
- •Renal diseases
- •Kidney functions
- •Nephron - functional unit of the kidney
- •Investigation methods of kidneys and urinary tract
- •CAUSES OF POLYURIA
- •Some renal symptoms and their causes
- •Some renal symptoms and their causes
- •Anamnesis
- •Anamnesis
- •Physical examination
- •Facies nephritica (Acute GN)
- •Edema (Acute GN)
- •Edema (nephrotic syndrome)
- •Edema (nephrotic syndrome)
- •Paranephral abscess
- •Palpation of right kidney
- •Palpation of left kidney
- •Striking test
- •Auscultation of renal arteries
- •Laboratory methods
- •Laboratory methods
- •Laboratory methods
- •Proteinuria
- •Proteinuria
- •Urine color
- •Some renal symptoms and their causes
- •Haematuria
- •Haematuria
- •CAUSES OF RED OR DARK URINE
- •Leucocyturia - more then 2000 cells in 1 ml
- •Crystalluria
- •Measurement of the glomerular filtration rate
- •Markers of renal functional state
- •Creatinin clearance (90-140 ml/min/l.73 m2)
- •Creatinin clearance
- •Calculation of GFR with Cokroft-Gault formula
- •INVESTIRATION OF URINARY TRACT
- •Эхоангиография правой почки
- •Пиелоуретероэктазии справа (экскреторная урография)
- •Бессимптомные камни мочевого пузыря
- •Аплазия правой почки (КТ)
- •Нефрокальциноз
- •Опухоль почки (ангиография)
- •Проходимость артерии восстановлена после стентирования
- •Сцинтиграфия почек, б-ой Б., 52 лет. Хр. гломерулонефрит
- •RENAL BIOPSY
- •Нормальный

Renal diseases
Symptoms
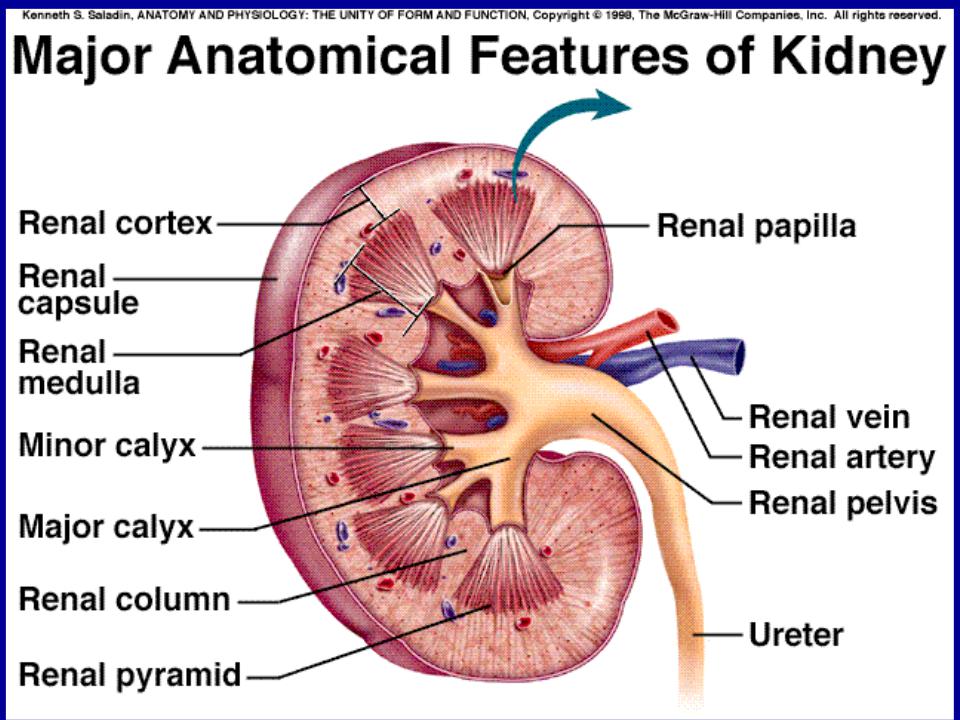

Kidney functions
•Excretion of nitrogen metabolism rests (urea, uric acid, creatinin)
•Excretion of organic substances (glucose, amino acides)
•Regulation of water-electrolyte balance (Na, K, Mg, Cl, HCO3, PO4)
•Regulation of acid-base balance (absorption of HCO3, excretion of H+)
•Production of hormones and bioactive substances (renin, prostaglandins, kinins, erythropoietin, active forms of D3, urokinase)
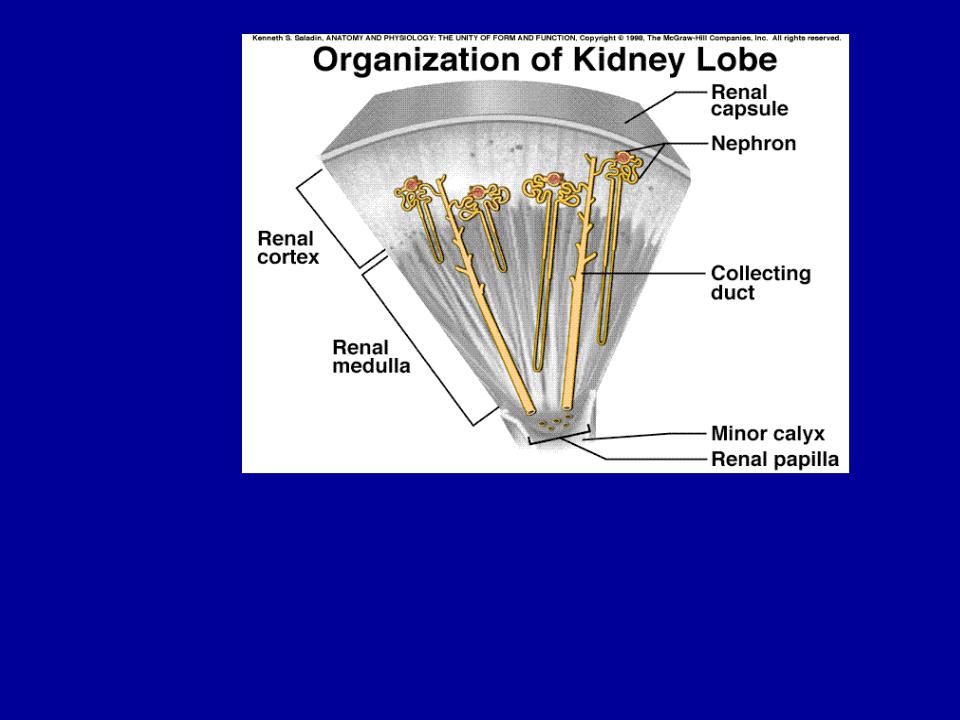
Nephron - functional unit of the kidney
Found in cortex and medulla
Urine is created in the enthrones and drains into the collecting ducts

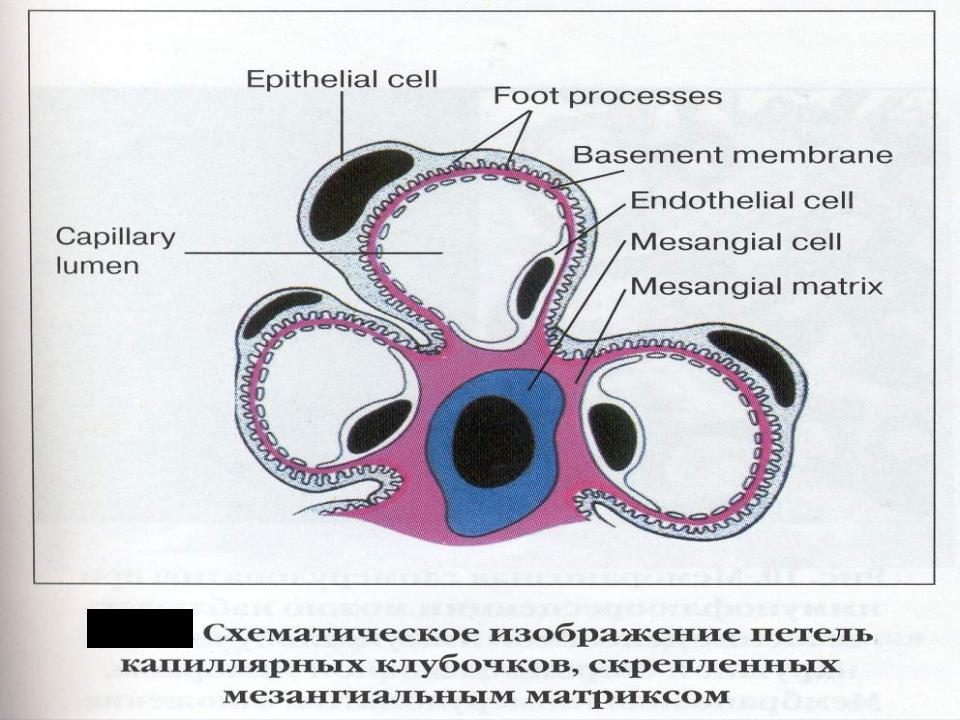
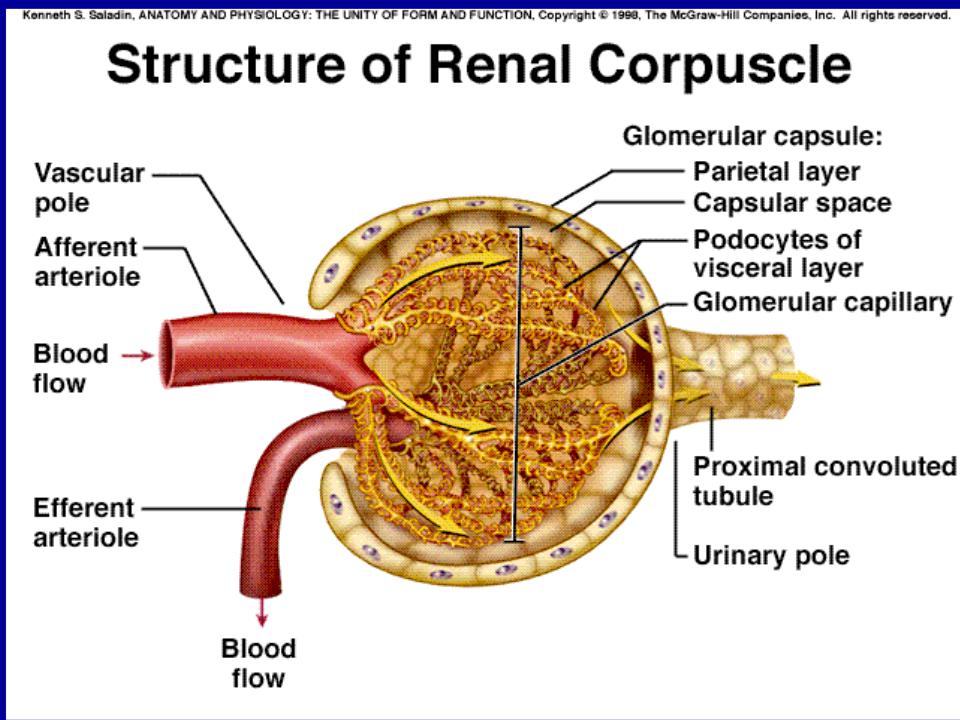


Investigation methods of kidneys and urinary tract
•Complains
•Anamnesis morbi (illness history)
•Anamnesis vitae (life history)
•Physical examination
•Laboratory investigations
•Visualizing techniques

• |
|
Complains |
Nonspecific (feebleness, head ache, dyspnea, fever, nausea, diarrhea, itching, |
||
• |
arthritis, bruises and hemorrhages) |
|
Edema (face, eyelids) |
||
• |
Changes of diuresis |
|
|
|
-oliguria (<500 ml/24 h) |
|
|
-anuria (<100 ml/24 h) |
|
|
-ischuria (acute urinary tract obstruction) |
|
|
-polyuria (>2 l/24 h) |
• |
Pain |
-nycturia (predominance of night diuresis) |
|
||
|
-loin region (acute pyelonephritis, acute glomerulonephritis, kidney |
|
|
infarction, |
kidney colic, paranephritis, nephroptosis) |
|
-suprapubic (urinary bladder) |
|
• |
-perineum (prostatic gland) |
|
Abnormalities of urination (disuria): painful, frequent (pollakiuria), |
||
|
difficult (stranguria), incontinence |
|
• |
Changed urine: red (macrohematuria), «meat slops», foggy, sand and stones |
|
