures, such as renal biopsy or nephrostomy. It is also a good way for standardizing renal length measurements in children. (Middle) Posterior longitudinal color Doppler ultrasound of the left kidney is shown. This assessment of the position of major vessels is useful for avoiding major vessels when performing renal interventional procedures, such as renal biopsy or nephrostomy. (Bottom) In this posterior longitudinal power Doppler ultrasound of the left kidney, note the absence of information about flow direction on power Doppler. Motion artifact is more evident on power Doppler.
Abdomen Anatomy:
63
