
- •Пояснительная записка.
- •Пятый – dc generator characteristics.
- •Cедьмой – Alternators
- •I семестр.
- •II семестр.
- •Unit 1. Electrical safety. Lesson 1.
- •Find the equivalents of following word combinations.
- •Make up the negative from the following words using the negative prefixes: dis-, un-, im-, non-, ill-. Translate them.
- •Translate into English the words in brackets.
- •Give adequate Russian equivalents of the italicized words.
- •Read and translate the following text. The main reasons of electrical traumatism and means of protection against it.
- •Vocabulary
- •6. Complete the table choosing the right words in each column.
- •7. Translate into English.
- •Grammar exercises.
- •1. Прочитайте, переведите предложения на русский язык, определите формы герундия.
- •2. Поставьте данные глаголы во все формы герундия.
- •3. Поставьте глаголы в скобках в форму Active или Passive.
- •4. Выберите соответствующую форму герундия.
- •Lesson 2.
- •Find the equivalents of following word combinations.
- •Complete the sentences with words given in previous exercise.
- •Translate into Russian. Make up your own sentences with these word combinations.
- •Give adequate Russian equivalents of the italicized words.
- •Read and translate the text. Some rules for safe practice and avoiding electric shocks.
- •7. Make sure you have properly understood the meaning of the text:
- •8. Translate into English.
- •9. Translate the sentences into Russian.
- •Grammar exercises.
- •1. Поставьте следующие глаголы во все формы герундия.
- •2. Прочитайте, переведите и сравните.
- •3. Поставьте глаголы в активной или пассивной форме герундия.
- •4. Сопоставьте части предложений.
- •5. Определите форму герундия и переведите предложения на русский язык.
- •Homereading. First aid for electric shock.
- •Vocabulary:
- •Определите правильное окончание предложений.
- •2. Ответьте на вопросы.
- •3. Выберите соответствующий предлог из предложенных.
- •4. Восстановите отрывок из текста, вставив пропущенные слова.
- •5. Расскажите наизусть три правила, которые надо выполнять, оказывая помощь при поражении электрическим током.
- •6. Переведите на английский язык.
- •1. Find the equivalents of following word combinations.
- •2. Complete the sentences with words given in previous exercise and translate them into Russian
- •3. What part of speech do the given words belong to: noun, verb, preposition, adjective, adverb, conjunction, cardinal numeral.
- •Give adequate Russian equivalents of the italicized words.
- •5. Read and translate the text.
- •Vocabulary.
- •6. Answer the questions.
- •7. Complete word combinations.
- •8. Complete the sentences.
- •9. Make up the sentences putting the words in right order.
- •10. Translate into English.
- •Grammar exercises.
- •1. Переведите предложения, содержащие герундий (в форме Indefinite Active) в роли подлежащего. Помните, что после герундия может использоваться прямое дополнение (без предлога!)
- •2. Переведите предложения, в которых герундий играет роль смысловой части сказуемого.
- •3. Переведите на английский, используя словосочетания worth(while) – стоит, cannot help – нельзя не, no use – нет смысла, после которых используется герундий.
- •Lesson 5. Main Switchboard.
- •Find the equivalents of following word combinations.
- •Insert some of word combinations of ex. 1 into the following sentences.
- •Find the international words in text.
- •Give adequate Russian equivalents of the italicized words.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Complete word combinations consulting the text, translate them into Russian.
- •Make up the sentences.
- •Speak about:
- •Translate into English.
- •Grammar exercises.
- •1. Восстановите предложения, поставив данные глаголы в форму герундия.
- •2. Поставьте глаголы в активную или пассивную форму герундия.
- •4. Переведите предложения, выделяя герундий в роли обстоятельства. Особое внимание уделяйте предлогам.
- •Переведите предложения, определите функции подлежащего, определения и обстоятельства.
- •Lesson 6. Motor Controls.
- •Find the equivalents of following word combinations.
- •Insert some of word combinations of ex. 1 into the following sentences.
- •Name the antonyms for following words.
- •Give adequate Russian equivalents of the italicized words.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Vocabulary
- •Answer the questions.
- •Complete the sentences inserting the missing words.
- •Speak about:
- •Translate into English.
- •Grammar exercises.
- •1. Переведите следующие предложения, обращая внимание на предлоги, стоящие перед герундием:
- •2. Переведите предложения, в которых дополнение выражено герундием.
- •4. Переведите на английский язык.
- •Lesson 7. Ship's Auxiliary Services.
- •Find the equivalents of following word combinations.
- •Insert some of word combinations of ex. 1 into the following sentences.
- •Make up words using the following suffixes and translate them.
- •Give adequate Russian equivalents of the italicized words.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Vocabulary.
- •Translate the sentences.
- •Complete the word combinations. Translate them into Russian.
- •Insert the missing words:
- •Translate into English.
- •Speak about:
- •Grammar exercises.
- •Определите функции герундия и переведите предложения на русский язык.
- •Homereading. Magnets. Magnetism.
- •Vocabulary.
- •Exercises.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Complete the sentences.
- •Restore the sentences.
- •Choose the correct word corresponding the content of the sentence.
- •Correspond the term and its explanation.
- •Translate into English.
- •Unit 3. Elementary concepts of Rotating Machines. Lesson 9-11.
- •Find the equivalents of following word combinations.
- •Complete the sentences with words given in previous exercise and translate them into Russian.
- •Write down from the text 5 words corresponding to one of following parts of speech. Complete the table.
- •Give adequate Russian equivalents of the italicized words.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Vocabulary.
- •5. Answer the questions.
- •6. Translate word combinations in brackets into English.
- •7. Complete the sentences with given words.
- •8. Explain the meaning of the following terms in English.
- •8. Speak about:
- •9. Translate into English.
- •Grammar exercises.
- •2. Образуйте герундиальный оборот.
- •3. Перефразируйте предложения, используя герундиальный оборот.
- •5. Переведите на английский язык.
- •Unit 4. Dc machines constructing parts. Lessons 12-14.
- •1. Find the equivalents of following word combinations.
- •2. Complete the sentences with words given in previous exercise and translate them into Russian.
- •3. Translate into Russian the following word chains with the same root and explain the means of their formation.
- •4. Give adequate Russian equivalents of the italicized words.
- •5. Read and translate the text.
- •Vocabulary. Grooves - канавки
- •Answer the questions.
- •What do we call:
- •Check your comprehension of the text by answering the following multiple-choice questions:
- •A. The rotating part of the dc generator
- •B. Converter
- •Translate into English.
- •9. Speak about:
- •Grammar exercises.
- •1. Расположите по порядку:
- •2. Расположите по порядку:
- •3. Переведите предложения, определяя, какой частью речи является ing-форма: герундием, отглагольным существительным или причастием.
- •Vocabulary.
- •Translate into English.
- •Find the answers to the questions.
- •Write down what of these features of a generator and an electric motor are common, what features belong to the generator and what features belong to the electric motor.
- •Translate into English.
- •Unit 5. Dc generator characteristics. Lesson 1-2.
- •Find the equivalents of following word combinations.
- •Complete the sentences with words given in previous exercise and translate them into Russian.
- •Give adequate Russian equivalents of the italicized words.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Vocabulary.
- •Answer the questions.
- •What do we call:
- •Read and the following text.
- •Translate into English.
- •Speak about:
- •Grammar exercises.
- •Read and translate the sentences with subject clause.
- •Read and translate the sentences with predicative clause.
- •Unit 6. Dc motor characteristics. Lessons 3-4.
- •Find the equivalents of following word combinations.
- •Complete the sentences with words given in previous exercise and translate them into Russian.
- •Give adequate Russian equivalents of the italicized words.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Torque vs. Armature current
- •2. Comparing torque of cumulative compound 3. Compare speed of cumulative compound
- •Comparison of torque and speed characteristics
- •Motor torque characteristics Motor speed characteristics
- •Vocabulary.
- •5. Answer the following questions:
- •6. Check your comprehension of the text by answering the following multi-choice questions:
- •Translate into English.
- •Speak about:
- •Grammar exercises.
- •Read and translate the following sentences. Define the object clauses.
- •Unit 7. Alternators. Lesson 6.
- •1. Find the equivalents of following word combinations.
- •Complete the sentences with words given in previous exercise and translate them into Russian.
- •Give adequate Russian equivalents of the italicized words.
- •Read and translate the following text.
- •1 Gramme-ring single-phase armature 2 Gramme-ring three-phase armature
- •Vocabulary
- •Make up word combinations. Translate them and find them in the text.
- •Check your comprehension of the text by finding the right variant of questions:
- •Translate into English.
- •Grammar exercises.
- •1. Переведите предложения, определите придаточные определительные.
- •Lesson 7-8.
- •1. Find the equivalents of following word combinations.
- •2. Complete the sentences with words given in previous exercise and translate them into Russian.
- •3. Give adequate Russian equivalents of the italicized words.
- •4. Read and translate the text.
- •Vocabulary.
- •5. Answer the questions.
- •6. Never looking into the text try to complete the following sentences:
- •7. Listen to the texts one more time and check your comprehension of the texts by answering the following multi-choice questions:
- •8. Speak about:
- •Grammar exercises.
- •1. Read and translate the adverbial clause of time.
- •2. Read and translate the adverbial clause of place.
- •3. Define the adverbial clauses: of place or of time.
- •Unit 8. Synchronous machines. Lesson 10.
- •1. Find the equivalents of following word combinations.
- •2. Complete the sentences with words given in previous exercise and translate them into Russian.
- •3. Give adequate Russian equivalents of the italicized words.
- •4. Read and translate the text.
- •1 Synchronous-motor-rotor pole
- •Vocabulary.
- •5. Answer the questions.
- •6. Never looking into the text try to complete the following sentences:
- •7. Translate into English.
- •Speak about:
- •Grammar exercises.
- •Read and translate the sentences with adverbial clause of reason.
- •2. Read and translate the sentences with adverbial clause of purpose.
- •3. Define sentences with clause of reason and clause of purpose.
- •Lesson 11.
- •Find the equivalents of following word combinations.
- •Complete the sentences with words given in previous exercise and translate them into Russian.
- •Give adequate Russian equivalents of the italicized words.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Vocabulary
- •Answer the questions.
- •Complete the sentences while translating word combinations into English.
- •Check your comprehension of the text by finding the right variant of questions:
- •Translate into English.
- •Speak about:
- •Grammar exercises.
- •Read and translate the sentences with the adverbial clause of condition.
- •Read and translate the sentences with the clause of manner.
- •Define the sentences with the clauses of condition and manner.
- •Lesson 12.
- •Find the equivalents of following word combinations.
- •Complete the sentences with words given in previous exercise and translate them into Russian.
- •Give adequate Russian equivalents of the italicized words.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Vocabulary.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Fill in the missing words:
- •Translate into English.
- •Speak about constructional features of synchronous machines. Grammar exercises.
- •Read and translate the sentences with the adverbial of comparison.
- •Read and translate the sentences with the adverbial of concession.
- •Define the sentences with the adverbials of comparison and concession.
- •Unit 9. Troubleshooting and repair. Lesson 13.
- •1. Find the equivalents of following word combinations.
- •2. Complete the sentences with words given in previous exercise and translate them into Russian.
- •3. Read and translate the text.
- •Instrument Use.
- •Vocabulary.
- •4. Answer the questions.
- •5. Fill in the blanks with proper words and phrases.
- •6. Check your comprehension by answering the following multi-choice questions:
- •7. Translate into English.
- •8. Speak about:
- •Lesson 14. Motor Troubleshooting.
- •Translate this table into Russian in writing.
- •Match symptoms with probable faults. Try not to use the table.
- •Read and translate the text.
- •Testing
- •Repairs
- •Translate into English.
- •Read and translate the table in writing.
- •Match symptoms with probable faults. Try not to use the table.
- •Read and translate the text
- •Answer the questions.
- •9. Fill in the blanks with proper words and phrases:
- •10. Speak about:
- •11. Below you will find multiple choice questions on the troubleshooting and repair. By answering them you will be able to check your knowledge on the topic.
- •Homereading.
- •Translate into Russian.
- •Translate into Russian.
- •Vocabulary.
- •Find the answers to the questions of the left column.
- •Complete the sentences.
- •Fill in the gabs with the missing words.
- •Приложение.
- •1. Герундий
- •3. Типы придаточных предложений в английском языке
- •Лексический минимум.
- •I семестр.
- •II семестр.
- •Использованная литература.
Lesson 7-8.
1. Find the equivalents of following word combinations.
Field construction с гидроприводом
Salient (definite) pole осевая длина
Design consideration выступающий, явный полюс
Hydraulically driven конструкция обмотки возбуждения
Axial length рассеяние тепла
Compatible с учетом конструкции
Speed consideration взаимозаменяемый
Heat dissipation с учетом скорости
2. Complete the sentences with words given in previous exercise and translate them into Russian.
1. There are two types of _____ used on alternators: salient or round-rotor.
2. The _____construction is required when there are many poles on the rotor.
3. One of the first _____ is to account for the type of prime mover.
4. The _____ alternator must have many poles.
5. The length of the individual conductors lying in the magnetic field can be small, since each one need not generate a high voltage, and hence a slow-speed machine requires a small _____.
6. A design is developed that is _____ with the space limitations, speed considerations, and heat _____ for both electrical machines.
3. Give adequate Russian equivalents of the italicized words.
Subject - общий элемент смысла: подверженность внешнему воздействию. Частотные русские эквиваленты: subject to (Adj.) - подчиненный, зависимый; подверженный; подлежащий и т.п.; subject (N) - предмет, тема; предмет изучения; подданный; подлежащее и т.д.; to subject - подчинять, подвергать и т.д.; subject to (Adv.) - из-за, ввиду, при условии, в зависимости от и т.д.
1. Everything and everybody are subject to the laws of nature. 2.The principles are subject to change or elimination as new scientific facts are added to our knowledge. 3. The process is subject to fluctuations. 4. The plan is sub- subject to governmental approval. 5. This is highly complicated and interesting subject. 6. The subject of my thesis is occupational diseases as a function of industry geography. 7. This decision is not a subject for discussion. 8. The
subject-matter of the book is plasma. 9. The library has an excellent subject catalogue. 10. As a rule the subject opens the sentence. 11. He studied four subjects in his first year at college. 12. The soldiers happened to be subjects of France. 13. The idea was subjected to severe criticism and rejected. 14. To harden the metal it was subjected to intense heat. 15. The construction of the plant was delayed subject to restriction on deliveries of some types of equipment.
4. Read and translate the text.
Field construction. There are two types of field construction used on alternators: salient, or definite-pole, and round-rotor, or cylindrical-pole. Salient, meaning standing out or projecting, is shown in Fig. 6a the cylindrical rotor is shown in Fig.6b.
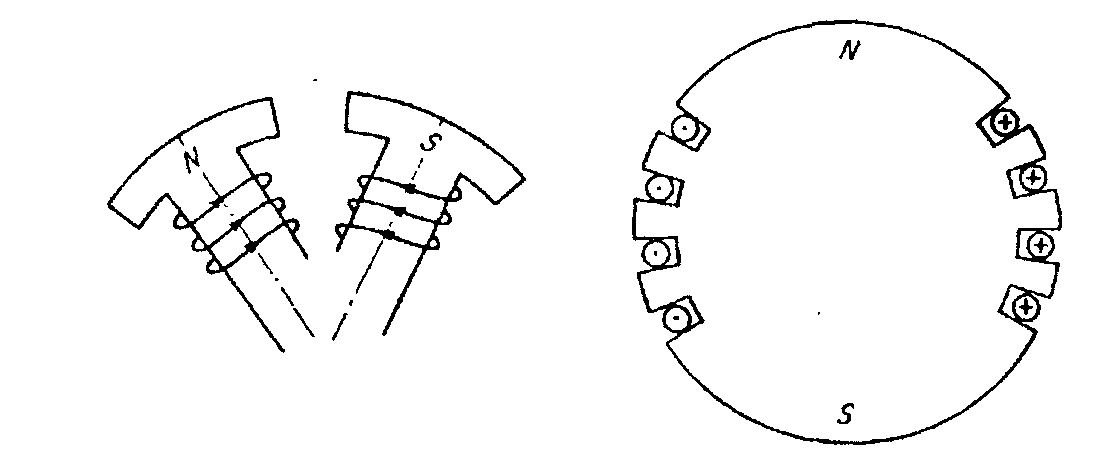
Fig. 6a Fig. 6b
The salient-pole construction is required when there are many poles on the rotor and is used for medium- and slow-speed machines. The cylindrical rotor is used almost exclusively for two-pole alternators, although it may occasionally be found on a four-pole rotor and therefore is used for the higher speeds. Salient poles are wound very much the same as are the field poles on a dc generator with the coils wound around the center of the pole. The conductors of a cylindrical-pole winding are placed in slots which are parallel to the rotor shaft. It is the placement of the slots which creates the magnetic poles since there actually are no physical poles to be seen as in the salient-pole construction. Indeed, at first glance, the round-rotor field closely resembles a dc armature without the commutator connections.
What determines the type of field construction to be used for a particular ac generator? Although there are certain advantages of one type over the other, these of themselves are of secondary consideration. Basically, it is geography that determines the type of field construction. The major cost of operating a power plant or even an individual alternator lies in the prime mover. This is true because electric machines have efficiencies which are quite high compared with the efficiencies of steam- or gas-driven units. Thus one of the first design considerations is to account for the type of prime mover. This is essentially a slow-speed machine. Since the frequency had already been predetermined by the locality, there is very little choice left in selecting or calculating the number of poles on the rotor. The hydraulically driven alternator must have many poles. In order to accommodate the large number of poles, a large diameter is necessary, and hence the salient-pole construction is used. The prime mover determines the construction in still another manner. Since a large diameter is required for the many poles of a slow-speed alternator, the armature has a large circumference and can hold many conductors to generate the required voltage. The length of the individual conductors lying in the magnetic field can be small, since each one need not generate a high voltage, and hence a slow-speed machine requires a small axial length.
Steam turbines are most efficient at high speeds, and therefore nearly all turbo alternators are two-pole machines. A two-pole machine obviously does not require a large-diameter rotor. Moreover, because of the increased centrifugal force at the high speed, a large diameter is prohibited. The small diameter necessitates fewer armature conductors, and in order to obtain the required generated voltage, a greater length of conductor must lie within the magnetic field. Thus the axial length is increased to permit the use of longer armature conductors.
Summarizing, we can say that cylindrical rotors will most likely be on alternators located where steam power is readily available. Salient-pole rotors will be found where water power is the prime mover source of energy, Diesel engine, gas engine, and gas turbine prime movers are considered medium-speed machines, and their alternators will also have salient poles. Where alternators are driven by other electrical machines, either ac or dc motors, there are no such restrictions on the rotor construction. A design is developed that is compatible with the space limitations, speed considerations, and heat dissipation for both electrical machines. It may be noted here that the terms high-speed and low-speed rotors are sometimes used synonymously with cylindrical- and salient-pole rotors, respectively.
