
- •Государственное образовательное учреждение высшего профессионального образования
- •Английский язык
- •Содержание
- •Пояснительная записка
- •Тема №1 Наука, выдающиеся ученые и их открытия
- •Тема №2 Металлы
- •Текст 1
- •Текст 2
- •Текст 3
- •Тема №3 Обработка металла
- •Текст 1
- •Текст 2
- •Текст 3
- •Тема №4 Материалы и технологии
- •Текст 1
- •Текст 2
- •Тема №5 Станки, станки с числовым программным управлением
- •Текст 1
- •Текст 2
- •Текст 3
- •Текст 4
- •Текст 5
- •1 Вариант
- •2 Вариант
- •Тема №6 Сварка, виды сварки
- •Текст 1
- •Текст 2
- •Тема №7 Автоматизация, виды автоматизации. Роботы в промышленности
- •Текст 1
- •Текст 2
- •Текст 3
- •Текст 4
- •Список литературы
- •1. Что говорят при встрече и прощании
- •2. Как подбодрить, посочувствовать, предложить свою помощь
- •3. Как поблагодарить, ответить на благодарность
- •4. Как выразить (не) согласие с мнением собеседника
- •5. Как выразить сомнение, предостережение, совет, предложение
- •6. Как спросить, попросить о чем-нибудь и как ответить
- •Тексты о наиболее значимых достижениях науки и технологии и великих ученых и их открытиях
- •Тексты для дополнительного чтения
- •Англо-русский словарь
Текст 2
Lathe
Задание 1 Выучить данную лексику и подготовиться к лексическому диктанту:
lathe — токарный станок
circular cross-section — круглое, поперечное сечение
surface — поверхность
stationary — неподвижный, стационарный
sideways — в сторону
variety — разнообразие, разновидность
depth — глубина
headstock — передняя бабка
spindle — шпиндель
chuck — зажим, патрон
faceplate — планшайба
lathe bed — станина станка
to enable — давать возможность
tolerance — допуск
Задание 2 Прочитайте и переведите текст:
Lathe
Lathe is still the most important machine-tool. It produces parts of circular cross-section by turning the workpiece on its axis and cutting its surface with a sharp stationary tool. The tool may be moved sideways to produce a cylindrical part and moved towards the workpiece to control the depth of cut. Nowadays all lathes are power-driven by electric motors. That allows continuous rotation of the workpiece at a variety of speeds. The modern lathe is driven by means of a headstock supporting a hollow spindle on accurate bearings and carrying either a chuck or a faceplate, to which the workpiece is clamped. The movement of the tool, both along the lathe bed and at right angle to it, can be accurately controlled, so enabling a part to be machined to close tolerances. Modern lathes are often under numerical control.
Задание 3 Выполните задания к текстам «Machine tools» и «Lathe»
Задание 3.1 Ответьте на вопросы:
1. What are machine-tools used for?
2. How are most machine-tools driven nowadays?
3. What facilities have all machine-tools?
4. How are the cutting tool and the workpiece cooled during machining?
5. What other machining methods have been developed lately?
6. What systems are used now for the manufacture of a range of products without the use of manual labour?
7. What parts can be made with lathes?
8. How can the cutting tool be moved on a lathe?
9. How is the workpiece clamped in a lathe?
10. Can we change the speeds of workpiece rotation in a lathe?
11. What is numerical control of machine tools used for?
Задание 3.2 Найдите эквиваленты русских слов и словосочетаний:
1. обрабатываемый материал
2. электропривод
3. более точный
4. отдельные детали
5. процесс массового производства
6. приспособления для держания резца и детали
7. операции по механической обработке детали
8. высоковольтный разряд
9. сверление ультразвуком
10. резание с помощью лазерного луча
11. гибкие производственные системы
12. детали круглого сечения
13. поворачивать деталь вокруг ее оси
14. двигать в сторону, двигать по направлению к детали
15. глубина резания
16. непрерывное вращение детали
17. движение резца вдоль станины
Задание 3.3 Переведите на английский язык:
1. Токарный станок позволяет производить детали круглого сечения.
2. Деталь зажимается в патроне или на планшайбе токарного станка.
3. Резец может двигаться как вдоль станины, так и под прямым углом к ней.
4. Современные токарные станки часто имеют цифровое управление.
Задание 4 Прочтите текст и переведите на русский язык в письменной форме абзацы 3,4 и 5; используя данные слова и словосочетания:
1. engine lathe 2. turning 3. drilling 4. screw cutting 5. headstock 6. tailstock 7. saddle 8. lever 9. apron 10. carriage 11. guideways 12. handle |
токарно-винторезный станок обточка сверление нарезание винтов передняя бабка задняя бабка суппорт рычаг фартук (суппорта) каретка направляющие (станка) рукоятка |
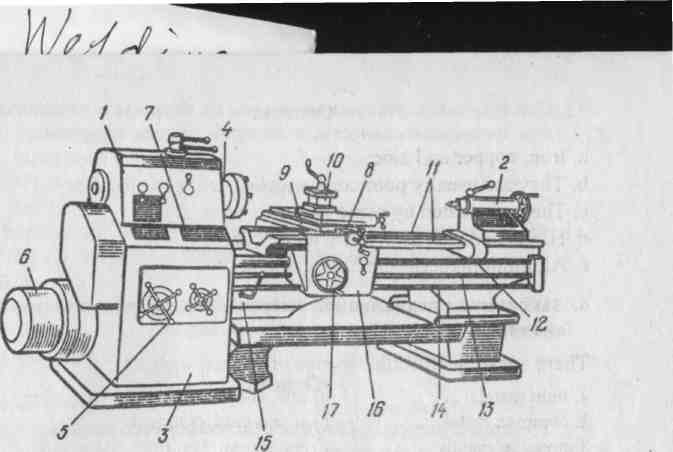
ENGINE LATHE
1. The engine lathe is the most commonly used machine-tool. It is used for great variety of metal operations, such as turning, drilling, screwcutting and many others.
2. The principal units of the lathe are the bed, the headstock, the tailstock and the carriage with the apron.
3. The bed is the base of any machine-tool and it is made of grey iron casting on which the saddle and the tailstock slide along special guideways. The headstock is also located and bolted on the bed.
4. The headstock contains the spindle and the speed gearbox. The spindle is the part of the machine to which power is applied to rotate the work. The changing of the spindle speed is effected by levers.
5. The tailstock consists of a casting fitted to the bed. The function of the tailstock is to support one end of the work turned between centres and to mount the tools.
6. The carriage of the lathe, which carries the tool, is made up of two principal parts: the saddle and the apron. The saddle travels along the guideways of the bed. The apron represents the front wall of the carriage. On the front of the apron are mounted the handles and levers by which the actions of the tool are controller.
