
- •Introduction
- •Basic principles of constitutionalism and associations.
- •NgOs: definition, characteristics, functions.
- •NgOs in Ukraine: overview of the constitutional legislation.
- •International standards and the current national problems of ngos.
- •Foreign experience and the basics of the comparative analysis of the constitutional staus of ngOs.
- •1. Introduction
- •2. Aspects of Corporate Sustainability and Corporate (Social) Responsibility
- •3. A philosophical contribution to cs
- •4. A practical contribution to Corporate Sustainability
- •5. Proposals for defining csr and Corporate Sustainability
- •Seminar 2. NgOs: definition, characteristics, functions (2 hours).
- •Seminar 3. NgOs in Ukraine: overview of the constitutional legislation (2 hours).
- •Introduction1
- •Internal Developments Among ngOs
- •Seminar 4.
- •International standards and the current national problems of ngos (2 hours).
- •Legal Mechanisms for ngo-Government Partnership in Ukraine Author(s): Alexander Vinnikov
- •Seminar 5. Foreign experience and the basics of the comparative analysis of the constitutional staus of ngOs (2 hours).
- •Mandatory readings
- •Mandatory reading – lecture 2
- •Figure 3. Government
- •Figure 4. Business
- •Mandatory reading – lecture 3
- •Introduction
- •Mandatory reading – lecture 4 case of koretskyy and others V. Ukraine (Application no. 40269/02)
- •3 April 2008
- •Мішина Наталя Вікторівна конституційний статус неурядових організацій
Figure 3. Government
Figure 4. Business
The voluntary, nonprofit, independent sector is central to the definition and function of civil society. At times, this sector of activity is mistakenly considered to be all of civil society. Not everything that occurs in the nonprofit realm is necessarily a part of civil society , and certainly some charities are identified more with self-interest than public benefit, but most of the country’s vast charitable endeavor is very much a part of civil society (see Figure 5).
Civil society exists at the intersection where the various elements of society come together to protect and nurture the individual and where the individual operates to provide those same protections and liberating opportunities for others (see Figure 6).
Figure
5. Voluntary

Figure 6. Intersecting Diagram
Civil society might be symbolized by the star that results from putting all these sectors and forces into common perspective. The rays are the influence of citizens on every part of society, and citizens are the common focus of all elements of society (see Figure 7).
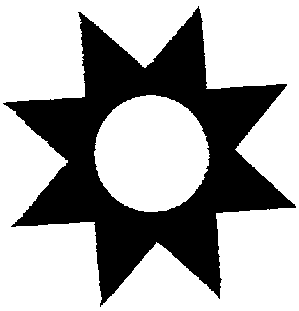
Figure 7. Civil Society Star Symbol
The important mix of all the players in civil society and their influence on each other are becoming more visible thanks to those scholars who compare the overall health of various communities and countries. In “The Prosperous Community,” from Making Democracy Work, a study of the relative health of different regions of Italy, Robert Putnam writes that “Civic was a major influence, not just on the social fabric, but also on the quality of government and commerce.” He concludes, They [the healthy communities] have become rich because they were civic. The social capital embodied in norms and networks of civic engagements seems to be a precondition for economic development, as well as for effective government. (p. 2).
The importance of getting to a more ac cu rate definition and description of civil society was underscored by a recent piece in Foreign Policy, in which Thomas Carothers (1999-2000) takes the various different interpretations of civil society and argues why each is inadequate as an overall argument for the importance of civil society. For example, he indicates that nongovernmental organizations have limitations and in some cases are even undemocratic, that a strong civil society does not ensure strong democracy, and that it is not essential to economic success. I agree with his cogent analysis of the limitations of each part of civil society, but he treats each as though it were the entire definition and never puts them all together as part of a larger concept. He sees the shortcomings of each part to qualify as suitable argument for the importance of civil society but fails to ac knowledge the composite social, political, and economic advantages when each part reflects impressive commitment to community and country , which in my experience is what our civil society is all about. The symbiosis of all these parts of our civil society produces an extra dimension that is far greater than the sum of the parts.
The importance of our civil society to our democracy is indeed a secret of our success as a nation, but the very fact that it is so little understood means that it is always in danger of neglect and attack, and with any significant alteration or diminution of civil society , our freedoms are similarly weakened. Unfortunately, we generally prefer to rely on structures such as representative government and the courts to maintain the marvels of American democracy, but even they deteriorate without the devotion and investment of their citizen masters. The ultimate preservation rests on the forceful awareness of the populace that ultimately our social fabric, our democratic government, and our freedom depend on us. As the great jurist Learned Hand expressed it, I often wonder whether we do not rest our hopes too much upon constitutions, upon laws and courts. These are false hopes; believe me, these are false hopes. Liberty lies in the hearts of men; when it dies there, no constitution, no law, no court can save it. (Hand, 1991, p. 12).
There is one other fairly basic definitional matter to cover concerning the relationship between democracy and civil society , including which comes first and is the more important. In some quarters, particularly Europe, the two are increasingly referred to interchangeably. Although I agree that civil society is necessary to effective democracy , I do not believe it is a synonym for it. My experience is that the order of importance is democracy and then civil society, with full awareness that a vibrant civil society is most likely to thrive in a vibrant democracy and vice versa. Civil society exists in nondemocratic countries: It is growing in size and importance in Saudi Arabia, for example, and there are democracies where civil society is weak, as in Japan. The central point is that a healthy, vibrant civil society is both the fullest indication of and a precondition for a healthy democracy.
In the United States, we need to be particularly careful not to confuse a public already comfortable with and proud of our democracy. We should not do anything that takes our eyes off its glory and the need to maintain and strengthen it. Therefore, I emphasize that civil society is absolutely necessary to a fully functioning democracy and democracy is the ultimate form of government of, by, and for the people.
References
Barber, B. (1996, September 5). Strengthening democracy by recreating civil society. Paper presented at the Independent Sector Conference on Civil Society , Washing ton, DC.
Carothers, T. (1999-2000). Civil society . Foreign Pol icy. pp. 21-36.
Evans, S. M., & Boyte, H. C. (1992). Free spaces: The sources of democratic change in America. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Hand, L. (1991). In C. F . Bahmueller, J. H. Buchanan, Jr ., & C.N. Quigley (Eds.), Civitas: A framework for civic education. Calabasas, CA: Center for Civic Education. (National Council for the Social Studies Bul le tin No. 86.
O’Connell, B. (1985, March 17). Citizen ship and community services: Are they a concern and responsibility on higher education? Paper presented at the National Conference on Higher Education, Chicago.
