
- •Meaning and goals of macroeconomic.
- •Gross National Product / Gross Domestic Product.
- •Gdp: expenditures and income approaches.
- •5. System of national accounts.
- •6.Measuring Unemployment
- •7. Types of unemployment:
- •8. Levels of unemployment. «Full-employment».
- •9. Economic costs of unemployment.
- •10. Inflation: meaning and measurement. Rule of 70.
- •11. Types of inflation
- •15. Economic growth: definition and ingredients.
- •16. The theories of economic growth.
- •17. Aggregate demand (ad). Ad curve.
- •19. Aggregate supply (as); Determinants of as.
- •20. Segments of as curve.
- •21. As: the Keynesian vs. Classical Debate.
- •22. Equilibrium - classical model. Ratchet effect.
- •31. Multiplier effect of Taxation. Multiplier effect of Government Purchases. ?
- •32. Discretionary Fiscal Policy.
- •33. Cases of discretionary fiscal policy: expansionary and conctractionary policy.
- •34. Nondiscretionary Fiscal Policy. Built-in stabilizers.
- •35. Problems and complications of fiscal policy. ?
- •36. Money: functions and types.
- •37. Supply for money.
- •38. The role of banking sector - creation process.
- •39. Money – creation system. Money multiplier.
- •40. Monetary policy: goals and instruments.
- •41. Types of monetary policy.
- •42. Effectiveness of monetary policy. ?
- •44. The Phillips curve.
- •45. The adaptive and rational expectations theories.
- •46. Supply – side economics. Laffer curve.
- •47. International trade. Comparative advantage.
17. Aggregate demand (ad). Ad curve.
T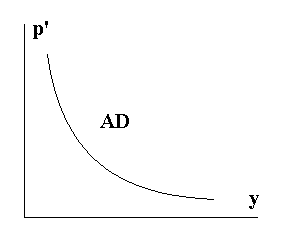 he
total amounts of notion’s output that buyers collectively desire to
purchase at each possible price level.
he
total amounts of notion’s output that buyers collectively desire to
purchase at each possible price level.
There is an inverse relationship between a nation’s price level and the amount of output demanded
p'- price level
y - real output or income
2 economic explanations for the inverse relationship between the price level and real output or income:
Wealth effect - Higher price levels reduce the purchasing power or real value of the nation's wealth or accumulated saving.
Net export effect - With an increase in the domestic price level, consmers and firms find foreign goods and input more attractive, thus the quantity of domestic output demanded decreases.
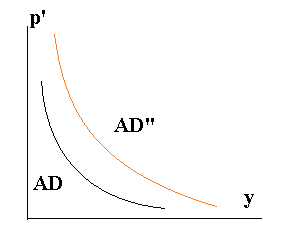
18. Determinants of AD.
Consumption - Wealth (If wealth increases, consumption increases and savings decrease.)
- Expectations (If household expect prices to rise tomorrow, then today C will shift up, S down)
- Real interest rates (Lower real interest rates lead to more C, less S and vise versa.)
- Household debt (if debt gets too high, C will have to shift down as households try to pay off their loans.) - Taxation (Increase in taxes shifts BOTH C and S curves downwards, Decrease in taxes shifts BOTH C and S curves upwards)
Investment
- Refers to the expenditures by firms on new plants, capital equipment, inventories etc.
- a firm's decision to invest is a COST and BENEFIT decision.
- Costs of investment: the interest rate changed by the bank on a loan to buy new capital
- Benefit of investment: the expected rate of return the investment will earn for the firm.
- expectations
- technology
- business taxes
- inventories
- degree of excess capacity
government spending
net export - Exchange rates,tastes and preferenees
A change in one of the four expenditures will cause the AD curve to shift.The distance between the old AD and the new AD represents the amount of new spending plus the multiplier effect: The ultimate change in output(GDP) will be greater than the initial change in spending.
19. Aggregate supply (as); Determinants of as.
- the total amount of goods and services that all industries in the
economy will produce at every given price level
the total amount of goods and services that all industries in the
economy will produce at every given price level
AS represents the sum of the supply curves of all the industriesin the economy
The relationship between the price level output businesses offer for sole
is direct or positive.
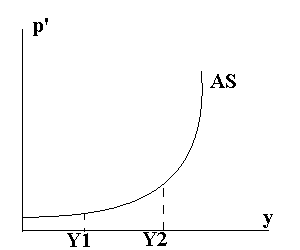
20. Segments of as curve.
AS curve consists of 3 segments:
1) horizontal (O-Y1)
-Real levels of output are less than the full - employment output
-The economy is in a recession
-the large amounts of unused machinery and unemployed workers are available for production
-workers unemployed for a few months will hardly expect a wage increase
-the price is on the same level
2) Intermediate (up sloping) Y1- Y2
- Real out put rises!
-an expansion of real output is accompanied by a rising price level
per-unit production costs rise and firms must receive higher product prices for their output to be profitable
3) Vertical Y2
-the economy reaches full capacity real OR FULL EMPLOYMENT real output-Individual firms may try to expand production by bidding resources away from other firms Thus bidding will raise resources price (costs) and product prices-
-BUT real output will remain UNCHANGED (is stable)
