
- •Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education "Kuban State Medical University" of
- •Electrocardiography (ECG)
- ••Registration of electrical processes occurring in the heart to one degree or another
- •Первые электрокардиограммы были записаны Габриелем Липпманом
- •Виллем Эйнтховен (Willem Einthoven; 1860 - 1927)
- •The ECG standard provides 12-lead recording:
- •Normal ECG (12-leads)
- •Recording of 6 limb leads.
- •ГРУДНЫЕ отв. chest leads
- •An ECG of a healthy subject has the following elements:
- •Generation of ECG waves and intervals:
- •Длительность.
- •Other characteristics.
- •Interpretation of ECG
- •The sequence of ECG analysis:
- •4. Heart rate (HR)
- •6. The position of the electrical axis of heart changes with changes of
- •7. Analysis of waves and intervals. The length and size of ECG
- •Normal sinus rhythm.
- •ELECTRICAL AXIS
- •normal electrical axis
- •left electrical axis
- •right electrical axis
- •The 6 frontal plane ECG leads form a hexaxial reference system
- •normal electrical axis
- •left electrical axis
- •right electrical axis
- •Thus, based on the above, we can assume that:
- •The chest leads also reflect the balance between the right and left sides
- •normal electrical axis
- •Left ventricular hypertrophy
- •left-ventricular hypertrophy
- •left-ventricular hypertrophy
- •right-ventricular hypertrophy
- •Right ventricular hypertrophy options
- •right-ventricular hypertrophy R-type
- •right-ventricular hypertrophy: rSR -type
- •right-ventricular hypertrophy: S –type
- •Hypertrophy of auricles is determined by changes of P-wave.
- •Left atrium hypertrophy
- •Left atrium hypertrophy
- •Right atrium hypertrophy
- •ECG in left bundle branch block is characterized: - the QRS interval is
- •left bundle branch block
- •left bundle branch block
- •ECG in right bundle branch block is characterized:
- •right bundle branch block

normal electrical axis
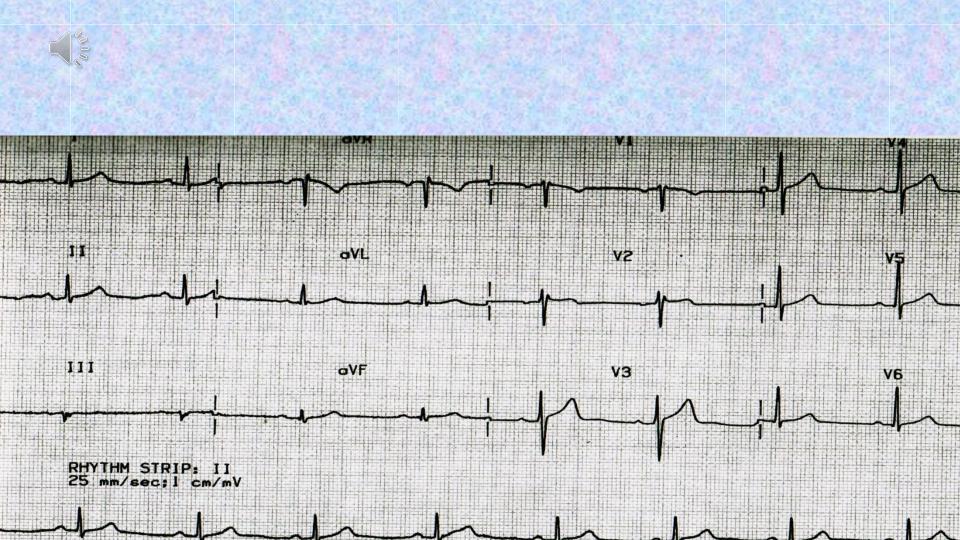
left electrical axis

right electrical axis

Thus, based on the above, we can assume that:
I, AVL leads characterize changes in the left heart;
III, AVF leads characterize changes in the right heart;
II, AVR total leads in them reflect changes from the left and right departments.
Changes to these pairs must be duplicated.

The chest leads also reflect the balance between the right and left sides of the heart:
V1 and V2 - right chest
V5 and V6 - left chest
V3 - V4 - transition zone

normal electrical axis

Left ventricular hypertrophy
-An increase in the amplitude of the R waves in V5 and V6 (it is higher than in V4), and S in V1 and V2, R in I and R in aVL.
-QRS width grows = 0.10 - 0.12 s
-Deviation of the electrical axis of the heart to the left (angle α <0º). R I> R II> R III, high R in lead I and deep S in III.
-An increase in the time of internal deviation in V5, V6 leads (from the beginning of the R wave to its apex)> 0.05 s.
-With severe left ventricular hypertrophy: ST segment in I, AVL, V5, V6 below the isoline ("trough-shaped"), T is negative.
-Displacement of the transition zone to the right chest leads.
Sokolov - Lyon amplitude criteria.
R in I> 15 mm; R in I + S in III (or II)> 25 mm.
R in aVL> 11 mm.
R in V5 or V6> 25 mm.
R in V5 or V6 + S in V1 or V2> 35 mm.

left-ventricular hypertrophy
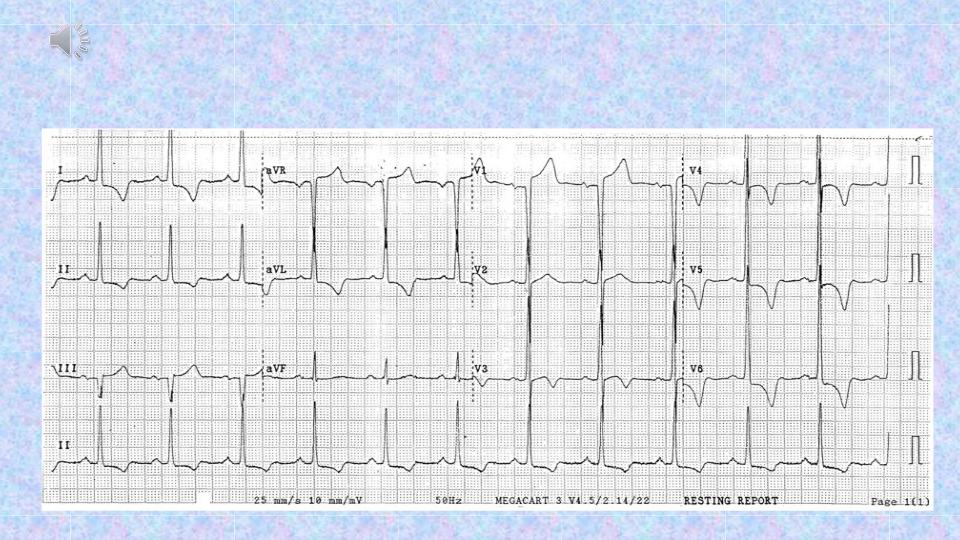
left-ventricular hypertrophy

