
- •Preface
- •Contents
- •1: The Eye Scanning
- •1 An Overview of Anatomy
- •2.1 Scanning Method
- •2.2 Section Structure
- •2.4 Clinical Value
- •2.5 Notice
- •3.1 Scanning Method
- •3.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.4 Clinical Value
- •4.1 Scanning Method
- •4.2 Sectional Structure
- •4.4 Clinical Value
- •5.1 Scanning Method
- •5.2 Sectional Structure
- •5.4 Clinical Value
- •6.1 Scanning Method
- •6.2 Sectional Structure
- •6.4 Clinical Value
- •2: Transcranial Ultrasonography
- •1.1 Scanning Method
- •1.2 Section Structure
- •1.4 Clinical Application Value
- •2.1 Scanning Method
- •2.2 Section Structure
- •2.4 Clinical Application Value
- •3.1 Scanning Method
- •3.2 Section Structure
- •3.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •4.1 Scanning Method
- •4.2 Section Structure
- •4.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •5.1 Scanning Method
- •5.2 Section Structure
- •5.4 Clinical Application Value
- •6.1 Scanning Method
- •6.2 Section Structure
- •6.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.1 Scanning Method
- •1.2 Section Structure
- •1.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.5 Notice
- •2.1 Scanning Method
- •2.2 Section Structure
- •2.3 Clinical Application Value
- •3 Para-parotid Gland (Transverse Scan)
- •3.1 Scanning Method
- •3.2 Section Structure
- •3.3 Clinical Application Value
- •4 Longitudinal Scan of the Submandibular Gland
- •4.1 Scanning Method
- •4.2 Section Structure
- •4.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5.1 Scanning Method
- •5.2 Section Structure
- •5.3 Clinical Application Value
- •4: Thyroid Scanning
- •1.1 Scanning Method
- •1.2 Section Structure
- •2 The Longitudinal View of the Thyroid
- •2.1 Scanning Method
- •2.2 Section Structure
- •2.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.1 Scanning Method
- •3.2 Section Structure
- •3.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •4 Color Doppler Flow Image of the Thyroid
- •4.1 Scanning Method
- •4.2 Section Structure
- •4.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •5.1 Scanning Method
- •5.2 Section Structure
- •5.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •6.1 Scanning Method
- •6.2 Section Structure
- •6.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •7 Doppler Spectrum Flow Imaging of the Inferior Thyroid Artery
- •7.1 Scanning Method
- •7.2 Section Structure
- •7.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •5: The Breast Scanning
- •1.1 Scanning Method
- •1.2 Section Structures
- •1.4 Clinical Application Value
- •2.1 Scanning Method
- •2.2 Section Structures
- •2.3 Clinical Application Value
- •3.1 Scanning Method
- •3.2 Section Structures
- •3.4 Clinical Section Value
- •4.1 Scanning Method
- •4.2 Section Structures
- •4.3 Clinical Application Value
- •5.1 Scanning Method
- •5.2 Section Structures
- •5.3 Clinical Application Value
- •6.1 Scanning Method
- •6.2 Section Structures
- •6.3 Clinical Application Value
- •7 Color Doppler Imaging of Normal Breast in Lactating Women
- •7.1 Scanning Method
- •7.2 Section Structures
- •7.3 Clinical Application Value
- •8 Doppler Spectrum of Normal Breast in Lactating Women
- •8.1 Scanning Method
- •8.2 Section Structures
- •8.3 Clinical Application Value
- •9.1 Scanning Method
- •9.2 Section Structures
- •9.3 Clinical Application Value
- •10.1 Scanning Method
- •10.2 Section Structures
- •10.3 Clinical Application Value
- •11.1 Scanning Method
- •11.2 Section Structures
- •11.3 Clinical Value
- •Bibliography
- •6: Echocardiography
- •1.1 Parasternal Left Ventricular Long-Axis View: M-Mode, Echo Pattern of Heart Base (Aortic Root)
- •1.1.1 Scanning Method
- •1.1.2 Section Structure
- •1.1.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •1.1.4 The Clinical Application
- •1.2 Parasternal Left Ventricular Long-Axis-View M-Mode, Echo Pattern of Mitral Valve
- •1.2.1 Scanning Method
- •1.2.2 Section Structure
- •1.2.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •1.2.4 The Clinical Application
- •1.3 The Parasternal Left Ventricular Long-Axis-View M-Mode, Echo Pattern of Left Ventricle
- •1.3.1 Scanning Method
- •1.3.2 Section Structure
- •1.3.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •1.3.4 The Clinical Application
- •1.4 Great Artery Short-Axis View (M-Mode Scan at Pulmonary Valve Level)
- •1.4.1 Scanning Method
- •1.4.2 Section Structure
- •1.4.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •1.4.4 The Clinical Application
- •2.1.1 Scanning Method
- •2.1.2 Section Structure
- •2.1.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.1.4 The Clinical Application
- •2.2.1 Scanning Method
- •2.2.2 Section Structure
- •2.2.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.2.4 The Clinical Application
- •2.3.1 Scanning Method
- •2.3.2 Section Structure
- •2.3.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.3.4 The Clinical Application
- •2.4.1 Scanning Method
- •2.4.2 Section Structure
- •2.4.3 The Clinical Application
- •2.5.1 Scanning Method
- •2.5.2 Section Structure
- •2.5.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.5.4 The Clinical Application
- •2.6.1 Scanning Method
- •2.6.2 Section Structure
- •2.6.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.6.4 The Clinical Application
- •2.7.1 Scanning Method
- •2.7.2 Section Structure
- •2.7.3 The Clinical Application
- •2.8.1 Scanning Method
- •2.8.2 Section Structure
- •2.8.3 The Clinical Application
- •2.9.1 Scanning Method
- •2.9.2 Section Structure
- •2.9.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.9.4 The Clinical Application
- •2.10 Apical Four-Chamber View
- •2.10.1 Scanning Method
- •2.10.2 Section Structure
- •2.10.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.10.4 The Clinical Application
- •2.11.1 Scanning Method
- •2.11.2 Section Structure
- •2.11.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.11.4 The Clinical Application
- •2.12.1 Scanning Method
- •2.12.2 Section Structure
- •2.12.3 The Clinical Application
- •2.13.1 Scanning Method
- •2.13.2 Section Structure
- •2.13.3 The Clinical Application
- •2.14.1 Scanning Method
- •2.14.2 Scanning Section Structure
- •2.14.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.14.4 The Clinical Application
- •2.15 Coronary Sinus View
- •2.15.1 Scanning Method
- •2.15.2 Section Structure
- •2.15.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.15.4 The Clinical Application
- •2.16.1 Scanning Method
- •2.16.2 Section Structure
- •2.16.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.16.4 The Clinical Application
- •2.17.1 Scanning Method
- •2.17.2 Section Structure
- •2.17.3 The Clinical Application
- •2.18 Apical Five-Chamber View
- •2.18.1 Scanning Method
- •2.18.2 Section Structure
- •2.18.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.18.4 The Clinical Application
- •2.19 Short-Axis View of the Inferior Vena Cava
- •2.20.1 Scanning Method
- •2.20.2 Section Structure
- •2.20.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.20.4 The Clinical Application
- •2.21.1 Scanning Method
- •2.21.2 Section Structure
- •2.21.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.21.4 The Clinical Application
- •2.22.1 Scanning Method
- •2.22.2 Section Structure
- •2.22.3 The Clinical Application
- •2.23 Subxiphoid Four-Chamber View
- •2.23.1 Scanning Method
- •2.23.2 Section Structure
- •2.23.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.23.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.24 Subxiphoid Two-Atrium View
- •2.24.1 Scanning Methods
- •2.24.2 Section Structure
- •2.24.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.24.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.25 Subxiphoid Aortic Ventricular View
- •2.25.1 Scanning Methods
- •2.25.2 Section Structure
- •2.25.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.25.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.26 Subxiphoid Inferior Vena Cava (Long-Axis) View
- •2.26.1 Scanning Methods
- •2.26.2 Section Structure
- •2.26.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.26.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.27 Subxiphoid Ventricular Short-Axis View
- •2.27.1 Scanning Methods
- •2.27.2 Section Structure
- •2.27.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.27.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.28 Suprasternal Aortic Arch Short-Axis View
- •2.28.1 Scanning Methods
- •2.28.2 Section Structure
- •2.28.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.28.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.29 Suprasternal Superior Vena Cava Long-Axis View
- •2.29.1 Scanning Methods
- •2.29.2 Section Structure
- •2.29.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.29.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.30 Suprasternal Aortic Arch Short-Axis View
- •2.30.1 Scanning Methods
- •2.30.2 Section Structure
- •2.30.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.30.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.31 Main Pulmonary Artery Long-Axis View by Subxiphoid
- •2.31.1 Scanning Methods
- •2.31.2 Section Structure
- •2.31.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.31.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.32 Transesophageal Two-Atrium View
- •2.32.1 Scanning Method
- •2.32.2 Section Structure
- •2.32.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.32.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.33 Transesophageal Left Atrial Appendage View
- •2.33.1 Scanning Methods
- •2.33.2 Section Structure
- •2.33.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.33.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.34 Transesophageal Aortic Root Long-Axis View
- •2.34.1 Scanning Methods
- •2.34.2 Section Structure
- •2.34.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •2.34.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.1.1 Scanning Methods
- •3.1.2 Section Structure
- •3.1.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •3.1.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.1.5 Notice
- •3.2.1 Scanning Methods
- •3.2.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.3.1 Scanning Method
- •3.3.2 Section Structure
- •3.3.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •3.3.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.4.1 Scanning Method
- •3.4.2 Section Structure
- •3.4.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.4.4 Notice
- •3.5.1 Scanning Method
- •3.5.2 Section Structure
- •3.5.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.5.5 Notice
- •3.6.1 Scanning Method
- •3.6.2 Section Structures
- •3.6.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.6.4 Notice
- •3.7.1 Method
- •3.7.2 Section Structure
- •3.7.3 Measuring Method and Normal Value
- •3.7.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.7.5 Notice
- •3.8.1 Scanning Method
- •3.8.2 Section Structure
- •3.8.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.8.4 Notice
- •7: Vascular System Scanning
- •1 Artery System
- •1.1.1 Scanning Method
- •1.1.2 Sectional Structure
- •1.1.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.2.1 Scanning Method
- •1.2.2 Sectional Structure
- •1.2.3 Measurement Methods
- •1.2.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.3.1 Scanning Method
- •1.3.2 Sectional Structure
- •1.3.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.4.1 Scanning Method
- •1.4.2 Sectional Structure
- •1.4.3 Measurement Methods
- •1.4.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.4.5 Note
- •1.5.1 Scanning Method
- •1.5.2 Sectional Structure
- •1.5.3 Measurement Methods
- •1.5.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.5.5 Note
- •1.6.1 Scanning Method
- •1.6.2 Section Structure
- •1.6.3 Measurement Methods
- •1.6.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.7 Doppler Spectrum of the External Carotid Artery
- •1.7.1 Scanning Method
- •1.7.2 Section Structure
- •1.7.3 Measurement Methods
- •1.7.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.8.1 Scanning Method
- •1.8.2 Sectional Structure
- •1.8.3 Measurement Methods
- •1.8.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.9.1 Scanning Method
- •1.9.2 Sectional Structure
- •1.9.3 Measurement Methods
- •1.9.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.10.1 Scanning Method
- •1.10.2 Sectional Structure
- •1.10.3 Measurement Methods
- •1.10.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.11.1 Scanning Method
- •1.11.2 Sectional Structure
- •1.11.3 Clinical Significance
- •1.12.1 Scanning Method
- •1.12.2 Sectional Structure
- •1.12.3 Measurement Methods
- •1.12.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.12.5 Note
- •1.13.1 Scanning Method
- •1.13.2 Sectional Structure
- •1.13.3 Measurement Methods
- •1.13.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.14.1 Scanning Method
- •1.14.2 Sectional Structure
- •1.14.3 Measurement Methods
- •1.14.4 Clinical Significance
- •2.1.1 Scanning Method
- •2.1.2 Sectional Structure
- •2.1.3 Measurement Methods
- •2.1.4 Clinical Significance
- •2.1.5 Note
- •2.2.1 Scanning Method
- •2.2.2 Sectional Structure
- •2.2.3 Measurement Methods
- •2.2.4 Clinical Significance
- •2.2.5 Note
- •2.3.1 Scanning Method
- •2.3.2 Sectional Structure
- •2.3.3 Measurement Methods
- •2.3.4 Clinical Significance
- •2.4.1 Scanning Method
- •2.4.2 Sectional Structure
- •2.4.3 Measurement Methods
- •2.4.4 Clinical Significance
- •2.5.1 Scanning Method
- •2.5.2 Section Structure
- •2.5.3 Measuring Method
- •2.5.4 Clinical significance
- •2.6.1 Scanning Method
- •2.6.2 Sectional Structure
- •2.6.3 Measurement Methods
- •2.6.4 Clinical Significance
- •2.7.1 Scanning Method
- •2.7.2 Sectional Structure
- •2.7.3 Measurement Methods
- •2.7.4 Clinical significance.
- •2.8.1 Scanning Method
- •2.8.2 Sectional Structure
- •2.8.3 Measurement Methods
- •2.8.4 Clinical Significance
- •2.9.1 Scanning Method
- •2.9.2 Sectional Structure
- •2.9.3 Measurement Methods
- •2.9.4 Clinical Significance
- •2.10.1 Scanning Method
- •2.10.2 Sectional Structure
- •2.10.3 Measurement Methods
- •2.10.4 Clinical Significance
- •2.11.1 Scanning Method
- •2.11.2 Sectional Structure
- •2.11.3 Measurement Methods
- •2.11.4 Clinical Significance
- •2.12.1 Sectional Structure
- •2.12.2 Measurement Methods
- •2.12.3 Clinical Significance
- •2.13.1 Sectional Structure
- •2.13.2 Measurement Methods
- •2.13.3 Clinical Significance
- •2.14.1 Scanning Method
- •2.14.2 Sectional Structure
- •2.14.3 Measurement Methods
- •2.14.4 Clinical Significance
- •2.15.1 Scanning Method
- •2.15.2 Sectional Structure
- •2.15.3 Measurement Methods
- •2.15.4 Clinical Significance
- •2.16.1 Scanning Method
- •2.16.2 Sectional Structure
- •2.16.3 Measurement Methods
- •2.16.4 Clinical Significance
- •2.17.1 Scanning Method
- •2.17.2 Sectional Structure
- •2.17.3 Measurement Methods
- •2.17.4 Clinical Significance
- •2.18.1 Scanning Method
- •2.18.2 Sectional Structure
- •2.18.3 Measurement Methods
- •2.18.4 Clinical Significance
- •2.18.5 Note
- •2.19.1 Scanning Method
- •2.19.2 Sectional Structure
- •2.19.3 Measurement Methods
- •2.19.4 Clinical Significance
- •2.19.5 Note
- •3 Vein System
- •3.1.1 Scanning Method
- •3.1.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.1.3 Measurement Methods
- •3.1.4 Clinical Significance
- •3.2 Transverse scannng of the internal jugular vein
- •3.2.1 Scanning Method
- •3.2.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.2.3 Measurement Methods
- •3.2.4 Clinical Significance
- •3.3.1 Scanning Method
- •3.3.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.3.3 Measurement Methods
- •3.3.4 Clinical Significance
- •3.3.5 Note
- •3.4.1 Scanning Method
- •3.4.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.4.3 Measurement Methods
- •3.4.4 Clinical Significance
- •3.5.1 Scanning Method
- •3.5.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.5.3 Measurement Methods
- •3.5.4 Clinical Significance
- •3.6.1 Scanning Method
- •3.6.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.6.3 Measurement Methods
- •3.6.4 Clinical significance
- •3.7.1 Scanning Method
- •3.7.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.7.3 Clinical Significance
- •3.8.1 Scanning Method
- •3.8.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.8.3 Measurement Methods
- •3.8.4 Clinical Significance
- •3.9.1 Scanning Method
- •3.9.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.9.3 Measurement Methods
- •3.9.4 Clinical Significance
- •3.10.1 Scanning Method
- •3.10.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.10.3 Measurement Methods
- •3.10.4 Clinical Significance
- •3.11.1 Scanning Method
- •3.11.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.11.3 Measurement Methods
- •3.11.4 Clinical Significance
- •3.12.1 Scanning Method
- •3.12.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.12.3 Measurement Methods
- •3.12.4 Clinical Significance
- •3.13.1 Scanning Method
- •3.13.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.13.3 Measurement Methods
- •3.13.4 Clinical Significance
- •3.14.1 Scanning Method
- •3.14.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.14.3 Measurement Methods
- •3.14.4 Clinical Significance
- •3.15.1 Scanning Method
- •3.15.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.15.3 Measurement Methods
- •3.15.4 Clinical Significance
- •3.17.1 Scanning Method
- •3.17.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.17.3 Measurement Methods
- •3.17.4 Clinical Significance
- •3.18.1 Scanning Method
- •3.18.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.18.3 Measurement Methods
- •3.18.4 Clinical Significance
- •3.19.1 Scanning Method
- •3.19.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.19.3 Measurement Methods
- •3.19.4 Clinical Significance
- •3.20.1 Scanning Method
- •3.20.2 Sectional Structure
- •3.20.3 Measurement Methods
- •3.20.4 Clinical Significance
- •3.20.5 Notes
- •1 Liver Scanning
- •1.1.1 Scanning Method
- •1.1.2 Section Structure
- •1.1.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.1.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.2 Longitudinal Scanning of the Liver through the Inferior Vena Cava on Subxiphoid
- •1.2.1 Scanning Method
- •1.2.2 Section Structure
- •1.2.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.2.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.2.5 Notice
- •1.3 Transverse Scan of the Left and Right Liver Through the Porta Hepatis on Subxiphoid
- •1.3.1 Scanning Method
- •1.3.2 Section Structure
- •1.3.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.3.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.4 Transverse Scanning of the Left Hepatic Lobe Through the Left Portal Vein Branches by Subxiphoid
- •1.4.1 Scanning Method
- •1.4.2 Section Structure
- •1.4.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.4.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.5.1 Scanning Method
- •1.5.2 Section Structure
- •1.5.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.5.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.6.1 Scanning Method
- •1.6.2 Section Structure
- •1.6.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.7.1 Scanning Method
- •1.7.2 Section Structure
- •1.7.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.8 Longitudinal scanning of the hepatic left lobe and the ligament teres hepatis by subxiphoid
- •1.8.1 Scanning Method
- •1.8.2 Section Structure
- •1.8.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.8.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.9 Oblique scanning of the ligament teres and the left liver by subxiphoid
- •1.9.1 Scanning Method
- •1.9.2 Section Structure
- •1.9.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.10 Oblique scanning of the liver through the gallbladder and inferior vena cava by the right subcostal margin
- •1.10.1 Scanning Method
- •1.10.2 Section Structure
- •1.10.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.11.1 Scanning Method
- •1.11.2 Section Structure
- •1.11.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.11.5 Notes
- •1.12 Transversely Scanning the Upper Part of the Porta Hepatis
- •1.12.1 Scanning Method
- •1.12.2 Section Structure
- •1.12.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.12.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.13.1 Scanning Method
- •1.13.2 Section Structure
- •1.13.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.13.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.14.1 Scanning Method
- •1.14.2 Section Structure
- •1.14.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.14.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.15 Longitudinal Scanning of the Liver Through the Middle Hepatic Vein on Subxiphoid
- •1.15.1 Scanning Method
- •1.15.2 Section Structure
- •1.15.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.15.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.16.1 Scanning Method
- •1.16.2 Section Structure
- •1.16.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.16.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.17 Oblique Scanning of the Right Anterior Liver and the Left Medial Lobe of the Liver by Right Intercostal Space
- •1.17.1 Scanning Method
- •1.17.2 Section Structure
- •1.17.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.18.1 Scanning Method
- •1.18.2 Section Structure
- •1.18.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.19 Oblique Scanning of the Right Liver Through Right the Portal Vein by the Right Subcostal Space Approach
- •1.19.1 Scanning Method
- •1.19.2 Section Structure
- •1.19.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.19.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.20 Longitudinal Scanning of the Right Liver and Right Kidney from the Right Subcostal
- •1.20.1 Scanning Method
- •1.20.2 Section Structure
- •1.20.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.20.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.20.5 Notes
- •1.21 Oblique Scanning of the Right Liver Through Right Hepatic Veins on Subxiphoid
- •1.21.1 Scanning Method
- •1.21.2 Section Structure
- •1.21.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.21.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.22.1 Scanning Method
- •1.22.2 Section Structure
- •1.22.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.22.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.23.1 Scanning Method
- •1.23.2 Section Structure
- •1.23.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.23.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.24.1 Scanning Method
- •1.24.2 Section Structure
- •1.24.3 Clinical Application Value
- •1.25 Transverse Scanning of the Right Liver and the Right Kidney from the Right Subcostal
- •1.25.1 Scanning Method
- •1.25.2 Section Structure
- •1.25.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.26.1 Scanning Method
- •1.26.2 Section Structure
- •1.26.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.27 Longitudinal Scanning of the Common Hepatic Artery and Splenic Artery from the Upper Abdomen
- •1.27.1 Scanning Method
- •1.27.2 Section Structure
- •1.27.3 Measuring Method and the Normal
- •1.27.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.28 Common Hepatic Artery Blood Flow Spectrum
- •1.28.1 Scanning Method
- •1.28.2 Measuring Method and the Normal
- •1.28.3 Clinical Application Value
- •1.29 Longitudinal Scanning of the Proper Hepatic Artery from Upper Abdomen
- •1.29.1 Scanning Method
- •1.29.2 Section Structure
- •1.29.3 Measuring Method and the Normal
- •1.29.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.30 The Proper Hepatic Artery Blood Flow Spectrum
- •1.30.1 Scanning Method
- •1.30.2 Measuring Method and the Normal
- •1.30.3 Clinical Application Value
- •1.31 Portal Vein Blood Flow Spectrum from Right Subcostal Margin
- •1.31.1 Scanning Method
- •1.31.2 Section Structure
- •1.31.3 Measuring Method and the Normal
- •1.31.4 Clinical Application Value
- •2.1.1 Scanning Method
- •2.1.2 Section Structure
- •2.1.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •2.1.4 Clinical Application Value
- •2.1.5 Notice
- •2.2.1 Scanning Method
- •2.2.2 Section Structure
- •2.2.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •2.2.4 Clinical Application Value
- •2.2.5 Notice
- •2.3.1 Scanning Method
- •2.3.2 Section Structure
- •2.3.3 Clinical Application Value
- •2.4.1 Scanning Method
- •2.4.2 Section Structure
- •2.4.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •2.4.4 Clinical Application Value
- •2.5.1 Scanning Method
- •2.5.2 Section Structure
- •2.5.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •2.5.4 Clinical Application Value
- •2.6.1 Scanning Methods
- •2.6.2 Section Structure
- •2.6.4 Clinical Application Value
- •2.7 Longitudinal Scanning of the Intrapancreatic Port and the end Part of the Common Bile Duct by the Right Subcostal and Right Upper Abdomen
- •2.7.1 Scanning Method
- •2.7.2 Section Structure
- •2.7.4 Clinical Application Value
- •2.8 Transverse Scanning of the Common Bile Duct at the Level of the Upper Part of the Pancreatic Head by the Right Subcostal
- •2.8.1 Scanning Method
- •2.8.2 Section Structure
- •2.8.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •2.8.4 Clinical Application Value
- •2.9 Transverse Scanning of the Middle Segment of the Common Bile Duct at the Level of the Lower Part of the Pancreatic Head by Right Subcostal
- •2.9.1 Scanning Method
- •2.9.2 Section Structure
- •2.9.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •2.9.4 Clinical Application Value
- •3 The Pancreas
- •3.1.1 Scanning Method
- •3.1.2 Section Structure
- •3.1.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •3.1.4 Clinical Application Value
- •3.2.1 Scanning Method
- •3.2.2 Section Structure
- •3.2.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •3.2.4 Clinical Application Value
- •3.3 Transverse Scanning of the Lower Port of the Pancreatic Head by Subxiphoid
- •3.3.1 Scanning Method
- •3.3.2 Section Structure
- •3.3.3 Clinical Application Value
- •3.4.1 Scanning Method
- •3.4.2 Section Structure
- •3.4.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •3.4.4 Clinical Application Value
- •3.5 Sagittal Scanning of the Pancreatic Body by the Subxiphoid
- •3.5.1 Scanning Method
- •3.5.2 Section Structure
- •3.5.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •3.5.4 Clinical Application Value
- •3.6.1 Scanning Method
- •3.6.2 Section Structure
- •3.6.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •3.6.4 Clinical Application Value
- •3.7 Oblique Scanning of the Left Kidney, Spleen and Pancreatic Tail by the Left Intercostal Space
- •3.7.1 Scanning Method
- •3.7.2 Section Structure
- •3.7.3 Clinical Application Value
- •4 Spleen
- •4.1.1 Method
- •4.1.2 Section Structure
- •4.1.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •4.1.4 Clinical Application Value
- •4.2 The Image of the Accessory Spleen (Splenules) in the Longitudinal Scan of the Spleen by the Left Intercostal
- •4.2.1 Scanning Method
- •4.2.2 Section Structure
- •4.2.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •4.2.4 Clinical application value
- •4.3.1 Scanning Method
- •4.3.2 Section Structure
- •4.3.3 Clinical Application Value
- •4.4.1 Scanning Method
- •4.4.2 Section Structure
- •4.4.3 Clinical application value
- •4.5.1 Scanning Method
- •4.5.2 Section structure
- •4.5.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •4.5.4 Clinical Application Value
- •4.6.1 Scanning Method
- •4.6.2 Section Structure
- •4.6.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •4.6.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5 The Gastrointestinal Scanning
- •5.1.1 Scanning Method
- •5.1.2 Section Structure
- •5.1.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •5.1.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •5.2 Transverse Scanning of the Lower Segment of the Esophagus
- •5.2.1 Scanning Method
- •5.2.2 Section Structure
- •5.2.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •5.2.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5.3.1 Scanning Method
- •5.3.2 Section Structure
- •5.3.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •5.3.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5.4.1 Scanning Method
- •5.4.2 Section Structure
- •5.4.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •5.4.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5.6 Scanning Method
- •5.6.1 Section Structure
- •5.6.2 Measuring Method and Normal
- •5.6.3 Clinical Application Value
- •5.7 Short Axis Scanning of the Stomach Body by the Upper Abdomen
- •5.7.1 Scanning Method
- •5.7.2 Section Structure
- •5.7.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •5.7.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5.8.1 Scanning Method
- •5.8.2 Section Structure
- •5.8.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •5.8.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5.9 Short Axis Scanning of the Stomach Antrum by the Right Upper Abdomen
- •5.9.1 Scanning Method
- •5.9.2 Section Structure
- •5.9.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •5.9.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5.10.1 Scanning Method
- •5.10.2 Section Structure
- •5.10.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •5.10.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5.11.1 Scanning Method
- •5.11.2 Section Structure
- •5.11.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •5.11.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5.12.1 Scanning Method
- •5.12.2 Section Structure
- •5.12.3 Clinical Application Value
- •5.13.1 Scanning Method
- •5.13.2 Section Structure
- •5.13.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •5.13.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5.14 Longitudinal Scanning of the Ascending Colon from the Right Lower Abdomen Approach
- •5.14.1 Scanning Method
- •5.14.2 Section Structure
- •5.14.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •5.14.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5.15.1 Scanning Method
- •5.15.2 Section Structure
- •5.15.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •5.15.4 Clinical Application Value
- •9: Abdominal Vascular Scanning
- •1 Artery System
- •1.1.1 Scanning Method
- •1.1.2 Section Structure
- •1.1.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •1.1.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.2.1 Scanning Method
- •1.2.2 Section Structure
- •1.2.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.2.5 Notes
- •1.3 Transverse View of the Abdominal Aorta
- •1.3.1 Scanning Method
- •1.3.2 Section Structure
- •1.3.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •1.3.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.3.5 Notice
- •1.4 Color Doppler Flow Image of the Abdominal Aorta
- •1.4.1 Scanning Method
- •1.4.2 Section Structure
- •1.4.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •1.4.4 Clinical Application Value
- •1.5 Doppler Spectrum of the Abdominal Aorta
- •1.5.1 Scanning Method
- •1.5.2 Section Structure
- •1.5.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •1.5.4 Clinical Application Value
- •2 Celiac Artery (CA)
- •2.1 Long-Axis View of the Celiac Artery
- •2.1.1 Scanning Method
- •2.1.2 Section Structure
- •2.1.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •2.1.4 Clinical Application Value
- •2.1.5 Notice
- •2.2 Doppler Spectrum of the Celiac Artery
- •2.2.1 Scanning Method
- •2.2.2 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •2.2.3 Clinical Application Value
- •2.3 Aberrance of the Celiac Artery
- •2.3.1 Scanning Method
- •2.3.2 Section Structure
- •2.3.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •2.3.4 Clinical Application Value
- •3 Hepatic Artery
- •3.1 Longitudinal Scan of the Common Hepatic Artery and Splenic Artery from the Upper Abdomen
- •3.1.1 Scanning Method
- •3.1.2 Section Structure
- •3.1.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •3.1.4 Clinical Application Value
- •3.2 Common Hepatic Artery Blood Flow Spectrum
- •3.2.1 Scanning Method
- •3.2.2 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •3.2.3 Clinical Application Value
- •3.3 Longitudinal Scan of the Proper Hepatic Artery from the Upper Abdomen
- •3.3.1 Scanning Method
- •3.3.2 Section Structure
- •3.3.4 Clinical Application Value
- •3.4 Proper Hepatic Artery Blood Flow Spectrum
- •3.4.1 Scanning Method
- •3.4.2 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •3.4.3 Clinical Application Value
- •4 Superior Mesenteric Artery
- •4.1.1 Scanning Method
- •4.1.2 Section Structure
- •4.1.4 Clinical Application Value
- •4.2 Transverse Section of the Superior Mesenteric Artery
- •4.2.1 Scanning Method
- •4.2.2 Section Structure
- •4.2.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •4.2.4 Clinical Application Value
- •4.3 Long-Axis View of the Superior Mesenteric Artery
- •4.3.1 Scanning Method
- •4.3.2 Section Structure
- •4.3.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •4.3.4 Clinical Application Value
- •4.4 Doppler Spectrum of the Superior Mesenteric Artery
- •4.4.1 Scanning Method
- •4.4.2 Section Structure
- •4.4.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •4.4.4 Clinical Application Value
- •4.4.5 Notice
- •5 Renal Artery
- •5.1.1 Scanning Method
- •5.1.2 Section Structure
- •5.1.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •5.1.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5.1.5 Notice
- •5.2 Coronal Section at the Lumbar Region: Longitudinal View of the Renal Artery
- •5.2.1 Scanning Method
- •5.2.2 Section Structure
- •5.2.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •5.2.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5.3 Transverse Section at the Right Subcostal Region: Longitudinal View of the Right Renal Artery and Vein
- •5.3.1 Scanning Method
- •5.3.2 Section Structure
- •5.3.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •5.3.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5.4 Coronal Section of the Kidney: Evaluation of Intrarenal Artery Branches
- •5.4.1 Scanning Method
- •5.4.2 Section Structure
- •5.4.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •5.4.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5.5 Doppler Spectrum of the Main Renal Artery and Branches
- •5.5.1 Scanning Method
- •5.5.2 Section Structure
- •5.5.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •5.5.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5.6 Measurement of the AC and AT in Different Types of Normal Spectrum
- •5.6.1 Scanning Method
- •5.6.2 Section Structure
- •5.6.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •5.6.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5.7 Accessory Renal Artery
- •5.7.1 Scanning Method
- •5.7.2 Section Structure
- •5.7.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •5.7.4 Clinical Application Value
- •5.8 Congenital Small Renal Artery
- •5.8.1 Scanning Method
- •5.8.2 Section Structure
- •5.8.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •5.8.4 Clinical Application Value
- •6 Common Iliac Artery
- •6.1.1 Scanning Method
- •6.1.2 Section Structure
- •6.1.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •6.1.4 Clinical Application Value
- •7 Inferior Vena Cava
- •7.1.1 Scanning Method
- •7.1.2 Section Structure
- •7.1.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •7.1.4 Clinical Application Value
- •7.2.1 Scanning Method
- •7.2.2 Section Structure
- •7.2.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •7.2.4 Clinical Application Value
- •7.2.5 Notes
- •7.3 Doppler Spectrum of the Inferior Vena Cava
- •7.3.1 Scanning Method
- •7.3.2 Section Structure
- •7.3.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •7.3.4 Clinical Application Value
- •8 Superior Mesenteric Vein
- •8.1 Transverse View of the Superior Mesenteric Vein
- •8.1.1 Scanning Method
- •8.1.2 Section Structure
- •8.1.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •8.1.4 Clinical Application Value
- •8.2 Long-Axis View of the Superior Mesenteric Vein
- •8.2.1 Scanning Method
- •8.2.2 Section Structure
- •8.2.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •8.2.4 Clinical Application Value
- •9 Renal Vein
- •9.1.1 Scanning Method
- •9.1.2 Section Structure
- •9.1.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •9.1.4 Clinical Application Value
- •9.2 Longitudinal Section of the Right Renal Vein: Transverse Section of the Right Subcostal Region
- •9.2.1 Scanning Method
- •9.2.2 Section Structure
- •9.2.4 Clinical Application Value
- •9.3 Longitudinal Scanning of the Common Iliac Vein
- •9.3.1 Scanning Method
- •9.3.2 Section Structure
- •9.3.3 Measurement Method
- •9.3.4 Clinical Application Value
- •9.4 Color Doppler Flow Imaging of the Common Iliac Vein
- •10 Hepatic Vein
- •10.1.1 Scanning Method
- •10.1.2 Section Structure
- •10.1.3 Measurement Method and Normal Value
- •10.1.4 Clinical Application Value
- •10.1.5 Notice
- •1 Kidney Scanning
- •1.1.1 Scanning Method
- •1.1.2 Section Structure
- •1.1.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.1.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.1.5 Notice
- •1.2.1 Scanning Method
- •1.2.2 Section Structure
- •1.2.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.2.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.3.1 Scanning Method
- •1.3.2 Section Structure
- •1.3.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.3.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.3.5 Notices
- •1.4 Longitudinal Plane of the Right Kidney from the Right Back
- •1.4.1 Scanning Method
- •1.4.2 Section Structure
- •1.4.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.4.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.5 Coronal View of the Left Kidney Through the Lateral Lumbar Region
- •1.5.1 Scanning Method
- •1.5.2 Section Structure
- •1.5.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.5.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.6 Transverse Plane of the Left Kidney in the Left Upper Abdomen
- •1.6.1 Scanning Method
- •1.6.2 Section Structure
- •1.6.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.6.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.7 Longitudinal Plane of the Left Kidney from the Back
- •1.7.1 Scanning Method
- •1.7.2 Section Structure
- •1.7.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.7.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.8 Duplex Pelvis Shown in the Longitudinal Plane of the Kidney
- •1.8.1 Scanning Method
- •1.8.2 Section Structure
- •1.8.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •2 Bladder Scanning
- •2.1 Longitudinal Plane of the Bladder from Suprapubic Symphysis
- •2.1.1 Scanning Method
- •2.1.2 Section Structure
- •2.1.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •2.1.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.2 Transverse Plane of the Bladder from Suprapubic Symphysis
- •2.2.1 Scanning Method
- •2.2.2 Measuring Method and Normal
- •2.2.3 Section Structure
- •2.2.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.2.5 Notice
- •3 Prostate Scanning
- •3.1 Sagittal Aspect of the Prostate from the Pubic Symphysis
- •3.1.1 Scanning Method
- •3.1.2 Section Structure
- •3.1.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •3.1.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.2 Semicoronal View of the Prostate from the Suprapubic Symphysis
- •3.2.1 Scanning Method
- •3.2.2 Section Structure
- •3.2.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •3.2.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.3 Transverse (Axial) Plane of the Prostate by Transrectal Ultrasound (TRUS)
- •3.3.1 Scanning Method
- •3.3.2 Section Structure
- •3.3.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •3.3.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.4 Longitudinal Plane of the Prostate by Transrectal Ultrasound (TRUS)
- •3.4.1 Scanning Method
- •3.4.2 Section Structure
- •3.4.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •3.4.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.5 Transverse Aspect of the Seminal Vesicle from the Pubic Symphysis
- •3.5.1 Scanning Method
- •3.5.2 Section Structure
- •3.5.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •3.5.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •4.1 Sagittal View of the Testis
- •4.1.1 Scanning Method
- •4.1.2 Section Structure
- •4.1.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •4.1.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •4.2 Axial View of the Testis
- •4.2.1 Scanning Method
- •4.2.2 Section Structure
- •4.2.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •4.2.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •4.3 Axial View of Both Testes
- •4.3.1 Scanning Method
- •4.3.2 Section Structure
- •4.3.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •4.3.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •4.4 Longitudinal Plane of the Head of the Epididymis
- •4.4.1 Scanning Method
- •4.4.2 Section Structure
- •4.4.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •4.4.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •4.5 Longitudinal Plane of the Tail of the Epididymis
- •4.5.1 Scanning Method
- •4.5.2 Section Structure
- •4.5.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •4.5.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •4.6 Longitudinal Plane of Spermatic Cord
- •4.6.1 Scanning Method
- •4.6.2 Section Structure
- •4.6.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •4.6.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1 Retroperitoneal Space
- •1.1.1 Scanning Method
- •1.1.2 Section Structure
- •1.1.3 Clinical Application Value
- •1.2.1 Scanning Method
- •1.2.2 Section Structure
- •1.2.3 Clinical Application Value
- •1.3.1 Scanning Method
- •1.3.2 Section Structure
- •1.3.3 Clinical Application Value
- •1.4.1 Scanning Method
- •1.4.2 Section Structure
- •1.4.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.5.1 Scanning Method
- •1.5.2 Section Structure
- •1.5.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.5.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.6.1 Scanning Method
- •1.6.2 Section Structure
- •1.6.3 Clinical Application Value
- •2 Adrenal Gland
- •2.1.1 Scanning Method
- •2.1.2 Section Structure
- •2.1.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •2.1.4 Clinical Application Value
- •2.2.1 Scanning Method
- •2.2.2 Section Structure
- •2.2.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •2.2.4 Clinical Application Value
- •2.2.5 Notice
- •12: Gynecologic Ultrasound Scanning
- •1.1 Longitudinal Section of the Childhood Uterus
- •1.1.1 Method
- •1.1.2 Section Structure
- •1.1.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.1.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.2.1 Method
- •1.2.2 Section Structure
- •1.2.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.2.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.3 Longitudinal Section of the Anteposition Uterus in Fertile Woman
- •1.3.1 Method
- •1.3.2 Section Structure
- •1.3.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.3.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.4 Transection of Anteposition Uterus in Fertile Woman
- •1.4.1 Method
- •1.4.2 Section Structure
- •1.4.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.4.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.5 Longitudinal Section of Mesoposition Uterus in Fertile Woman
- •1.5.1 Method
- •1.5.2 Section Structure
- •1.5.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.5.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.6 Transection of Mesoposition Uterus in Fertile Woman
- •1.6.1 Method
- •1.6.2 Section Structure
- •1.6.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.6.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.7 Longitudinal Section of the Retroposition Uterus in Fertile Woman
- •1.7.1 Method
- •1.7.2 Section Structure
- •1.7.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.7.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.8 Transection of the Retroposition Uterus in Fertile Woman
- •1.8.1 Method
- •1.8.2 Section Structure
- •1.8.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.8.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.9 Longitudinal Section of Postmenopausal Gerontism Uterus
- •1.9.1 Method
- •1.9.2 Section Structure
- •1.9.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.9.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •1.10 Transection of Postmenopausal Gerontism Uterus
- •1.10.1 Method
- •1.10.2 Section Structure
- •1.10.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •1.10.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.1 Longitudinal Section of the Anteposition Uterus in Fertile Woman
- •2.1.1 Method
- •2.1.2 Section Structure
- •2.1.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •2.1.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.2 Transection of the Anteposition Uterus in Fertile Woman
- •2.2.1 Method
- •2.2.2 Section Structure
- •2.2.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •2.2.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.3 Longitudinal Section of the Mesoposition Uterus in Fertile Woman
- •2.3.1 Method
- •2.3.2 Section Structure
- •2.4 Coronal Section of the Mesoposition Uterus in Fertile Woman
- •2.4.1 Method
- •2.4.2 Section Structure
- •2.5 Longitudinal Section of the Retroposition Uterus in Fertile Woman
- •2.5.1 Method
- •2.5.2 Section Structure
- •2.5.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.6 Transection of Retroposition Uterus in Fertile Woman
- •2.6.1 Method
- •2.6.2 Section Structure
- •2.6.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.7.1 Method
- •2.7.2 Section Structure
- •2.7.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •2.7.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.8.1 Method
- •2.8.2 Section Structure
- •2.8.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •2.8.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.9 Longitudinal Section of Postmenopausal Gerontism Uterus
- •2.9.1 Method
- •2.9.2 Section Structure
- •2.9.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •2.9.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.10 Transection of the Postmenopausal Gerontism Uterus
- •2.10.1 Method
- •2.10.2 Section Structure
- •2.10.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •2.10.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.1 Childhood Ovary
- •3.1.1 Method
- •3.1.2 Section Structure
- •3.1.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •3.1.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.2.1 Method
- •3.2.2 Section Structure
- •3.2.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •3.2.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.3 Luteal Phase Ovary Scan in Fertile Woman
- •3.3.1 Method
- •3.3.2 Section Structure
- •3.3.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •3.3.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.4.1 Method
- •3.4.2 Section Structure
- •3.4.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •3.4.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.5.1 Method
- •3.5.2 Section Structure
- •3.5.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •3.5.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •4.1.1 Method
- •4.1.2 Section Structure
- •4.1.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •4.1.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •4.2.1 Method
- •4.2.2 Section Structure
- •4.2.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •4.2.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •4.3 Ovary Corpus Luteum in Fertile Woman
- •4.3.1 Method
- •4.3.2 Section Structure
- •4.3.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •4.3.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •4.4 Ovary in Postmenopause-Phase Women
- •4.4.1 Method
- •4.4.2 Section Structure
- •4.4.3 Measuring Method and Normal
- •4.4.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •13: Normal Pregnancy
- •1 First Trimester Scanning
- •1.1.1 Scanning Method
- •1.1.2 Section Structures
- •1.1.3 Measuring Method and Normal Reference Values
- •1.1.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.2.1 Scanning Method
- •1.2.2 Section Structures
- •1.2.3 Measuring Method and Normal Reference Values
- •1.2.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.3.1 Scanning Method
- •1.3.2 Section Structures
- •1.3.3 Measuring Method
- •1.3.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.4.1 Scanning Method
- •1.4.2 Section Structures
- •1.4.3 Measuring Method
- •1.4.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.5.1 Scanning Method
- •1.5.2 Section Structures
- •1.5.3 Measuring Method
- •1.5.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.6.1 Scanning Method
- •1.6.2 Section Structures
- •1.6.3 Measuring Method
- •1.6.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.7.1 Scanning Method
- •1.7.2 Section Structures
- •1.7.3 Measuring Method
- •1.7.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.8.1 Scanning Method
- •1.8.2 Section Structures
- •1.8.3 Measuring Method
- •1.8.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.9.1 Scanning Method
- •1.9.2 Section Structures
- •1.9.3 Measuring Method
- •1.9.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.9.5 Normal Reference Values
- •1.10 Nuchal Translucency (NT)
- •1.10.1 Scanning Method
- •1.10.2 Section Structures
- •1.10.3 Measuring Method
- •1.10.4 Clinical Significance
- •1.10.5 Normal Reference Values
- •3.1.1 Cephalic Presentation of Fetus
- •3.1.2 Breech Presentation of Fetus
- •3.1.3 Scanning Methods
- •3.1.4 Section Structures
- •3.1.5 Clinical Significance
- •3.2.3 Scanning Method
- •3.2.4 Section Structures
- •3.2.5 Clinical Significance
- •4.2.1 Scanning Method
- •4.2.2 Section Structures
- •4.2.3 Measuring Method
- •4.2.4 Clinical Significance
- •4.2.5 Normal Reference Values
- •4.3.1 Scanning Method
- •4.3.2 Section Structures
- •4.3.3 Measuring Method
- •4.3.4 Clinical Significance
- •4.3.5 Normal Reference Values
- •4.6.1 Scanning Method
- •4.6.2 Section Structures
- •4.6.3 Measuring Method
- •4.6.4 Clinical Significance
- •4.6.5 Normal Reference Values
- •4.9.1 Scanning Method
- •4.9.2 Section Structures
- •4.9.3 Clinical Significance
- •4.10.1 Scanning Method
- •4.10.2 Section Structures
- •4.10.3 Clinical Significance
- •4.12.1 Scanning Method
- •4.12.2 Section Structures
- •4.12.3 Measuring Method
- •4.12.4 Clinical Significance
- •4.12.5 Normal Reference Values
- •4.13.1 Scanning Method
- •4.13.2 Section Structures
- •4.13.3 Measuring Method
- •4.13.4 Clinical Significance
- •4.13.5 Normal Reference Values
- •4.15.1 Scanning Method
- •4.15.2 Section Structures
- •4.15.3 Measuring Method
- •4.15.4 Clinical Significance
- •4.15.5 Normal Reference Values
- •4.16 Short Axis View of Fetal Heart
- •4.17.1 Scanning Method
- •4.17.2 Section Structures
- •4.17.3 Measuring Method
- •4.17.4 Clinical Significance
- •4.18 Scanning of Fetal Lung
- •4.18.1 Scanning Method
- •4.18.2 Section Structures
- •4.18.3 Clinical Significance
- •4.19.1 Scanning Method
- •4.19.2 Section Structures
- •4.19.3 Clinical Significance
- •4.20.1 Scanning Method
- •4.20.2 Section Structures
- •4.20.3 Measuring Method
- •4.20.4 Clinical Significance
- •4.20.5 Normal Reference Values
- •4.22.1 Scanning Method
- •4.22.2 Section Structures
- •4.22.3 Clinical Significance
- •4.25.1 Scanning Method
- •4.25.2 Section Structures
- •4.25.3 Measuring Method
- •4.25.4 Clinical Significance
- •4.28.1 Scanning Method
- •4.28.2 Section Structures
- •4.28.3 Clinical Significance
- •4.31.1 Scanning Method
- •4.31.2 Section Structures
- •4.31.3 Measuring Method
- •4.31.4 Clinical Significance
- •Placenta
- •4.32 Placenta of Grade I
- •4.33 Placenta of Grade II
- •4.34 Placenta of Grade III
- •4.34.1 Scanning Method
- •4.34.2 Section Structures
- •4.34.3 Measuring Method
- •4.34.4 Clinical Significance
- •4.35 Low-Lying Placenta
- •4.36 Placenta Previa
- •4.36.1 Scanning Method
- •4.36.2 Section Structures
- •4.36.3 Measuring Method
- •4.36.4 Clinical Significance
- •Amniotic Fluid
- •4.37 Amniotic Fluid Depth
- •4.37.1 Scanning Method
- •4.37.2 Section Structures
- •4.37.3 Measuring Method
- •4.37.4 Clinical Significance
- •4.37.5 Normal Reference Values
- •4.38 Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI)
- •4.38.1 Scanning Method
- •4.38.2 Section Structures
- •4.38.3 Measuring Method
- •4.38.4 Clinical Significance
- •4.38.5 Normal Reference Values
- •5.1 Umbilical Artery
- •Scanning Method
- •Section Structures
- •Measuring Method
- •Clinical Significance
- •Normal Reference Values
- •5.2 Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA)
- •Scanning Method
- •Section Structures
- •Measuring Method
- •Clinical Significance
- •Normal Reference Values
- •5.3 Ductus Venous (DV)
- •5.3.1 Position of the Ductus Venous
- •5.3.3 Doppler Measurement of DV
- •Scanning Method
- •Section Structures
- •Measuring Method
- •Clinical Significance
- •Normal Reference Values
- •Bibliography
- •1.1 Scanning Method
- •1.2 Section Structure
- •1.3 Measuring Method
- •1.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •2.1 Scanning Method
- •2.2 Section Structure
- •2.3 Measuring Method
- •2.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •3.1 Scanning Method
- •3.2 Section Structure
- •3.3 Measuring Method
- •3.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •4 Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Sonogram in the Face of the Young Women
- •4.1 Method
- •4.2 Section Structure
- •4.3 Measuring Method
- •4.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •5.1 Method
- •5.2 Section Structure
- •5.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •6.1 Method
- •6.2 Section Structure
- •6.3 The Clinical Application Value
- •7.1 Method
- •7.2 Section Structure
- •7.3 Measuring Method
- •7.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •8 Neck Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Scanning in the Young Women
- •8.1 Method
- •8.2 Section Structure
- •8.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •9 Thoracic Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Scanning
- •9.1 Method
- •9.2 Section Structure
- •9.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •10 Skin and subcutaneous tissue scanning in the middle line of the upper abdomen
- •10.1 Method
- •10.2 Section Structure
- •10.4 The Clinical Application Value
- •11.1 Method
- •11.2 Section Structure
- •11.4 The Clinical Application Value

198 |
B. Su and Q. Yong |
|
|
3.17\ Longitudinal Scanning
of the Anterior Tibial Vein
LATV
LATA
Fig. 7.50 longitudinal view of the anterior tibial vein
3.17.1\ Scanning Method
The patient takes a supine position or sitting position; the probe is placed in the anterolateral tibia and scans in the beginning of the anterior tibial vein from bottom to top.
3.17.2\ Sectional Structure
The anterior tibial artery and the anterior tibial vein stand side by side on the cross section, the vein locates at the lateral of the anterior tibial artery. The lumen of the anterior tibial vein is oval and can become flat by the probe pressure.
The longitudinal section shows the long axis of the anterior tibial vein.
3.17.3\ Measurement Methods
To measure the inner diameter of the anterior tibial vein.
3.17.4\ Clinical Significance
To judge whether there is stenosis, thrombosis, or arteriovenous fistula in the anterior tibial vein and to diagnose anterior tibial vein thrombosis, varicose veins, arteriovenous fistula disease, etc.
7 Vascular System Scanning |
199 |
|
|
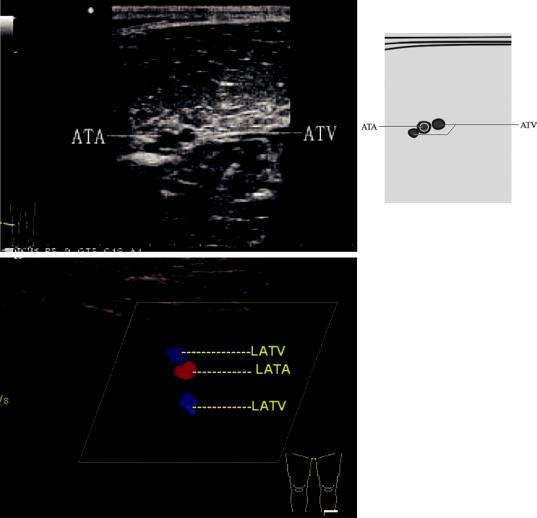
3.18\ Transverse Scanning
of the Anterior Tibial Vein
|
|
|
|
|
ATA |
ATV |
Fig. 7.51 Transverse view of the anterior tibial vein
3.18.1\ Scanning Method
The patient takes a supine position or sitting position. The probe is placed in the anterolateral tibia and the anterior tibial vein along the anterior- lateral crus down.
3.18.2\ Sectional Structure
The lumen of the anterior tibial vein is circle and locates behind the posterolateral anterior tibial artery; its lumen can be crushed flat under the probe pressure.
3.18.3\ Measurement Methods
The inner diameter of the anterior tibial vein.
3.18.4\ Clinical Significance
To judge whether there is arteriosclerosis obliterans, arterial embolism, thrombosis, arterial aneurysm, or arteriovenous fistula in the common femoral artery, superficial femoral artery, and deep femoral artery.
200 |
B. Su and Q. Yong |
|
|
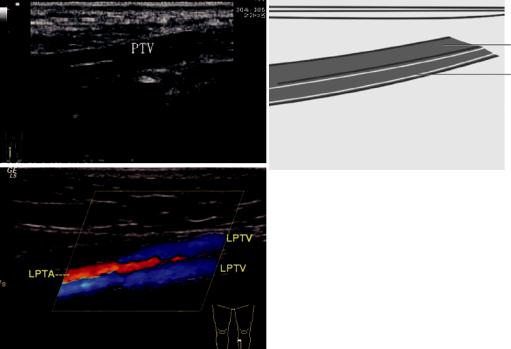
3.19\ Longitudinal Scanning of
the Posterior Tibial Vein
PTV
PTA
Fig. 7.52 Longitudinal view of the posterior tibial vein
3.19.1\ Scanning Method
The patient takes a supine position or sitting position; the probe is placed inside the crus. The posterior tibial vein locates in the lateral anterior tibial artery, and the location is superficial.
3.19.2\ Sectional Structure
Longitudinal view shows the long axis of the posterior tibial vein; its lumen can be crushed flat under the probe pressure.
3.19.3\ Measurement Methods
The inner diameter of the posterior tibial vein and blood flow spectrum.
3.19.4\ Clinical Significance
To judge whether there is stenosis or occlusion, thrombosis, or other diseases in the posterior tibial vein.

7 Vascular System Scanning |
201 |
|
|
3.20\ Transverse Scanning
of the Posterior Tibial Vein
Fig. 7.53 Transverse view of the posterior tibial vein
