Data – Information
The terms data and information are not interchangeable. Bits of data are combined in a logical way to impart (передавать) specific information.
For example, the numbers 9990909 constitute an item of data, but they don’t constitute information until modified with special characters: 999-09-09. Then the numbers become information in the form of a telephone number. We can also interpret them as an order number, the interval in milliseconds between two actions and so on and so far. It depends on the context.
Managers can use information to obtain knowledge. Knowledge is understanding, a model, about people, objects, or events, derived from information about them. Knowledge provides a structure for interpreting information, usually explaining variations over time or space. For example, managers at a hotel obtain knowledge about customers’ preferences from the information obtained as a result of accumulating data about specific customer requests.
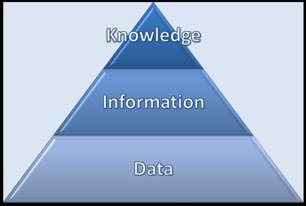
This relationship is often presented as a pyramide:
But the process can go further on:
Wisdom is the ability to use knowledge for a purpose. Computer systems collect data, produce and present information and help create knowledge.
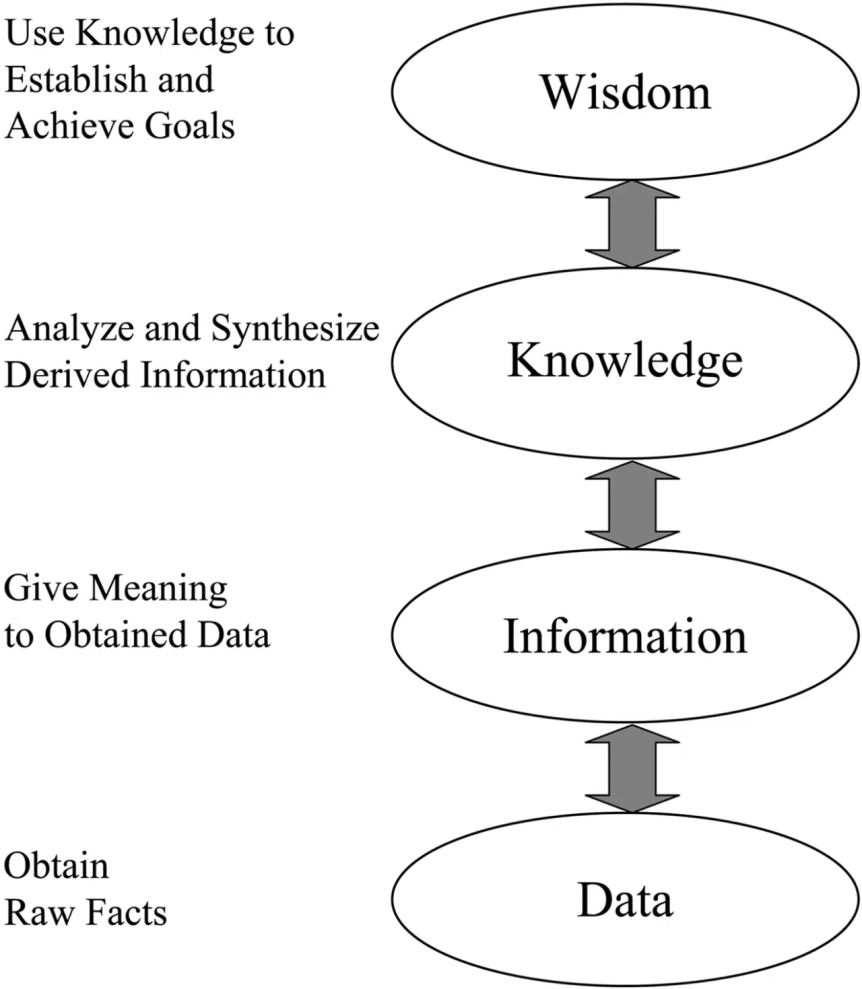
Or as a pyramide:

The role of Information in organisations
Resource. Information is a resource, an input into production of goods and services. Managers can use information to replace capital and labor, often reducing costs at the same time. For example, managers at Scottish Courage Brewing (SCB), the leading brewer in the UK, use information about demand, production rules, inventory, and supplies to make better use of their brewing tanks. As a result, they have been able to reduce need for more production capacity and generally accepted better meet urgent customer orders.
Informationmation
products
services
organization
labour
capital
Asset. Asset, the property of a person or an organization that contributes to company’s output. In this way information resembles plant, equipment, goodwill, and other corporate assets. Managers may view information as an investment that they can use strategically to give their company competitive advantage. Although generally accepted accounting rules typically prevent companies from listing information as an asset on their public balance sheets, many companies internally assign a value to their information to calculate a return on investment for proposed information systems.
Product. Companies can also sell information, the output of its production, as a product or service or as an embedded component of a product. In our service-oriented economy, an increasing number of companies view information in this way. Publishers of directory, television guides, and airline guides make a profit from selling information. Information is an embedded component of LG Electronics’ high-end microwave oven. The oven stores a certain number of frequently used settings and can download recipes and cooking information over the internet.



You understand that IT has allowed individuals, groups and organisations to manage information effectively and efficiently.
ITs ease communication. A company can track thousands of products in its warehouses, sales of the products in hundreds of retail outlets.
IT includes computer hardware, software, database management systems, and data communication technologies.
Computer hardware refers to the equipment used in electronic information processing.
Input hardware captures raw data and information from interactive users.
Processing hardware converts or transforms data.
Storage hardware includes removable and fixed media that allow rapid access to information.
Output hardware provides copies of data on paper, microform or video screens.
Computer software provides the instructions, in the form of computer code and its accompanying documentation, for processing data electronically.
Systems software directs the functioning of the hardware.
Applications software assists in he acquisition, processing, storage, retrieval, and communication of information.
Software development tools facilitate building and modifying software to respond to an organisation’s information needs.
Database management systems (DBMS) offer vehicles (средства) for storing and supporting the processing of large quantities of business information, such as data on employees, products, customers, and suppliers. This technology allows managers to easily access, sort and analyse databases of information along a variety of dimensions.
Data communication technologies, specifically company networks and the Internet, have dramatically improved the communication of information across small and large distances. Managers and other employees can easily send data from one location to another or access data located halfway around the world using computer networks, videoconferencing, wireless and other electronic media. Advances in communication technologies reduce costs and increase the accuracy and speed of communication.
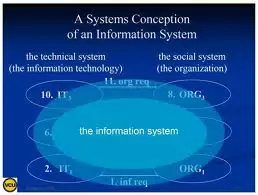
Managing Information with Information Systems
An Information system combines information technology with data, procedures for processing data, and people who collect, and use data.
An HR department might have an IS that tracks all current and potential employees’ work and salary history, training experience, and performance evaluations (оценка работы, производительности) and regularly provides reports to their managers summarizing the data.
Microsoft, eg, uses a human resources information system to store information about each employee, such as Social Security number, manager, hire date, employment status, as well as manage processes such as benefit enrollment, vacation and sick time reporting, payroll (платежная ведомость), and stock purchase programs (программа покупки акций компании).
Organizations and their employees use a variety of computerized systems to help manage information. Managers may use them to maintain information about employee performance, customer preferences, industry trends, as well as to motivate and develop employees, communicate with other managers, make decisions, negotiate agreements, manage resources. As managers become more sophisticated in performing their tasks, they require increasingly sophisticated systems to help them meet their information needs.